Discipline: Geography
Subject: « Introduction. Sources of geographical information".
Practical lesson No. 1.
Subject: Familiarization With geographical cards various topics. Compilation kart (schemes), reflecting various geographical phenomenaAnd processes. Usage statistical materials And geographic information systems
Type of lesson: Learning new things
Type of lesson: Lecture - visualization
Number of hours: 2 hours
Purpose of the lesson: Forming an idea of the sources of geographic
information.
Tasks:
To give an idea of the role and place of modern geographical information in solving problems of the development of human civilization.
To form students’ ideas about various sources of geographic information, which are designed to help in mastering the new educational course.
Continue to develop testing and lecture note-taking skills.
Assess the volume and level of residual geographic knowledge of students to determine the degree of readiness of the audience to learn new material.
Equipment, visibility, TSO– laptop, plasma TV, presentation, outline map, atlas,
Progress of the lesson:
Geography as a science.
A geographic map is a special source of information about
Organizational moment.
Setting goals and objectives.
Requirements for organizing the educational process.
Lecture visualization.
reality.
Statistical materials.
Geography as a science.
Geography is one of the most interesting and important sciences. It studies the territory (territorial complexes of different levels), the conditions and patterns of its formation and development. Economic and social geography as a branch of geography examines the place and role of man and his diverse activities in a given territory. His comfortable living there depends on how competently a person settles and masters his habitat. Geography makes it possible to deeply scientifically and, most importantly, comprehensively take into account all the factors of the development of the territory - natural (geological structure, climatic features, features of internal waters and natural complexes), economic (peculiarities of economic activity) and social (human behavior). It is for this reason that it so widely uses the achievements of a wide variety of sciences.
Traditional and new methods of geographical research.
Research methods (methods) are specific techniques for studying geographical objects and phenomena.
![]()
![]()
Geographic Information System (GIS) is an information system that provides collection, storage, processing, access, display and analysis of spatial (spatially coordinated) data.
GIS structure:
Data (spatial data):
Positional (geographic): location of an object on the earth’s surface, its coordinates in the selected coordinate system;
Non-positional (attributed, or metadata) - descriptive text, electronic documents, graphic data, including photographs of objects, three-dimensional images of objects, video materials, etc.
Hardware (computers, computer networks, drives, scanners, digitizers, etc.);
Software (OS, application and add-ons);
Technologies (methods, procedures, etc.);
Operators, administrators, users.
Types of geographic information, its role and use in people's lives.
Task No. 1 ( Read the text. Make a diagram “Sources of geographic information”)
Geography is a science in which you should not be afraid to get too much information. There are quite a few sources of geographic information.
Firstly, a geographical map. It provides a one-time, broad and comprehensive view of the study area. It is no coincidence that the famous geographer N.N. Baransky, the founder of Soviet economic and social geography, called the geographical map the “language” of geography. True, you must be able to read a geographical map, that is, have the skill of obtaining all the necessary information from it. Secondly, this is literature, and the most diverse - reference, scientific, popular science and even fiction. Thirdly, these are the media (newspapers, magazines, television and radio broadcasts, films). Fourthly, this is the Internet. Fifthly, these are personal impressions. When studying the features of the territory, no information will be superfluous. It is necessary to “absorb” it from everywhere - read books, newspapers and magazines, watch television programs and films, use Internet services, go on tourist trips.
The modern world is on the threshold of globalization. Nowadays, goods, money, and any information easily travel across vast distances and state borders that once seemed like impregnable bastions. In this regard, there is an inevitable averaging, or unification, of human behavior patterns. Of course, this process is not easy. But he is objective. Enormous differences in the cultural traditions of certain peoples further aggravate the seemingly already acute interstate and interethnic contradictions. Geography can help us understand their nature and understand all their intricacies.
A geographic map is a special source of reality information.
Geographic map- models from to in reduced form.
Statistical materials.
Statistics is an integral part of the global information system, which is formed in accordance with the concept of informatization developed in the Russian Federation.
Statistical materials- this is massive quantitative data on important indicators of life and the relationships between them. Statistical data includes population censuses, tax collection, and land calculations.
Starting testing on economic and social geography of Russia
Countries with land borders with Russia:
Norway
Lithuania
Mongolia
Finland
China
Belarus
Turkmenistan
Russian city with a population of more than 1 million people:
Serpukhov
Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk
Murmansk
Nizhny Novgorod
The largest basin in terms of coking coal volumes in Russia:
Kansko-Achinsky
Kuznetsky
Podmoskovny
Donetsk
4. Full cycle ferrous metallurgy center in Russia:
Magnitogorsk
Murmansk
Saint Petersburg
5. Fine-fleece and semi-fine-fleece sheep breeding is most developed in
economic region:
Northern
North Caucasian
Central
Central Black Earth
6.The Trans-Siberian Railway passes through the territory
economic regions of Russia:
North Caucasian
Ural
Far Eastern
Northern
7. Arrange the stages of textile production in technological order - from raw materials to the production of finished fabric
Production of raw materials
Fiber production
Yarn production
Answer: 3,4,2,1
8. Three centers of the oil refining industry,
located on the Volga:
Saratov
Yaroslavl
Smolensk
Khabarovsk
Volgograd
Arkhangelsk
9. Identify the subject of the Russian Federation based on its brief description:
“This subject is located in the eastern part of the country, its territory is not washed by the waters of the World Ocean. One of the largest rivers in Russia with its largest influx flows through its territory. There are no hydroelectric power stations on these rivers. There are no nuclear power plants in the region, but powerful thermal power plants operate using fuel produced in the same region."
