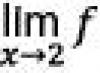Many people strive to get rid of fears, which occurs due to discomfort, shame, possible development. But in fact, nothing is created in nature without a reason, and if something exists, it matters for the life of each of us. The article provides various examples of the manifestation of fear. The benefits of fear and the harm of fear are integral companions of this feeling, so whether it is worth getting rid of it depends only on the individual perception of events.
Fear in evolution
Fear is actually not as bad as it might seem at first glance. It arose in the process of evolution to protect people from environmental danger. But gradually man managed to protect himself from possible natural troubles that threatened him during the primitive system. These could be threats from predators, wind, rain, snowfall, poisonous plants and other examples of fear.
The benefits of fear and the harm of fear are seemingly opposite phenomena, but in fact they protect the body from possible negative external factors. Now the dangers of the primitive world do not threaten people, but the “watchdog” often helps to maintain health and even material well-being. For example, someone who is afraid to leave the house and leave the iron on will check several times whether the cord is unplugged from the socket. As a result, this person will protect himself from material damage that may occur due to forgetfulness.
Fear is salvation from danger
For the most part, people avoid walking along dimly lit alleys and parks at night for fear of being attacked. Many people are not tempted to swim during a storm or swim behind buoys. Also, the benefit of fear is to not just turn the handle of the gas stove without lighting the burners. Not everyone can walk on high roofs, especially near the edge.

In addition, if a person was frightened by some event, he remembers it well and is guided by this information from negative experience in the future. How does fear benefit? Examples are that we are afraid of losing our apartment keys, our new expensive phone, or not removing a hot pan from the heat without protecting our hands. Or perhaps a child was once chased by a dog. Now this man has grown up and always bypasses owners walking their rather large pets without muzzles.
Mobilization of forces and internal experience
If a person finds himself in a critical situation, his body releases adrenaline into the blood. As a result, the muscles receive more oxygen and nutrients, developing significant power. Strength increases, and thoughts become brighter and lighter. Without fear it would not be possible to enter such a state. To increase adrenaline in the blood, many people have found extreme sports. They like to completely merge with nature, feel only themselves and obey their instincts, experiencing strength in their muscles and sobriety of mind.

When there is not enough information in any critical situation, it is impossible to use logic to resolve it. In cases where the mind is faced with the unknown, fear takes over and the body submits to instinctive behavior. Often the benefits of fear manifest themselves simply in flight, for example, from intruders.
Intuitive perception of the situation, fear of punishment
In a state of fear, all sensations become aggravated: an intuitive animal premonition of the slightest hint of a threat from something arises. It also happens that a person becomes restless in the absence of obvious danger. This indicates signals coming from subthreshold stimuli. Thus, the benefits of fear are manifested, but here it is important not to overdo it with overthinking yourself.

Too many people hold back inexplicable attacks of biological aggression because of the possible punishment. In the modern world, it is not at all difficult to steal an item from a supermarket or a small piece item from a counter at a market. But the desire to preserve one’s good name greatly inhibits such impulses. Crimes, even small ones, are deterred not by a high level of awareness, but by fear of responsibility.
Personal Development
And the most important meaning of fear is the possibility of personal improvement. Some skydivers noted that they might have been afraid of heights before, but they overcame themselves after making their first jump. In this case, the benefit of fear is to increase the self-esteem of the daredevil, as well as to open new horizons for him.

But a person must be ready for a parachute jump. You can’t force a friend to do this, whose soul sinks into his heels from climbing to the 5th floor of a building. In this case, the person, once in the air, will be very tight and make a mistake. But those people who are seriously involved in extreme sports are more self-confident. The endorphins produced during exercise help them stay in a good mood, cope with stress and keep their body in excellent physical shape.
The Harm of Fear
The negative side of fear consists of overthinking what might happen. A person may, for no apparent reason, begin to fear some kind of disease, animal, or microorganism. These are all examples of the manifestation of fear, the benefit of which is absent in principle, because if there is a fear of absolutely everything, then this indicates the possibility of a mental disorder. But it’s even sad when an acquaintance does not buy a new and beautiful car, which he has always dreamed of, only because of thoughts about the possibility of an accident. If an adult is afraid to get up at night to go to the kitchen and drink water, then this is also not normal.
The problem is that people are afraid of some diseases or disasters, but they may never happen. And carriers of such fear can expect reduced immunity and even nervous diseases. In addition, such people are capable of rash actions that can cause harm to themselves or loved ones.
