The satellite of the Earth has attracted the attention of people since prehistoric times. The moon is the most visible object in the sky after the sun, and therefore it has always been attributed the same significant properties as the daylight. Over the centuries, worship and simple curiosity have been replaced by scientific interest. The waning, full and growing moon are today the objects of the closest study. Thanks to the research of astrophysicists, we know a lot about the satellite of our planet, but a lot remains unknown.
Origin
The moon is a phenomenon so familiar that there is practically no question of where it came from. Meanwhile, it is precisely the origin of the satellite of our planet that is one of its most significant secrets. Today, there are several theories on this subject, each of which boasts both the presence of evidence and arguments in favor of its insolvency. The data obtained allow us to single out three main hypotheses.
- The Moon and Earth formed from the same protoplanetary cloud.
- The fully formed Moon was captured by the Earth.
- The formation of the Moon was caused by the collision of the Earth with a large space object.
Let's consider these versions in more detail.
Joint accretion
The hypothesis of the joint origin (accretion) of the Earth and its satellite was recognized in the scientific world as the most plausible until the beginning of the 70s of the last century. It was first put forward by Immanuel Kant. According to this version, the Earth and the Moon were formed almost simultaneously from protoplanetary particles. The cosmic bodies were in this case a binary system.
The Earth was the first to form. After it reached a certain size, particles from the protoplanetary swarm began to circle around it under the influence of gravity. They began to move in elliptical orbits around the nascent object. Some particles fell to the Earth, others collided and stuck together. Then the orbit gradually began to approach a circular one more and more, and the embryo of the Moon began to form from a swarm of particles.
Pros and cons
Today, the co-origination hypothesis has more refutation than evidence. It explains the identical oxygen-isotope ratio of the two bodies. The causes of the different composition of the Earth and the Moon, put forward in the framework of the hypothesis, in particular, the almost complete absence of iron and volatile substances on the latter, are doubtful.
Guest from afar
In 1909, Thomas Jackson Jefferson C put forward the hypothesis of gravitational capture. According to her, the Moon is a body formed somewhere in another region of the solar system. Its elliptical orbit intersected the Earth's trajectory. At the next approach, the Moon was captured by our planet and became a satellite.

In favor of the hypothesis, scientists cite quite common myths of the peoples of the world, telling about the time when the moon was not in the sky. Also indirectly, the theory of gravitational capture is confirmed by the presence of a solid surface on the satellite. According to Soviet research, the moon, which has no atmosphere, if it has been orbiting our planet for several billion years, should have been covered with a many-meter layer of dust coming from space. However, today it is known that this is not observed on the surface of the satellite.
The hypothesis can explain the small amount of iron on the Moon: it could have formed in the zone of giant planets. However, in this case, it should have a high concentration of volatile substances. In addition, according to the results of modeling of gravitational capture, its possibility seems unlikely. A body with a mass like that of the Moon would rather collide with our planet or be expelled out of orbit. Gravitational capture could occur only in the case of a very close passage of the future satellite. However, even in this variant, the destruction of the Moon under the action of tidal forces becomes more probable.
giant collision
The third of the above hypotheses is currently considered the most plausible. According to the giant impact theory, the Moon is the result of the interaction of the Earth and a rather large space object. The hypothesis was proposed in 1975 by William Hartman and Donald Davis. They suggested that a protoplanet called Theia collided with the young Earth, which managed to gain 90% of its mass. Its size corresponded to modern Mars. As a result of the impact, which fell on the "edge" of the planet, almost all of the matter of Teya and part of the earth's matter was ejected into outer space. From this "building material" the Moon began to form.
