November 11th, 2013
Numerous reforms of the Russian language from the beginning of the 18th century to the present day have never allowed the possibility of replacing the Cyrillic alphabet with the Latin alphabet.
Peter introduced the civil alphabet, had a big quarrel with the church, brought guest workers into the country, but did not encroach on the Slavic letters.
At the end of the 18th - beginning of the 19th centuries, when - according to gr. To L. Tolstoy - the court and high society spoke exclusively French, and the vast majority of the population was illiterate, the moment was extremely convenient. However, the important issue of transformation was not even considered. The nobles chose to start riots on Senate Street.
In 1918, during the last major reform, the Bolsheviks abolished several letters, but did not introduce a foreign alphabet even in the light of the approaching world revolution.
The need to use the Latin alphabet grew every year, but the position of the Soviet leadership on this issue remained unshakable. It was not affected by the accession of the Baltic republics and part of Romania to the USSR, nor the creation of a socialist bloc in Eastern Europe, nor relations with distant Cuba and close Finland.
Then the presidents one by one missed their chance:
- Gorbachev (after the fall of the Berlin Wall);
- Yeltsin (after completion of privatization);
- Medvedev (after meeting with Jobs).
The current head of state started small but important, marking the upcoming Olympics with the mysterious words sochi zoich (or hioz upside down), but was not understood by his compatriots.
As a result, we are forced to spend millions of rubles on infographics in cities, duplicating all names in Latin letters. And who counted the number of man-hours spent on switching languages on keyboards throughout the country?
However, enough words. The following is a new alphabet for Russia, integrated into the glittering Western world. Apparently, this is the least painful path for a country in which Chinese characters or Arabic calligraphy are about to triumph.
| A | A |
| B | B |
| IN | V |
| G | G |
| D | D |
| E | E |
| Yo | Yo |
| AND | ZH |
| Z | Z |
| AND | I |
| Y | J |
| TO | K |
| L | L |
| M | M |
| N | N |
| ABOUT | O |
| P | P |
| R | R |
| WITH | S |
| T | T |
| U | U |
| F | F |
| X | H |
| C | C |
| H | CH |
| Sh | SH |
| SCH | SCH |
| Kommersant | - |
| Y | Y |
| b | " |
| E | JE |
| YU | J.U. |
| I | JA |
The letters Q, W and X disappear. However, the first one can be used in words such as isqusstvo, ququshka. W is two ves in a row or v with a soft sign. X is suitable for words starting with X. We leave Ё because the monument has already been built and the ё-mobile is about to appear.
A couple of excerpts for practice:
1. Ne lepo li ny bjashet-, bratie,
nachjati starymi slovesy
trudnyh- povestij o p-lku Igoreve,
Igorja Svjat-slavlicha?
Nachati zhe sja t-j pesni
po bylinam- sego vremeni,
a ne po zamyshleniju Bojanju!
Bojan-bo veschij,
asche komu xotyashe pesn" tvoriti,
to rastekashetsja mysliju po drevu,
serym v-lkom po zemli,
shizym orlom-pod-oblaky.
2. Ja pomnju chudnoe mgnoven"e:
Peredo mnoj javilas" ty,
How mimoletnoe seen"e,
How genij pure beauty.
I heartce b"etsja v upoen"e,
I dlja nego voznikli vnov"
I bozhestvo, i vdohnoven"e,
I zhizn", i slezy, i ljubov".
The last stanza should also be given in another tradition, where the soft sign is replaced by a double consonant, "в" - by "w", and "е" is retained wherever possible.
I heartce bbеtsja v upoenne,
I dlja nego voznikli vnow
I bozhestvo, i vdohnovenne,
I zhiznn, i slёzy, i ljubow.
All the same, as an unbiased reader can see, it turns out clumsily. Apparently the Russian language is such that the text, even when written in the most foreign letters, retains its wild Eurasian originality, contradictory essence and reluctance to integrate into world culture and civilization. What can we say about its bearers?
Many people ask the question: “What are Latin letters?” In fact, everything is extremely simple. In fact, the Latin alphabet is the alphabetic characters of modern English. The only difference is the pronunciation.
Where are Latin letters and numbers currently used?
Today, more than 40% of the world's population writes in Latin. And in fact, Latin letters are generally accepted international alphabetic characters. You don’t have to look far for an example; just take out your foreign passport and look at it. Under the surname written in Russian, you will definitely see its Latin version.