The benefits and harms of fear are obvious: one must experience fear to some extent, and when the sensations of fear become too strong, some discomfort arises. But is it really worth getting rid of the "watchdog" that's doing its job completely?
As you know, fear is a kind of mental signal indicating that danger lurks somewhere. Like any human fear, fear has a positive effect on our body. True, it is worth remembering that it includes healthy and pathological fear. The latter type has a negative effect on personal development, and its roots can go far into the subconscious. It makes itself felt when there is not the slightest danger on the horizon. It manifests itself in the form of causeless anxious states, premonitions, and bodily manifestations are not excluded. Let's return to the first type: healthy fear and find out why it is useful.
The benefits of fear
Has it ever happened to you that in an instant you realized the falsity of some of your fears? Moreover, such fear helps you look at the situation differently; this emotion actually hides your true desires. So, when you are in a difficult period of life, which may be accompanied by sleep disturbances, frequent stressful situations and, most importantly, fear for something or someone, you should ask yourself a question. Ask yourself why you feel afraid. Don't be ashamed to admit it to yourself. Maybe he is preventing you from becoming the kind of person whose ideal you have strived for since childhood. Perhaps you are simply afraid to satisfy your true needs, as a result of which you create unnecessary problems for yourself and burden yourself.
Fear is an equally important emotion that affects your feelings towards loved ones, because it can improve them or, on the contrary, turn the relationship upside down. In many ways, the reason for this is the boundaries within yours. They were created by you. In summary, the second benefit of fear is that it helps to get rid of these  limits. Before you do the latter, admit that you are afraid of something, accept this state. Fear is like a room in which not a single light bulb is lit. Your acceptance acts like a lit candle, helping you to see what is hidden in the darkness.
limits. Before you do the latter, admit that you are afraid of something, accept this state. Fear is like a room in which not a single light bulb is lit. Your acceptance acts like a lit candle, helping you to see what is hidden in the darkness.
Fear is also a faithful assistant in mobilizing human power in the event of a critical, dangerous situation. In addition, thanks to it, you better remember unpleasant events and will not reach into an electrical outlet with wet hands for the second time.
If you attend my trainings and webinars on overcoming stress and fears, and complete all the necessary exercises given, then as a result you will get rid of most of your fears, and the remaining ones will become much weaker. However, before you do this, I would like to draw your attention to the positive role of fears for a person.
At first, superficial glance, fear brings little pleasure to a person - it brings him unpleasant sensations, deprives him of joy, prevents him from doing many pleasant things and can lead to psychosomatic diseases.
But fear, as it turns out, can also be useful. Initially, this emotion arose in the process of evolution in order to protect the human body from all sorts of dangers of primitive life. But then, when man changed nature and built a new habitat around himself, the fear reaction began to malfunction and lead to all sorts of troubles.
Fear, like pain, is the body’s watchdog, which protects it from harmful influences from the outside, from risky actions and danger, thereby helping to maintain health and well-being. Let us analyze the benefit that the body should have initially derived from the fear reaction, and see in which cases fear is useful for a person, and in which it causes harm to him.
First, fear saves our lives , stopping in front of a dangerous situation. We don't swim far out to sea, don't stick our fingers in electrical sockets, and try not to walk down dark alleys alone. As the ancient Somali proverb says, “A mother of a coward does not lose her son” - and in this regard, fear is useful for human life and health.
Secondly, fear mobilizes human strength for active work , which is often necessary in a critical situation. Fear dramatically increases physical strength, increases clarity and clarity of thinking. In fear, a person is able to undertake what without fear seems impossible to him. This occurs due to the release of adrenaline into the blood, which improves the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the muscles, allowing them to develop greater power.
Thirdly, fear acts as a regulator of aggressiveness and serves as a statement of social order . Fear of punishment restrains the manifestations of primary biological aggression, and also keeps many citizens within the bounds of the law. Fear of punishment is the main deterrent for people who intend to harm someone else's property or health. An example of this is the outbreaks of looting and violence that accompany almost any extreme event. One client once confessed to me that while visiting a flea market in Paris, she suddenly had an irresistible desire to steal a figurine she liked from the counter - even though she could afford to buy it. The saleswoman turned away for a minute and... But then she thought about the police, got scared - and saved her good name, and also got rid of possible troubles.