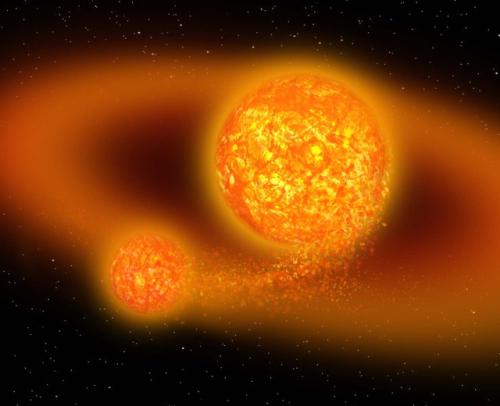
The hypothesis explains the current speed as well as the angle of inclination of its axis and many physical and chemical parameters of both bodies. The weak point of the theory is its reasons for the low iron content on the Moon. To do this, before the collision in the bowels of both bodies, complete differentiation had to occur: the formation of an iron core and a silicate mantle. To date, no confirmation has been found. Perhaps new data on the earth's satellite will clarify this issue as well. True, there is a possibility that they can refute the hypothesis of the origin of the Moon accepted today.
main parameters
For modern people, the Moon is an integral part of the night sky. The distance to it today is approximately 384 thousand kilometers. This parameter changes somewhat as the satellite moves (range - from 356,400 to 406,800 km). The reason lies in the elliptical orbit.
A satellite of our planet moves through space at a speed of 1.02 km/s. It completes a full revolution around our planet in about 27.32 days (sidereal or sidereal month). Interestingly, the attraction of the Moon by the Sun is 2.2 times stronger than by the Earth. This and other factors affect the movement of the satellite: the reduction of the sidereal month, the change in the distance to the planet.
The axis of the Moon has an inclination of 88 ° 28 ". The rotation period is equal to the sidereal month and that is why the satellite is always turned to our planet on one side.
reflective
It can be assumed that the Moon is a star very close to us (in childhood, such an idea could come to many). However, in reality, it does not have many of the parameters inherent in such bodies as the Sun or Sirius. So, the moonlight, sung by all romantic poets, is only a reflection of the sun. The satellite itself does not radiate.
The phase of the moon is a phenomenon associated with the absence of its own light. The visible part of the satellite in the sky is constantly changing, successively passing through four stages: the new moon, the growing month, the full moon and the waning moon. These are the stages of the synodic month. It is calculated from one new moon to another and lasts an average of 29.5 days. The synodic month is longer than the sidereal month, since the Earth also moves around the Sun and the satellite has to make up some distance all the time.
many-sided
The first phase of the moon in the cycle is the time when there is no satellite in the sky for an earthly observer. At this time, it faces our planet with a dark, unlit side. The duration of this phase is one to two days. Then a moon appears in the western sky. The moon is just a thin sickle at this time. Often, however, one can observe the entire disk of the satellite, but less bright, colored in gray. This phenomenon is called the ashy color of the moon. The gray disk next to the bright crescent is the part of the satellite illuminated by rays reflected from the Earth's surface.
After seven days from the beginning of the cycle, the next phase begins - the first quarter. At this time, the moon is exactly half lit. A characteristic feature of the phase is a straight line separating the dark and illuminated areas (in astronomy it is called the "terminator"). Gradually, it becomes more convex.
On the 14-15th day of the cycle, the full moon occurs. Then the visible part of the satellite begins to decrease. On the 22nd day, the last quarter begins. During this period, it is also often possible to observe an ashy color. The angular distance of the Moon from the Sun is set less and less, and after about 29.5 days it is again completely hidden.
eclipses
Several other phenomena are associated with the peculiarities of the satellite's motion around our planet. The plane of the Moon's orbit is inclined to the ecliptic by an average of 5.14°. This situation is not typical for such systems. As a rule, the orbit of a satellite lies in the plane of the planet's equator. The points where the moon's path crosses the ecliptic are called the ascending and descending nodes. They do not have an exact fixation, they are constantly, albeit slowly, moving. In about 18 years, the nodes traverse the entire ecliptic. In connection with these features, the Moon returns to one of them after a period of 27.21 days (it is called the draconic month).

With the passage of the satellite of the points of intersection of its axis with the ecliptic, such a phenomenon as an eclipse of the moon is associated. This is a phenomenon that rarely pleases (or upsets) us with itself, but has a certain periodicity. The eclipse occurs at the moment when the full moon coincides with the passage of the satellite of one of the nodes. Such an interesting "coincidence" occurs quite rarely. The same is true for the coincidence of the new moon and the passage of one of the nodes. At this time, a solar eclipse occurs.
Observations of astronomers have shown that both phenomena are cyclical. The length of one period is slightly more than 18 years. This cycle is called saros. During one period, there are 28 lunar and 43 solar eclipses (of which 13 are total).