Numbers are also widely used in all countries. In Russia they are used in contracts, laws, and for numbering clauses. In order to understand how to write in Latin letters, it is enough to select consonant letters and take into account complex combinations, the table with which is given below. Typically, transliteration tables can be found at the information desk of any foreign consulate.
The history of the emergence of Latin writing
It is believed that the roots of the Latin letter go back to the Etruscan and Greek alphabets. There is also an opinion that the Phoenician letter also had its influence. Some are inclined to think that there were also Egyptian alphabetic signs.

The first reliable studies date back to the 7th century BC. The archaic Latin alphabet consisted of 21 letters.
In 312 BC, Appius Claudius Russ abolished the letter Z, after which only 20 letters remained. In the 1st century, Z returned again, and with it a new symbol Y appeared, and the alphabet took on its now familiar form. Over the following years, some letters disappeared and reappeared, some of them eventually united and gave birth to new symbols. Most often, controversy surrounds the letter symbol W.
Influence of the Greek language
Speaking about the Latin alphabet, it is difficult not to mention the influence of the Greek language, since it made a huge contribution to the formation of the modern Latin spelling. If you are confused about the question: “What are Latin letters?”, then you can search or remember the Greek alphabet.

By the way, the letters x, y and z were borrowed from the Greeks. Interesting fact: in Greece they wrote not only from left to right, but also vice versa, which is why they had so many inscriptions that read the same way, no matter which end you start from. In fact, this phenomenon is often given a certain mystical character. There is even a magical "SATOR Square". All words written in it are read not only from right to left and vice versa, but, what is most interesting, the characters can also be read diagonally. There is a belief that by writing all these symbols, you can make a wish that will definitely come true.
How to write your first or last name in Latin
Very often, when submitting documents such as visas, you are required to indicate your personal data using exclusively the Latin alphabet, the letters of which must correspond as closely as possible to Russian. Let's look at the most common names and their spellings.
Pronunciation of Latin letters
If you are asking the question: “What are Latin letters?”, then, most likely, you will also be interested in learning how to pronounce them correctly. There are no difficulties here either, since, most likely, you heard this alphabet back in school.
Despite the identity of English letters, they should not be confused. There are no complex or unpronounceable sounds in Latin, so everything is extremely simple. For comparison: in the English language there is a whole list of sounds that are very difficult for a Russian speaker to pronounce.
Finally
We reviewed the topic: “What are Latin letters?”, and now you can easily fill out an application for a visa or for any other documents that you are going to send abroad. Convenience also lies in the fact that sometimes, when you need to dictate an email address or a link on the Internet over the phone, you can use the Latin alphabet - and the interlocutor will definitely understand you. Therefore, you don’t have to explain anything according to the principle “es is like a dollar,” etc.

Centuries have passed, but we still use this amazing language, developed not by scientists based on sociological surveys and other studies, but by people who did not know what electricity is, where the ozone holes are located and much more. Nevertheless, the legacy of ancient civilizations still makes itself felt, enchanting and amazing with its amazing solutions not only in art, but also in other areas.
Below is a table of correspondence between the letters of the Russian alphabet and the letters of the Latin alphabet.
|
Table of correspondence between Russian letters and Latin letters |
|||
| Russian | Latin | Russian | Latin |
| A | A | P | P |
| B | B | R | R |
| IN | V,W | WITH | S |
| G | G | T | T |
| D | D | U | U, OU |
| E | E | F | F, PH |
| Yo | YO | X | KH, H |
| AND | ZH | C | T.S. |
| Z | Z | H | CH, TCH |
| AND | I | Sh | SH |
| Y | Y | SCH | SCH |
| TO | K | Y | Y |
| L | L | E | E |
| M | M | YU | YU, IU |
| N | N | I | YA, JA |
| ABOUT | O | ||
A table of correspondence between Russian letters and Latin letters can be useful when selecting a domain name if the domain name must be read in Russian. The table is useful when creating file names that are intended to be published on the Internet. The correct Latin spelling of file names will undoubtedly tell the user what he is going to download from a particular link.
