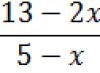2.2 Characteristics of psychological tools
The methodological support of the office includes methodological tools for carrying out psychodiagnostic procedures, materials for conducting psychocorrectional programs and the necessary props for various forms of psychotherapeutic influence (game therapy, music therapy, art therapy).
Requirements for choosing methods:
Methods must be valid and reliable.
Methods must be diverse and cover all aspects of a person’s mental life, including professional activity.
Methods must take into account the age characteristics of the subjects.
Techniques must take into account the feasibility of using the technique.
The material accumulated by the educational psychologist is systematized in the following order:
1) Diagnostic techniques (in a flexible folder):
diagnostics of cognitive development of children.
diagnostics of cognitive development of adolescents and adults,
diagnostics of the emotional-volitional sphere of children,
personality diagnostics,
diagnostics of child-parent relationships,
diagnostics of teachers.
Programs, plans.
Material for working with teachers.
Information and visual material for working with parents.
"Early age".
Folder "Documentation".
2.3 Analysis of documentation for compliance with requirements
The psychologist’s responsibilities include maintaining documentation and timely filling out reporting materials. Requirements for the quantity and content of basic documentation are determined by the administration of the educational institution.
Basic documents of a psychologist:
A program of experimental work on a specific topic relevant to a given educational institution;
Office work schedule;
Psychologist's work plan;
Card of medical, psychological and social support;
Card of psychological and pedagogical support;
Logbooks for accounting of consultative and group work.
The documentation meets the requirements. The list of documents used by the educational psychologist is presented in the appendix
In general, the design of the office and the psychological tools meet the requirements, but there is not enough space to organize more productive work.
3. Psychological and pedagogical support for younger schoolchildren
3.1 Psychological and pedagogical examination of children of primary school age
Psychodiagnostic examination program:
Goal: identifying the child’s level of readiness to begin regular education, adapting students to a new type of activity (educational).
Select appropriate methods and conduct diagnostics for children of primary school age;
To determine the initial motivation for learning in children entering school, i.e. find out if they have an interest in learning;
Finding out the general orientation of children in the world around them and their stock of everyday knowledge;
Psychodiagnostics of verbal and logical thinking of children;
Processing of received data;
Carrying out analysis of the received data;
Formulation of conclusions;
Drawing up a psychological profile of the subject (based on comparison and generalization of the results of a psychodiagnostic examination);
Correlation of age and individual psychological characteristics of the subject identified during the psychodiagnostic examination, i.e., the subject’s readiness for schooling;
Object: psychological readiness of the subjects to study at school.
Subject of psychodiagnostic examination: level of psychological readiness for learning at school.
3.2 Characteristics of diagnostic tools
Methodology No. 1. “Children’s general orientation in the world around them and their stock of everyday knowledge.”
This version of the technique is intended to assess the general orientation in the surrounding world of 1st grade children.
The general orientation of children just entering school in the world around them and the assessment of the stock of everyday knowledge they have is made based on answers to the following questions:
What is your last name, first name and patronymic?
How old are your mom and your dad?
What are the names of your grandmother and your grandfather?
What is the name of the capital of the state in which you live?
5. What is the name of the street where your relatives live?
(In answering this question, you must correctly name at least one street and say which relative lives on this street.)
What are the house number and apartment number where your relatives or friends live?
What are the names of the birds that can be found in the vicinity of your home?
(Here you must name at least two different birds.)
In what month does snow usually appear and when does it start to melt?
What time do you usually leave for school and come home from school? (The correct answer includes both hours and minutes.)

The effectiveness of the pedagogical activity of a particular teacher, the functioning of the school as a whole). So, we briefly examined the two main areas of work of a psychologist in a school - design and consulting. The school psychological service should carry out work aimed at correcting the existing situation, as well as create programs that would provide the opportunity...
... (1 staff unit); o cleaning lady (1 staff unit). So, the total number of staff members of the center is: 8. Volunteers can also be involved in the work of the methodological and psychological club “School of Adoptive Parents” to prepare families for the adoption of orphans, at orphanage No. 2 in Khabarovsk. 2.5 FINANCIAL SUPPORT OF THE PROJECT Calculation of costs for 1 month: No. Fixed costs...


Select psychodiagnostic tools, build programs of correctional and developmental work. Based on the calendar plan, the school psychologist went through the following stages of psychological and pedagogical social practice: 1. Organization and conduct of research work; 2. Conducting consultations on current topics; 3. Implementation of psychological education; 4. ...
