Plants vaporize a large number of water; more than is used for vital processes. Evaporation occurs mainly through leaves. Water enters the leaves from the roots along the stems. Roots absorb water from the soil.
The evaporation of water by plants is also called transpiration.
Evaporation value
Why do plants absorb large amounts of water from the soil if they then evaporate it anyway?
Firstly, plants absorb not only water, but also minerals dissolved in it. There aren't many of them. Therefore, in order to satisfy the need for minerals, the plant needs to “drive” a large amount of water through itself. Excess water evaporates. And the process of evaporation itself, along with root pressure, contributes to the rise of water from the roots to the leaves.
Secondly, evaporation helps cool the plant. The principle is the same as sweating in animals. Water has a large heat capacity (“contains”, “absorbs” a large amount of heat). Therefore, when a plant in the sun begins to overheat, it evaporates a large amount of water. Water vapor removes excess heat from the plant.
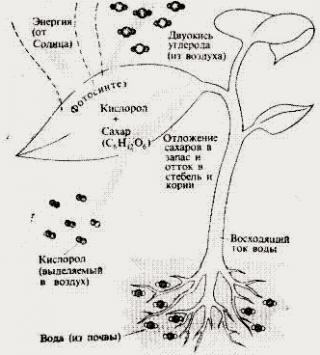
Thirdly, the plant itself needs water. A lot of water is contained in cells, it is involved in many chemical reactions in cells, is the medium for other reactions to occur. If there was no water on Earth, life would not have arisen. This is due to the fact that many chemical reactions take place in the cell, which are possible only in aquatic environment. It should be especially noted that water is involved in the process of photosynthesis. In particular, from water and carbon dioxide organic matter is formed.
Stomata
Most plants transpire water primarily from the underside of their leaves. Here, among the colorless cells of the integumentary tissue, there are special formations - stomata. They consist of a pair of green cells that can form a gap between themselves.
The number of stomata on the leaf is large, different types plants are different. It all depends on the adaptability of plants to specific living conditions.
When a plant needs to evaporate water, the stomata open, a gap is formed between their cells, and water vapor escapes through it. Inside the leaf there are many intercellular spaces where some of the water leaves the cells. In the intercellular spaces, water is in the form of steam. When the stomata open, water from the intercellular spaces leaves the leaf.
Typically, plants have stomata that are open during the day and closed at night. However, if the plant does not have enough water, it closes its stomata, trying to reduce evaporation.
Leaves and evaporation
In plants growing in different conditions The environment has developed some of its own adaptations to the evaporation of water by leaves.
In plants living in moist heat climate large leaf blades. Such plants evaporate a lot of water.
Plants in dry, hot places have very small leaves. This allows them to evaporate less water. Plants growing in cold climates have the same adaptation. Here the water is in liquid state also not enough.
There are other (not just the size of the leaf blade) adaptations to increase or decrease evaporation. Thus, the leaves of many plants are covered with hairs and a waxy coating. This prevents evaporation.
In aquatic angiosperms, stomata are located on the upper side of the leaf. This increases evaporation. This adaptation is due to the fact that such plants do not experience a lack of water, and it is almost impossible to evaporate with the underside of the leaf. After all, most of the leaves lie on the water.
Each representative of the flora kingdom evaporates impressive amounts of moisture. Water is necessary for plants to carry out life processes and is absorbed by them through the root system. It is pumped along the stems into the leaves, from where it consequently evaporates. As shown Scientific research, plants absorb only 3% of the water supplied to them, and the rest evaporates.
The process of evaporation of water from the surface of plants is called transpiration. In fact, this is the ridding of a living organism from excess water, as well as an analogue of sweating in representatives of the animal kingdom. Most plants evaporate water reverse side leaves, where there are special green cells (stomata), forming small gaps between themselves.
The role of water evaporation in plant life