Fourth, fear promotes better memory of dangerous or unpleasant events . Fear activates memory and makes its traces especially strong. So, our ancestors remembered places where they were attacked by wild animals or people from a hostile tribe. Another example: a child who gets burned once near an open fire remembers it for a long time.
Fifth important, the meaning of fear - ability to act in conditions of lack of information , when it is not enough to make a comprehensively thought-out decision. Then the behavior strategy is dictated by fear. If the brain does not know what to do in a critical situation, and the mind does not have a balanced and logic-tested recipe, then the body prefers to trust the age-old experience of instincts and emotions.
Another, sixth positive role of fear is exacerbation under its influence of all human senses , which allows you to see or even anticipate the smallest signs of danger. Polish psychotherapist A. Kempinski wrote about this: “Sometimes in some people one can observe the ability to predict an impending danger: in the picture of reality there is nothing that could indicate it, but, nevertheless, anxiety appears, which is accompanied in a dream or in reality by the picture approaching misfortune. In this case, subthreshold stimuli that do not penetrate consciousness can signal an impending danger.”
Another, seventh, positive meaning of fear is that through overcoming it, human improvement can occur . As Fritz Riemann wrote, “if we understand our painful fear also as an indication of the need to look for errors in our own behavior or as a fear of new demands of life, as a result of which we do not dare to take a new step in our development, we must accept and understand it as an invitation to enter a new stage of our development, as a call for new freedom and, at the same time, for a new order and new responsibility. In this sense, we must view fear in its positive, creative aspect, as an initiator of change." For example, since childhood I was afraid of heights, because I once climbed a tall poplar tree and for a long time could not get down from there. And as a result, to get rid of this fear, I jumped with a parachute - after which my self-esteem increased.
So, dear subscribers, if you intend to completely get rid of your fears, think - maybe you will keep for yourself a small amount of this faithful guard who protects your life, health and property? Surely we won’t kill an inappropriately barking dog whose only fault is that it is too zealous in guarding its owner’s property?
The phenomenon of fear has been studied in psychology since the 19th century. When a person perceives a situation as dangerous, the body reacts to it. The degree of manifestation and forms of fear are individual. They depend on temperament, character and experience.
Let us differentiate between the concepts of “fear” and “phobia”. And although in science these phenomena are close in meaning, fear still means a feeling of real danger, and phobia means an imaginary one. If you are giving a speech in front of an audience and suddenly forget what you were going to say, you are experiencing fear. And if you refuse to speak in front of an audience because you are afraid of making a mistake, this is a phobia.
What is fear
Doctor of Psychological Sciences E.P. Ilyin in his book “The Psychology of Fear” gives a definition: “Fear is an emotional state that reflects a protective biological reaction of a person or animal when experiencing a real or imaginary danger to health and well-being.”
The feeling of fear is reflected in human behavior. The usual reaction of a person in the face of danger is trembling of the limbs, lower jaw, loss of voice, wide open eyes, raised eyebrows, cringing of the whole body and rapid pulse. Severe forms of expression of fear include increased sweating, urinary incontinence and a hysterical attack.
Emotion is expressed in different ways: some run away from fear, others fall into paralysis, and others show aggression.
Types of fear
There are many classifications of human fears. In the article we will look at the two most popular ones - the classifications of E.P. Ilyina and Yu.V. Shcherbatykh.
Ilyin classification
Professor Ilyin in the above-mentioned book describes affective types of fear, differing in the strength of their manifestation - timidity, fear, horror, panic.
Timidity and shyness
In the Encyclopedic Dictionary of Psychology and Pedagogy, shyness is defined as “fear of social interactions, extreme timidity and preoccupation with thoughts of possible negative evaluations from others.” Shyness is caused by introversion - turning inward - low self-esteem and unsuccessful relationships.
Fright
The initial form of fear. Occurs as a reaction to an unexpected sharp sound, the appearance of an object, or loss in space. The physiological manifestation of fear is flinching.
Horror
An extreme form of fear. Manifested by numbness or trembling. Occurs after emotional experience of terrible events, not necessarily personally experienced.
Panic
Panic fear can catch you wherever you are. Panic is characterized by confusion in the face of an imaginary or real danger. In such a state, people are not able to think rationally. Panic occurs against the background of overwork or exhaustion in emotionally unstable people.