The level of practical workers of social and psychological services of educational institutions in matters of forming a school team and socio-psychological support for families and psychological support for the integration of disabled children into the educational space. Heads of educational institutions must ensure the inclusion of a work plan for socio-psychological service specialists in...
When using the term “psychological tools” in a broad sense, the system of methods and technologies of psychological activity of a practical psychologist is understood; in a narrow sense - a set of tools and materials necessary for introducing a subject into correctional and diagnostic interaction with a practical psychologist and its effective implementation.
Let us dwell on the classification of psychological tools, based on the second meaning of this term. There are two main types of psychological tools in relation to the practical activities of a psychologist. This is a specific type of psychological tools (actually psychological tools) and a non-specific type designed to accompany or technically support psychological activity. Further differentiation of means and materials is carried out in accordance with the species.
Classification of psychological tools
|
Specific tools |
Non-specific tools |
||
|
Stimulus material * |
Interpretive means |
Technical material |
Aids |
|
Set according to the “Box of forms” type Volumetric geometric shapes (cube, prism, cylinder, ball, cone) Folding pyramids Split matryoshka 3-4 sets of sequences bad pictures Sets of cards combined into given characteristic (group, etc.) Printed material with diagrams, matrices, contour and figurative images Set of planar geometric shapes of various shapes, colors and sizes |
Scales, tables, graphs, profiles, grids for converting quantitative data into qualitative characteristics Computer programs for correlating, comparing and interpreting data obtained as a result of psychological interaction |
Colored pencils, felt-tip pens, watercolor paints, landscape sheets of various formats, colored paper, scissors, etc. (see paragraph 2.1) |
Floppy disks and CDs with playback the use of musical and verbal accompaniment of correctional and diagnostic activities Attributes of the main role-playing games for preschoolers, complete with substitute items Some types of construction and modeling kits Balls and toys based on sexual differentiation, etc. (see paragraph 2.1) |
______________________________
* The table includes psychological tools necessary for some diagnostic methods: “Box of Forms”, “Pyramids”, “Matryoshka”, “Sequence of Pictures”, “Most Unlike”, “Classification”, “Wenger Complex”. This list is not complete or complete.
Stimulus and interpretive tools are a structural part of methods, tests and correctional diagnostic technologies. Consequently, a specific “set” (set, package) of psychological tools is determined by the complex of those applied tools of a psychologist that lie in the field of his theoretical and conceptual ideas, as well as in his professional competence. Thus, a practical psychologist, working only in line with the activity approach, operates with methods, the conceptual basis of which is the development of leading types of activity in preschool children. This means that his psychological tools will be composed of materials and means that provide a targeted solution to the assigned tasks in the process: visual activity (“Pictogram”, “Completing figures”, etc.), design activity (“Fish”), objective activity (“Fish”). Pyramids”, “Matryoshka”, etc.), verbal activities (“Completing phrases”, “Three wishes”, etc.) and gaming activities (“Game room”). Conversely, a practicing psychologist, whose theoretical basis is the psychodynamic approach, is equipped with tools that provide a mechanism for the projection of personal and emotional characteristics: photographs with a shaded image - CAT *, blurred colored spots - the Rorschach technique, image settings - “Drawing of a family”, “ Drawing of a non-existent animal" (you can read more about this toolkit on pp. 197-199).
_____________________
* CAT (Child Apperception Test) - Children's apperception test.
A practical psychologist who combines several theoretical approaches in his work, working in a multi-conceptual professional space, uses methodological and test bases depending on the request and the psychological problem.
Thus, the demand for various technologies in the work of a practical psychologist obliges him to prepare appropriate psychological tools, both specific and non-specific.
What are the requirements for psychological tools *.
___________________
* These requirements relate to a specific type of psychological instrument.
First of all, this compliance requirement. We are talking about compliance with the original, i.e. standards laid down in the original (author's) copy of the correctional diagnostic tool. This applies to all stimulus and interpretation material. Thus, the “Most Unlikely” method contains geometric figures of a circle and a square of a certain size and color (red and blue). Varying the specified parameters of size, color and shape is unacceptable. In the “Sequence of Pictures” method, a series of pictures with a cross-cutting plot and common characters cannot be replaced by pictures adding details to the subject, etc. In the CAT and TAT methods, photographs cannot be “finished” by drawing details and color design. As for interpretative means, they must correspond to the author’s (original) methodology and have the same quantitative and qualitative meanings.
Next - configuration requirement. It refers to the need to complete stimulus and interpretation materials. If the original method (test) contains a set of instruments, then the use of these diagnostic tools in the absence of one or another material is not recommended. Thus, the absence of score conversion scales in standardized methods makes it impossible to interpret diagnostic data.