- When a plant absorbs water, it absorbs various mineral components from the liquid. There are not very many of them in the water itself, so a large volume of liquid is driven through the stems per day. Gradually, due to root pressure, the water level in the plant rises, and it enters the leaves, from where it evaporates.
- By evaporating the liquid, the plant can cool itself. This is due to the effect of the maximum heat capacity of water. If a representative of the flora for a long time is in the sun, automatic transpiration begins, and water vapor carries away excess heat with it.
- Evaporation of moisture is also a necessity for plants, since water must rise to carry out various biochemical processes, such as photosynthesis.
For the environment, and in particular for humans, the evaporation of water by plants is also very significant. The intensity of this phenomenon, for example, reduces the nutritional value and taste of agricultural crops. The more often moisture evaporates, the poorer the soil becomes, constantly releasing water enriched with mineral components. Hence the need arises for regular improvement of lands and their fertilization.
The process of evaporation of water by a plant
As already noted, evaporation of water is possible due to the presence of stomata on the leaves. Their number in each organism is not the same and is determined by the habitat and characteristics of a particular representative of the flora (water level in the cells, age, osmotic pressure cell sap). The rate of moisture evaporation also depends on the presence of shade, air masses and water level in the ground.

When a plant accumulates excess water, the stomata expand and their cells form holes from which water vapor escapes. In the intercellular spaces, the liquid is always in a state of vapor, but it can leave the leaf only when the stomata open. Typically, the process of transpiration occurs during the day when the stomata are automatically open. But if a plant suffers from drought, it changes its regime and minimizes water evaporation.

Plants that grow in warm climates, such as the tropics, always have large leaves so that the maximum amount of water evaporates from their surface. short time. In cold or dry climates, the opposite is true. Also, if the plant is not interested in regularly getting rid of excess water, its leaves in the process of evolution become covered with a waxy coating or small villi. It is not uncommon for leaves to be curled in sunlight to reduce evaporation.
Angiosperms evaporate water not only from the back, but also from the front side of the leaf blades. This is due to the fact that the stomata are located on both sides, but the underside of the leaf is almost always in water and evaporation is impossible.
Plants constantly evaporate water. They do this mainly with leaves. Water enters the leaves through the stems from the roots, which absorb it from the soil.
The evaporation of water by leaves has the following meaning:
Thanks to evaporation, water rises from the roots. You could say the leaves act like a pump. In addition to evaporation, water is pushed upward and root pressure. Water in leaves not only evaporates, it is needed for many biochemical processes in cells, including photosynthesis.
As water evaporates, dissolved minerals rise into the stem and leaves. These substances were absorbed by the roots along with water. Then, with the flow of water, they move upward and are used in cells in various chemical reactions that ensure the life of the plant.
As a result of evaporation, the leaves cool. The fact is that water has a high heat capacity (one might say it takes away heat). When water droplets evaporate from the surface of the leaf, they take away excess heat and, therefore, protect the plant from overheating. This is especially important during the day, when photosynthesis occurs in the leaves under the scorching rays of the Sun, which can cause the leaves to become very hot.
The evaporation of water by leaves can be seen by performing different experiments. For example, if you place a glass container on a plant branch, then after a while you can see droplets of water on its walls. If you place a plant branch in water, and pour oil on top of the water (so that it does not evaporate), then the volume of water will decrease. This indicates that water is absorbed by the roots and then evaporated by the leaves.
In leaves, water vapor escapes from the cells into the intercellular spaces. From these, steam evaporates from the leaf surface through the stomata. By opening and closing, the stomata regulate the evaporation of water from the leaves. As is known, in most plants the stomata are located on bottom surface leaf. Consequently, in most plants, water mainly evaporates on the lower surface of the leaf blade.
The amount of water that plants evaporate depends on many factors. In any case, this is almost always a fairly large amount in terms of the body weight of the plant. For example, cabbage evaporates about one liter of water per day. The intensity of evaporation is affected by the age of the plant (young ones evaporate more), whether it grows in the shade or not (in the shade there is less evaporation), whether the wind is blowing or not (in windy weather there is more evaporation), there is enough water in the soil or not.
At sufficient quantity In the absence of water, the stomata in the leaves of the plant can be open both day and night. In some plants, stomata open only during the day. If there is not enough water in the soil, then the plants close their stomata even during the day. The leaves of some plants may curl in bright light, which also reduces evaporation.
Plants growing in warm, humid habitats (such as the tropics) usually have large leaf blades. Therefore, such plants evaporate large volumes of water. But since the water is in environment enough, it's not a problem. Another thing is plants of arid habitats (for example, semi-deserts and deserts). Their leaves are either small or modified into spines (cactus) or fleshy structures that store water in reserve (aloe). In any case, such leaves evaporate little water.