It won’t hurt to remember the abbreviation “CNC” (human-readable URL) or the foreign expression “Friendly URL” (URL - Uniform Resource Locator, a unique address of a page on the Internet). These concepts talk about the same thing, about readable and understandable addresses on WEB pages on the Internet. A clear URL gives the user more confidence when deciding whether to click on a given link or not.
It should also be noted that search engines are good at reading and translating the names of site pages and use them when responding to a search query. If the page name contains a word from the user's request, then it is highlighted in bold in the search engine results. Little is known to what extent page names influence the relevance of a site when a search engine responds to a user’s query. One thing is for sure, CNCs are useful for visitors to your site, which means they should be used. The table of correspondence between Russian letters and Latin analogues will help you with this.
A couple of CNC examples:
http://avto.ru/prodazha/bu_avtomobili/bmw_x5_2007.html
After reading this URL, it becomes clear that the page it represents contains an advertisement for the sale of a 2007 BMW X5.
http://lib.ru/arhiv/statya-kak-kormit-sobaku.html
Looking at this URL, you can tell that the link is an article that talks about how to feed a dog.
From the examples you can see that the words in the page titles are separated by a dash and an underscore. Folder names tell the user which group the page located at a particular address can be assigned to. Domain names make it clear what can be located on the sites that are linked to them.
Before as create a website page with a readable address, you can try typing the page name in Latin in Yandex or Google search. If the search engine tries to tell you how to correctly write a query in Russian, it means that the name of your page does not contain errors. Do not forget, before making a request in a search engine, remove all underscores and dashes from the page name.
§ 1. Latin alphabet
The Phoenicians are considered the creators of phonetic writing. Phoenician writing around the 9th century BC. e. borrowed by the Greeks, who added letters to the alphabet to represent vowel sounds. In different areas of Greece, writing was heterogeneous. So by the end of the 5th century BC. e. Two alphabetic systems are clearly distinguished: eastern (Milesian) and western (Chalcidian). Eastern alphabetic system in 403 BC was adopted as the common Greek alphabet. Latins presumably through the Etruscans around the 7th century BC. borrowed the Western Greek alphabet. In turn, the Latin alphabet was inherited by the Romanesque peoples, and during Christianity - by the Germans and Western Slavs. The original design of graphemes (letters) underwent a number of changes over time, and only by the 1st century BC. it acquired the form that still exists today under the name of the Latin alphabet.
The true Latin pronunciation is unknown to us. Classical Latin was preserved only in written monuments. Therefore, the concepts of “phonetics”, “pronunciation”, “sound”, “phoneme”, etc. can be applied to it only in a purely theoretical sense. The accepted Latin pronunciation, called traditional, has come to us thanks to the continuous study of the Latin language, which as an academic subject has not ceased to exist throughout time. This pronunciation reflects changes that occurred in the sound system of Classical Latin towards the end of the Late Western Roman Empire. In addition to the changes resulting from the historical development of the Latin language itself, traditional pronunciation was influenced for many centuries by phonetic processes that took place in the new Western European languages. Therefore, modern reading of Latin texts in different countries is subject to pronunciation norms in new languages.
At the end of the 19th - beginning of the 20th centuries. In the educational practice of many countries, the so-called “classical” pronunciation has become widespread, striving to reproduce the orthoepic norms of classical Latin. The differences between traditional and classical pronunciation boil down to the fact that traditional pronunciation preserves variants of a number of phonemes that arose in late Latin, while classical, if possible, eliminates them.
Below is the traditional reading of Latin letters, adopted in the educational practice of our country.
Note. For a long time, the Latin alphabet consisted of 21 letters. All of the above letters were used except Uu, Yy, Zz.
At the end of the 1st century BC. e. letters were introduced to reproduce the corresponding sounds in borrowed Greek words Yy And Zz.
Letter Vv first used to denote consonant and vowel sounds (Russian [у], [в]). Therefore, to distinguish them in the 16th century. started using the new graphic sign Uu, which corresponds to the Russian sound [у].
Was not in the Latin alphabet and Jj. In classical Latin the letter i denoted both the vowel sound [i] and the consonant [j]. And only in the 16th century, the French humanist Petrus Ramus added to the Latin alphabet Jj to indicate the sound corresponding to Russian [th]. But in publications by Roman authors and in many dictionaries it is not used. Instead of j still in use і .