Primorsky Krai
Murmansk region
Irkutsk region
Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous Okrug
10. Establish a correspondence between the economic regions of Russia and the production centers of cars and trucks:
Economic regions Production centers
Russian cars and trucks
Volgo-Vyatsky A. Serpukhov
Povolzhsky B. Naberezhnye Chelny
Central V. Izhevsk
Uralsky Nizhny Novgorod
D. Taganrog
Answer: 1-G, 2-B, 3-A, 4-B
Evaluation criteria: 0 errors – “5”, 1-3 errors – “4”, 4-5 errors – “3”, 6 or more – “2”.
Question number
Answer
1-G, 2-B, 3-A, 4-B
6. Frontal survey.
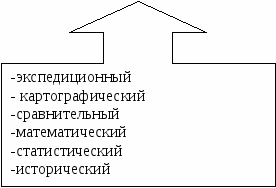
List the traditional methods of geographical research known to you.
Answer:
Expeditionary
Descriptive
Cartographic
Comparative
Mathematical
Statistical
Historical
Does the cartographic method belong to traditional methods and what is its role in understanding the world around us?
Answer:
Yes, this is the leading method in geography; with the help of maps we can get a lot of different information.
What role do space research methods play in modern geographical research?
Answer:
Space research methods are used to monitor and study economic components in the world and predict their changes.
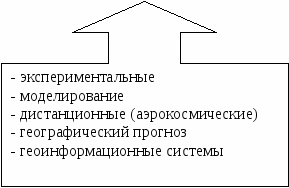
List the modern methods of geographical research known to you.
Answer:
Experimental
Modeling
Remote (aerospace)
Geographical forecast
Geographic information systems
Does geographical forecast belong to modern methods of geographical research and what is the purpose of its implementation:
Answer:
Yes, foreseeing the future state of geosystems.
Geosystems – these are natural-geographical unities of all possible categories, from the planetary geosystem (geographical envelope) to the elementary geosystem (physical-geographical facies)
definition by V. B. Sochava
PRACTICAL LESSON No. 1
Subject: Familiarization with geographical maps of various subjects. Drawing up maps (schemes) reflecting various geographical phenomena and processes. Use of statistical materials and geographic information systems.
1. Analysis of maps of various subjects.
As a result of completing practical tasks, each of you must study the stages of the formation of a modern political map of the world; modern processes of changing the political map of the world, the main international organizations of countries, to learn the features of the distribution of certain types of natural resources by region.
You must consolidate and develop the following skills:
Draw up maps (maps), diagrams based on the proposed simple or complex tasks using traditional or notations developed by you;
Select the necessary information to complete the task; - identify and explain the political and geographical aspects of current events and situations;
Evaluate and explain information obtained during selection and analysis;
Equipment: Internet resources, geographical atlas of the world for grade 10, outline map of the world, colored pencils, pen.
Tasks for work:
Task 1.
Consider the Atlas Geography (grade 10). List the topics of the map.
Answer:
Human Development Index
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
Economic structure
Mining industry
Electric power industry
Manufacturing industry
Agriculture
Transport
Foreign economic relations
Integration associations
Territorial structure of the economy
Political and economic maps of countries
Global demographic problem
Global environmental problem
Global food problem
Areas of political instability
World Heritage of Humanity
Political map
State structure
Mineral resources of land
Agroclimatic resources
Land and forest resources
Hydrosphere resources
Population
Population distribution
Task 2.
To complete the task, use various sources of geographic information, as well as your knowledge from a school course in history and geography. You can also obtain the necessary information using Internet resources.
Insert the missing names of some new countries (or their capitals) that appeared on the political map of the world at the end of the 20th and beginning of the 21st centuries. as a result of the division of larger federal states.
States that emerged on the territory of the former Soviet Union and their capitals: Russia - Moscow; Ukraine – Kyiv; Belarus – Minsk; Moldova– Chisinau; Georgia – Tbilisi; Azerbaijan– Baku; Armenia – Yerevan; Kazakhstan - Astana; Kyrgyzstan– Bishkek; Turkmenistan – Ashgabat; Tajikistan – Dushanbe; Uzbekistan – Tashkent; Estonia – Tallinn; Latvia– Riga; Lithuania – Vilnius.
States that arose on the territory of the former Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY), and their capitals: Serbia - Belgrade; Croatia – Zagreb; Montenegro – Cetinje; Macedonia– Skopje; Slovenia – Ljubljana; Bosnia and Herzegovina – Sarajevo.