Shcherbatykh classification
Doctor of Biological Sciences Yu.V. Shcherbatykh made a different classification, dividing fears into biological, social and existential.
Biological
Associated with phenomena that threaten health or life - fear of heights, fire and the bite of a wild animal.
Social
Fears and fears associated with the social status of the individual: fear of loneliness, public speaking and responsibility.
Existential
Associated with the essence of a person - fear of death, transience or meaninglessness of life, fear of change, space.
Children's fears
A group of children's fears stands apart from other classifications. Pay attention to children’s fears, because if the cause of fear is not identified and eliminated, it will carry on into adulthood.
Children, from their mother's weaning until adolescence, experience fears of various forms. At a younger age, biological fears appear, at an older age – social fears.
The benefits of fears
Let's give arguments in favor of fear and find out when a phobia has a positive effect.
General
Psychologist Anastasia Platonova in her article “Such Profitable Fear” notes that “being afraid publicly can be a very profitable undertaking.” The benefit is that when a person shares his experiences, including fears, he expects help, approval and protection. Awareness and acceptance of fears adds courage and sets you on the path of struggle.
Another useful property of fear is the feeling of pleasure. When the brain receives a signal of danger, adrenaline is released into the blood. It affects intelligence by speeding up thought processes.
Biological
The benefit of biological fears is that they perform a protective function. An adult will not stick his fingers into a meat grinder or jump into a fire. The phobia is based on the instinct of self-preservation.
Pain
Fears of pain or punishment are beneficial because they encourage a person to think about consequences.
4349There is probably not a single person in the world who has not experienced a feeling of fear at least once in their life. It is quite natural to feel it and there is no need to be ashamed of this feeling, since this reaction saves us from various dangers and the benefits of fear have long been a proven truth.
Examples of the benefits of fear
First, let's talk a little about human evolution and anthropology. Scientists working in these fields of science have long proven that it was fear that allowed humanity to survive and develop. Our distant ancestors, when a feeling of danger arose, tried to get as far away from the source of possible troubles as possible, which is why we did not disappear as a species, because otherwise, ancient people would simply have died from the most natural natural phenomena, for example, from the same lightning strike. Experiencing horror during a thunderstorm, our ancestors instinctively sought shelter, thereby saving their lives. It is these scientific studies that are the first and main argument in favor of fear, but let's discuss modern examples and evidence of this axiom.

Many people experience discomfort when they are in the dark, and this is what prevents them from performing potentially dangerous activities, such as walking along the streets at night, or moving around in an unlit apartment. In the first case, there is a fairly high chance of becoming a victim of criminals, in the second, of getting injured at home. But this is just one example of the benefits of fear of the dark or any other phenomenon that causes trembling in the knees; it is equally important that when a feeling of danger arises, adrenaline begins to be produced in the body, which mobilizes all forces, which means that a person experiences an extraordinary sense of his own power . By overcoming ourselves under the influence of adrenaline, we can feel our own capabilities, begin to respect ourselves and even discover new horizons for ourselves.
A good example of the benefits of fear of heights are rather banal stories about how a person, having decided to overcome himself and get rid of his phobia, begins to study with a skydiving instructor. Having overpowered themselves, such people often begin to achieve success in other matters, since they believe more in their capabilities. Just keep in mind that you need to get rid of the fear of heights with an experienced instructor, and not by walking on the roofs yourself, otherwise the matter may end in tragedy rather than triumph.
Another fact of the need for a person to have this feeling can be well illustrated by an example of the benefits of fear of water. Often a sense of danger forces a person to act instinctively, and without relying on logic, for example, we often simply run away from the same attackers. Therefore, imagine that a person who does not know how to swim suddenly falls into a deep river or lake, it would seem that he must drown and there is no chance of salvation. But the produced adrenaline can have an effect on the body that is popularly called “brains knocked out”, and the drowning person will begin to instinctively move his arms and legs in order to stay afloat.
To summarize briefly, the following can be noted:
1. Fear has helped humanity survive.
2. It protects us from provoking various potentially dangerous situations.
3. When a large amount of adrenaline is released into the blood, a person can begin to act instinctively, thereby saving himself.
4. Fear helps us improve ourselves, because by overcoming it, we begin to respect ourselves and believe in our strengths.
There is no need to be ashamed of your own fears; if they do not interfere with your life, then you don’t have to get rid of them at all, because this is a kind of protection system that everyone needs.