Letter Gg was also absent from the alphabet until the 3rd century BC. e. Its functions were performed by the letter Ss, as evidenced by the abbreviations of names: S. = Gaius, Cn. = Gnaeus.,
At first, the Romans used only capital letters (majusculi), and small letters (manusculi) arose later.
In Latin, proper names, names of months, peoples, geographical names, as well as adjectives and adverbs formed from them are written with a capital letter.
In the 5th century BC e. Latin language(self-name Lingua Latina) was one of the many Italic languages spoken in central Italy. Latin was used in the area known as Latium (modern name is Latium), and Rome was one of the cities in this area. The earliest inscriptions in Latin date back to the 6th century. BC e. and are made using an alphabet based on the Etruscan script.
Gradually, Rome's influence spread to other parts of Italy, and through them to Europe. Over time, the Roman Empire conquered Europe, North Africa and the Middle East. Throughout the empire, Latin came to be used as the language of law and authority, and, increasingly, the language of everyday life. The Romans were literate, and many of them read the works of famous Latin authors.
Meanwhile, in the eastern Mediterranean, Greek remained the lingua franca, and educated Romans were bilingual. The earliest examples of Latin literature known to us are translations of Greek plays and Cato's agricultural manual into Latin, dating back to 150 BC. e.
Classical Latin, which was used in early works of Latin literature, differed in many ways from colloquial, so-called Vulgar Latin. However, some writers, including Cicero and Petronius, used Vulgar Latin in their writings. Over time, the spoken variants of the Latin language moved further and further away from the literary standard, and gradually, on their basis, Italic/Romance languages (Spanish, Portuguese, etc.) appeared.
Even after the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in 476, Latin continued to be used as a literary language in Western and Central Europe. A huge amount of medieval Latin literature appeared in a variety of styles - from scientific works of Irish and Anglo-Saxon writers to simple tales and sermons intended for the general public.
Throughout the 15th century. Latin began to lose its dominant position and title as the main language of science and religion in Europe. It has been largely replaced by written versions of local European languages, many of which are derived from or influenced by Latin.
Modern Latin was used by the Roman Catholic Church until the mid-20th century, and currently continues to exist to some extent, especially in the Vatican, where it is recognized as one of the official languages. Latin terminology is actively used by biologists, paleontologists and other scientists to name species and preparations, as well as by doctors and lawyers.
Latin alphabet
The Romans used only 23 letters to write Latin:
There were no lowercase letters in Latin. The letters I and V could be used as consonants and vowels. The letters K, X, Y and Z were used only to write words of Greek origin.
The letters J, U and W were added to the alphabet later to write languages other than Latin.
The letter J is a variant of I and was first introduced into use by Pierre de la Ramais in the 16th century.
The letter U is a variant of V. In Latin, the sound /u/ was represented by the letter v, for example IVLIVS (Julius).
The letter W was originally a double v (vv) and was first used by Old English scribes in the 7th century, although the runic letter Wynn (Ƿ) was more commonly used to represent the /w/ sound in writing. After the Norman Conquest, the letter W became more popular and by 1300 had completely replaced Wynn.
Reconstructed phonetic transcription of classical Latin
Vowels and diphthongs
Consonants
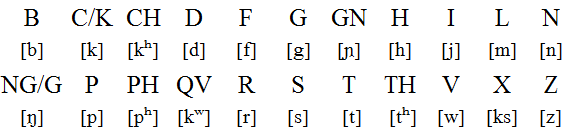
Notes
- Vowel length was not shown in writing, although modern editions of classical texts use a macron (ā) to indicate long vowels.
- The pronunciation of short vowels in the medial position is different: E [ɛ], O [ɔ], I [ɪ] and V [ʊ].
Phonetic transcription of ecclesiastical Latin
Vowels
Diphthongs
Consonants

Notes
- Double vowels are pronounced separately
- C = [ʧ] before ae, oe, e, i or y, and [k] in any other positions
- G = [ʤ] before ae, oe, e, i or y, and [g] in any other positions
- H is not pronounced except in words mihi And nihil, where the sound /k/ is pronounced
- S = [z] between vowels
- SC = [ʃ] before ae, oe, e, i or y, and in any other positions
- TI = before the vowel a and after all letters except s, t or x, and in any other positions
- U = [w] after q
- V = [v] at the beginning of a syllable
- Z = at the beginning of a word before vowels, and before consonants or at the end of a word.