States that arose on the territory of the former Czechoslovak Socialist Republic (CSSR), and their capitals: Czech Republic - Prague; Slovenia – Bratislava.
Task 3.
Make a map of the previously existing Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY), which shows the borders of the newly formed countries. Write the names of these countries and their capitals.
Answer:
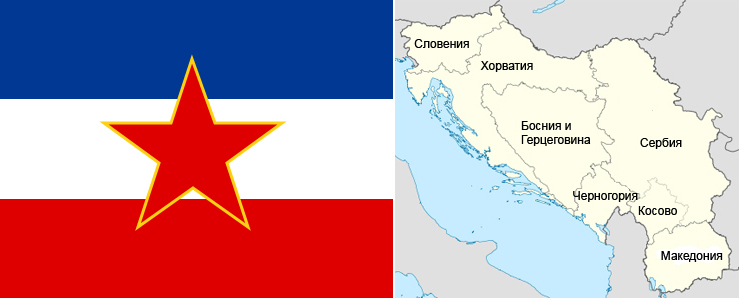
Thus, today there are six independent states in the territory that belonged to the former Yugoslavia:
Republic of Serbia (capital Belgrade)
Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina (capital Sarajevo)
Republic of Slovenia (capital Bratislava)
Republic of Macedonia (capital Skopje)
Republic of Montenegro (capital Cetinje, Podgorica)
Republic of Croatia (capital Zagreb)
(There is a slight confusion with the capitals in Montenegro. In the country’s constitution, the city is named as its official capital . It has historically been the center of faith and statehood; the royal residence was located here. In 1946, the capital was moved to Titograd, which in 1992 was returned to its previous name - . After Montenegro gained independence in 2006, the title of capital again passed to Cetinje, but most government institutions remained in Podgorica. In order not to transport the country's government, it was decided to make appropriate changes to the status of cities.
So now there are two capitals in Montenegro, for which new definitions have been invented. The official and cultural capital is Cetinje, where the president and metropolitan of the country live, and the actual business and political capital is Podgorica).
Task 4.
To complete the task, use an outline map of the world.
Find the countries that are part of the G7 on an outline map of the world. Highlight their borders, shade their territories, add shading to the legend of the contour map, write the names of the countries and their capitals.
Answer:
G7 countries - USA (capital - Washington), Japan (capital - Tokyo), Germany (capital - Berlin), France (capital - Paris), Great Britain (capital - London), Italy (capital - Rome), Canada ( the capital is Ottawa), (since 1994 Russia has been participating in the group’s meetings).
Task 5.
To complete the task, use the data in table No. 1.
Construct a pie chart of the ratio of iron ore reserves in the top five countries. To do this, the sum of the top five iron ore reserves must be taken as 100%, and then calculate the share of each country and mark the corresponding sector in the pie chart. Individual sectors must be highlighted with certain colors or types of shading. Write a legend for the diagram.
Table No. 1. Explored iron ore reserves in countries around the world (2005)
Place in the world
Country
Region
Stocks,
billion tons
Brazil
Latin America
Russia
Europe, Asia
Canada
North America
China
Asia
Australia
Australia
Ukraine
Europe
USA
North America
Kazakhstan
Asia
India
Asia
South Africa
Africa
Answer:
Iron ore reserves in countries of the world (2005)
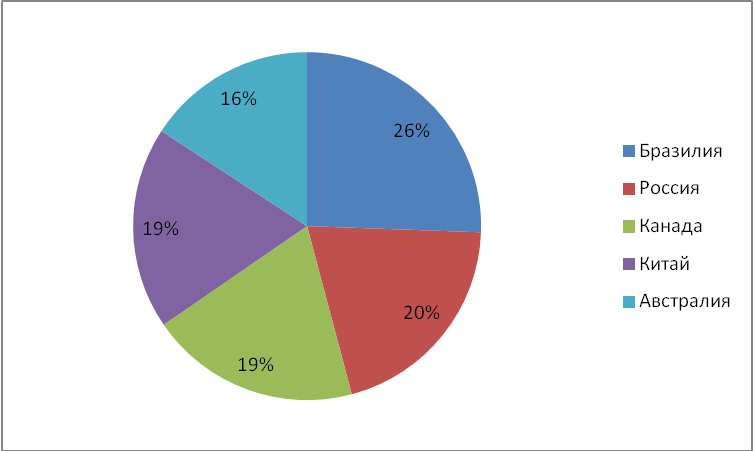
Task 5.
Suggest options for criteria for dividing the ten countries indicated in Table No. 1 into groups based on the volume of explored iron ore reserves. Write down your suggestions.
Answer:
The following criteria can be defined:
The country with the largest iron ore reserves
The country with the smallest iron ore reserves
Countries with the same amount of iron ore reserves
Which region has the largest iron ore reserves?
Which region has the smallest iron ore reserves?
7.Homework.
Purchase an atlas and outline map of Geography for grade 10, colored pencils.
Learn the notes in your notebook.
8. Summing up.
9. Extracurricular independent work
Message “Statistical materials”, “Types of geographical maps”.