In addition, psychological tools can be defined as monofunctional. This means that it is impossible to use stimulus or interpretative materials from one psychodiagnostic tool as a modification of another. Psychological tools are specific and in no way interchangeable. Thus, variants of printed stimulus material (Wenger complex) are designed for one-time individual use.
Thus, speaking about psychological tools as a means of professional activity, it is necessary to correlate it both with theoretical concepts, correctional and diagnostic technologies, and with the requirements for its selection and configuration.
When using the term “psychological tools” in a broad sense, the system of methods and technologies of psychological activity of a practical psychologist is understood; in a narrow sense - a set of tools and materials necessary for introducing a subject into correctional and diagnostic interaction with a practical psychologist and its effective implementation.
Let us dwell on the classification of psychological tools, based on the second meaning of this term. There are two main types of psychological tools in relation to the practical activities of a psychologist. This is a specific type of psychological tools (actually psychological tools) and a non-specific type designed to accompany or technically support psychological activity. Further differentiation of means and materials is carried out in accordance with the type.
Classification of psychological tools
|
Specific tools |
Non-specific tools |
||
|
Stimulus material * |
Interpretive means |
Technical material |
Aids |
|
Set according to the “Box of forms” type Volumetric geometric shapes (cube, prism, cylinder, ball, cone) Folding pyramids Split matryoshka 3-4 sets of sequences bad pictures Sets of cards combined into given characteristic (group, etc.) Printed material with diagrams, matrices, contour and figurative images Set of planar geometric shapes of various shapes, colors and sizes |
Scales, tables, graphs, profiles, grids for converting quantitative data into qualitative characteristics Computer programs for correlating, comparing and interpreting data obtained as a result of psychological interaction |
Colored pencils, felt-tip pens, watercolor paints, landscape sheets of various formats, colored paper, scissors, etc. (see paragraph 2.1) |
Floppy disks and CDs with playback of musical and verbal accompaniment of correctional and diagnostic activities Attributes of the main role-playing games for preschoolers, complete with substitute items Some types of construction and modeling kits Balls and toys based on sexual differentiation, etc. (see paragraph 2.1) |
______________________________
* The table includes psychological tools necessary for some diagnostic methods: “Box of Forms”, “Pyramids”, “Matryoshka”, “Sequence of Pictures”, “Most Unlike”, “Classification”, “Wenger Complex”. This list is not complete or complete.
Stimulus and interpretive tools are a structural part of methods, tests and correctional diagnostic technologies. Consequently, a specific “set” (set, package) of psychological tools is determined by the complex of those applied tools of a psychologist that lie in the field of his theoretical and conceptual ideas, as well as in his professional competence. Thus, a practical psychologist, working only in line with the activity approach, operates with methods, the conceptual basis of which is the development of leading types of activity in preschool children. This means that his psychological tools will be composed of materials and means that provide a targeted solution to the assigned tasks in the process: visual activity (“Pictogram”, “Completing figures”, etc.), design activity (“Fish”), objective activity (“Fish”). Pyramids”, “Matryoshka”, etc.), verbal activities (“Completing phrases”, “Three wishes”, etc.) and gaming activities (“Game room”). And vice versa, a practicing psychologist, whose theoretical basis is the psychodynamic approach, is equipped with tools that provide a mechanism for the projection of personal and emotional characteristics: photographs with a shaded image - CAT1 *, blurred colored spots - the Rohr Shah technique, image settings - “Family Drawing” , “Drawing of a non-existent animal” (you can read more about this toolkit on pp. 197-199).
_____________________
*CAT (Child Apperception Test) - Children's apperception test.
A practical psychologist who combines several theoretical approaches in his work, working in a multi-conceptual professional space, uses methodological and test bases depending on the request and the psychological problem.
Thus, the demand for various technologies in the work of a practical psychologist obliges him to prepare appropriate psychological tools, both specific and non-specific.
What are the requirements for psychological tools*2.
___________________
*These requirements relate to a specific type of psychological instrument.
First of all, there is a requirement for compliance. We are talking about compliance with the original, i.e. standards laid down in the original (author's) copy of the correctional diagnostic tool. This applies to all stimulus and interpretation material. Thus, the “Most Unlikely” method contains geometric figures of a circle and a square of a certain size and color (red and blue). Varying the specified parameters of size, color and shape is unacceptable. In the “Sequence of Pictures” method, a series of pictures with a cross-cutting plot and common characters cannot be replaced by pictures adding details to the subject, etc. In the CAT and TAT methods, photographs cannot be “finished” by drawing details and color design. As for interpretative means, they must correspond to the author’s (original) methodology and have the same quantitative and qualitative meanings.
Next is the configuration requirement. It refers to the need to complete stimulus and interpretation materials. If the original method (test) contains a set of instruments, then the use of these diagnostic tools in the absence of one or another material is not recommended. Thus, the absence of score conversion scales in standardized methods makes it impossible to interpret diagnostic data.
In addition, psychological tools can be defined as monofunctional. This means that it is impossible to use stimulus or interpretative materials from one psychodiagnostic tool as a modification of another. Psychological tools are specific and in no way interchangeable. Thus, variants of printed stimulus material (Wenger complex) are designed for one-time individual use.
Thus, speaking about psychological tools as a means of professional activity, it is necessary to correlate it both with theoretical concepts, correctional and diagnostic technologies, and with the requirements for its selection and configuration.
2.2. psychological tools
When using the term “psychological tools” in a broad sense, the system of methods and technologies of psychological activity of a practical psychologist is understood; in a narrow sense - a set of tools and materials necessary for introducing a subject into correctional and diagnostic interaction with a practical psychologist and its effective implementation.
Let us dwell on the classification of psychological tools, based on the second meaning of this term. There are two main types of psychological tools in relation to the practical activities of a psychologist. This is a specific type of psychological tools (actually psychological tools) and a non-specific type designed to accompany or technically support psychological activity. Further differentiation of means and materials is carried out in accordance with the type.
Stimulus and interpretive tools are a structural part of methods, tests and correctional diagnostic technologies. Consequently, a specific “set” (set, package) of psychological tools is determined by the complex of those applied tools of a psychologist that lie in the field of his theoretical and conceptual ideas, as well as in his professional competence. Thus, a practical psychologist, working only in line with the activity approach, operates with methods whose conceptual basis is the development of leading types of activity in preschool children. This means that his psychological tools will be composed of materials and means that provide a targeted solution to the assigned tasks in the process: visual activity (“Pictogram”, “Completing figures”, etc.), design activity (“Fish”), objective activity (“Fish”). Pyramids”, “Matryoshka”, etc.), verbal activities (“Completing phrases”, “Three wishes”, etc.) and gaming activities (“Game room”). And vice versa, a practicing psychologist, whose theoretical basis is the psychodynamic approach, is equipped with tools that provide a mechanism for the projection of personal and emotional characteristics: photographs with a shaded image - CAT1, blurred colored spots - the Rorschach technique, image settings - “Family Drawing”, “Drawing non-existent animal" (you can read more about this toolkit on pp. 197-199).
Classification of psychological tools
|
Specific tools |
Non-specific tools |
||
|
Stimulus material1 |
Interpretive means |
Technical material |
Aids |
|
Set according to the “Box of forms” type Volumetric geometric shapes (cube, prism, cylinder, ball, cone) Folding pyramids Split matryoshka 3-4 sets of sequences of plot pictures Sets of cards combined for given characteristic (group, etc.) Printed material with diagrams, matrices, contour and figurative images Set of planar geometric shapes of various shapes, colors and sizes |
Scales, tables, graphs, profiles, grids for converting quantitative data into qualitative characteristics Computer programs for correlating, comparing and interpreting data obtained as a result of psychological interaction |
Colored pencils, felt-tip pens, watercolor paints, landscape sheets of various formats, colored paper, scissors, etc. (see paragraph 2.1) |
Floppy disks and CDs with playback of musical and verbal accompaniment of correctional and diagnostic activities Attributes of the main role-playing games for preschoolers, complete with substitute items Some types of construction and modeling kits Balls and toys based on sexual differentiation, etc. (see paragraph 2.1) |
A practical psychologist who combines several theoretical approaches in his work, working in a multi-conceptual professional space, uses methodological and test bases depending on the request and the psychological problem.
Thus, the demand for various technologies in the work of a practical psychologist obliges him to prepare appropriate psychological tools, both specific and non-specific.
What are the requirements for psychological tools1.
First of all, there is a requirement for compliance. We are talking about compliance with the original, i.e. standards laid down in the original (author's) copy of the correctional diagnostic tool. This applies to all stimulus and interpretation material. Thus, the “Most Unlikely” method contains geometric figures of a circle and a square of a certain size and color (red and blue). Varying the specified parameters of size, color and shape is unacceptable. In the “Sequence of Pictures” method, a series of pictures with a cross-cutting plot and common characters cannot be replaced by pictures adding details to the subject, etc. In the CAT and TAT methods, photographs cannot be “finished” by drawing details and color design. As for interpretative means, they must correspond to the author’s (original) methodology and have the same quantitative and qualitative meanings.
Next is the configuration requirement. It refers to the need to complete stimulus and interpretation materials. If the original method (test) contains a set of instruments, then the use of these diagnostic tools in the absence of one or another material is not recommended. Thus, the absence of score conversion scales in standardized methods makes it impossible to interpret diagnostic data.
In addition, psychological tools can be defined as monofunctional. This means that it is impossible to use stimulus or interpretative materials from one psychodiagnostic tool as a modification of another. Psychological tools are specific and in no way interchangeable. Thus, variants of printed stimulus material (Wenger complex) are designed for one-time individual use.
Thus, speaking about psychological tools as a means of professional activity, it is necessary to correlate it both with theoretical concepts, correctional and diagnostic technologies, and with the requirements for its selection and configuration.
“Psychological tools” in a broad sense refers to the system of methods and technologies of psychological activity of a practical psychologist; in a narrow sense - a set of tools and materials necessary for introducing a subject into correctional and diagnostic interaction with a practical psychologist and its effective implementation.
Classification of psychological tools
|
Specific tools |
Non-specific tools |
||
|
Stimulus material * |
Interpretive means |
Technical material |
Aids |
|
Set according to the “Box of forms” type Volumetric geometric figures (cube, prism, cylinder, ball, cone) Folding pyramids Split matryoshka 3-4 sets of sequences su-- bad pictures Sets of cards combined for-- given characteristic (group, etc.) Printed material with diagrams, matrices, contour and figurative images A set of planar geometric shapes of various shapes, colors and sizes |
Scales, tables, graphs, profiles, grids for translating quantitative data into qualitative characteristics Computer programs for correlating, comparing and interpreting data obtained as a result of psychological interaction |
Colored pencils, felt-tip pens, watercolor paints, landscape sheets of different formats, colored paper, scissors, etc. |
Floppy disks and CDs with playback-- knowledge of musical and verbal accompaniment of correctional and diagnostic activities Attributes of the main role-playing games for preschoolers, complete with substitute items Some types of construction and modeling kits Balls and toys based on sexual differentiation, etc. |
* The table includes psychological tools necessary for some diagnostic techniques: “Box of Forms”, “Pyramids”, “Matryoshka”, “Sequence of Pictures”, “Most Unlike”, “Classification”, “Wenger Complex”. This list is not complete or complete.
Thus, a practical psychologist, working only in line with the activity approach, operates with methods whose conceptual basis is the development of leading types of activity in preschool children. This means that his psychological tools will be composed of materials and means that provide a targeted solution to the assigned tasks in the process: visual activity ("Pictogram", "Completing figures", etc.), design activity ("Fish"), objective activity (" Pyramids", "Matryoshka", etc.), verbal activities ("Completing phrases", "Three wishes", etc.) and gaming activities ("Game room"). And vice versa, a practicing psychologist, whose theoretical basis is the psychodynamic approach, is equipped with tools that provide a mechanism for the projection of personal and emotional characteristics: photographs with shaded images - CAT * ((Child Apperception Test) - Children's Apperception Test), blurred colored spots - Rorschach technique, image settings - “Drawing of a family”, “Drawing of a non-existent animal” (you can read more about this toolkit on pp. 197-199).
Requirements for psychological instruments:
First of all, there is a requirement for compliance. We are talking about compliance with the original, i.e. standards laid down in the original (author's) copy of the correctional diagnostic tool. This applies to all stimulus and interpretation material. Thus, the “Most Unlikely” method contains geometric figures of a circle and a square of a certain size and color (red and blue). Varying the specified parameters of size, color and shape is unacceptable. In the “Sequence of Pictures” method, a series of pictures with a cross-cutting plot and common characters cannot be replaced by pictures adding details to the subject, etc. In the CAT and TAT methods, photographs cannot be “finished” by drawing details and color design. As for interpretative means, they must correspond to the author’s (original) methodology and have the same quantitative and qualitative meanings.
Next is the configuration requirement. It refers to the need to complete stimulus and interpretation materials. If the original method (test) contains a set of instruments, then the use of these diagnostic tools in the absence of one or another material is not recommended. Thus, the absence of score conversion scales in standardized methods makes it impossible to interpret diagnostic data.
In addition, psychological tools can be defined as monofunctional. This means that it is impossible to use stimulus or interpretative materials from one psychodiagnostic tool as a modification of another. Psychological tools are specific and in no way interchangeable. Thus, variants of printed stimulus material (Wenger complex) are designed for one-time individual use.
Thus, speaking about psychological tools as a means of professional activity, it is necessary to correlate it both with theoretical concepts, correctional and diagnostic technologies, and with the requirements for its selection and configuration.