The influence of the night light
Since ancient times, the Moon has been considered one of the rulers of human destiny. According to the thinkers of that period, it influenced the character, attitudes, mood and behavior. Today, the effect of the moon on the body is studied from a scientific point of view. Various studies confirm that the dependence of some behavioral features and health status on the phases of the night star exists.
For example, Swiss doctors, who have been observing patients with problems in the cardiovascular system for a long time, found that the growing moon is a dangerous period for people prone to a heart attack. Most of the seizures, according to their data, coincided with the appearance of a young month in the night sky.
There are many similar studies. However, the collection of such statistics is not the only thing that interests scientists. They tried to find explanations for the revealed patterns. According to one theory, the Moon has the same effect on human cells as it does on the entire Earth: causes As a result of the influence of the satellite, the water-salt balance, membrane permeability, and the ratio of hormones change.

Another version puts the influence of the Moon on the planet's magnetic field at the forefront. According to this hypothesis, the satellite causes changes in the electromagnetic impulses of the body, which entails certain consequences.
Experts who are of the opinion that the night luminary has a huge influence on us recommend that we build our activities, coordinating it with the cycle. They warn: lanterns and lamps blocking moonlight can harm human health, because because of them the body does not receive information about the phase change.
On the moon
After getting acquainted with the night luminary from the Earth, let's walk along its surface. The moon is a satellite that is not protected from the effects of sunlight by the atmosphere. During the day, the surface heats up to 110 ºС, and at night it cools down to -120 ºС. In this case, temperature fluctuations are characteristic of a small zone of the crust of the cosmic body. The very low thermal conductivity does not allow the interior of the satellite to warm up.
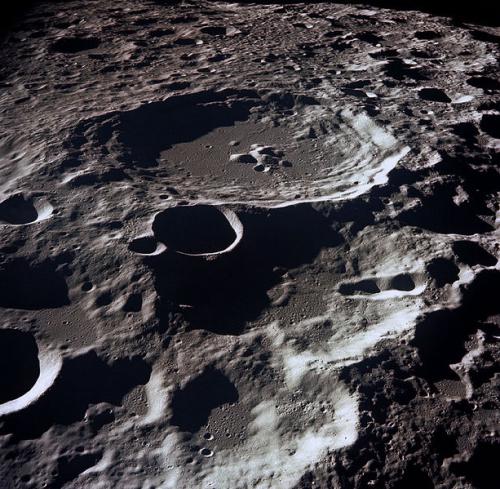
We can say that the Moon is lands and seas, vast and little explored, but with their own names. The first maps of the satellite surface appeared in the seventeenth century. Dark spots, previously taken as seas, turned out to be low plains after the invention of the telescope, but retained their name. Lighter areas on the surface are "continental" zones with mountains and ridges, often ring-shaped (craters). On the Moon you can meet the Caucasus and the Alps, the Seas of Crises and Tranquility, the Ocean of Storms, the Bay of Joy and the Swamp of Rot (the bays on the satellite are dark areas adjacent to the seas, the swamps are small spots of irregular shape), as well as the mountains of Copernicus and Kepler.
And only after that the far side of the moon was explored. It happened in 1959. The data received by the Soviet satellite made it possible to map the part of the night star hidden from telescopes. The names of the greats also sounded here: K.E. Tsiolkovsky, S.P. Koroleva, Yu.A. Gagarin.

Quite another
The absence of an atmosphere makes the Moon so unlike our planet. The sky here is never covered with clouds, its color does not change. On the Moon, above the astronauts' heads, there is only a dark starry dome. The sun rises slowly and slowly moves across the sky. A day on the Moon lasts almost 15 Earth days, and so is the duration of the night. A day is equal to the period for which the Earth's satellite makes one revolution relative to the Sun, or the synodic month.
There is no wind and precipitation on the satellite of our planet, and there is also no smooth flow of day into night (twilight). In addition, the Moon is constantly under the threat of meteorite impacts. Their number is indirectly evidenced by the regolith covering the surface. This is a layer of debris and dust up to several tens of meters thick. It consists of fragmented, mixed and sometimes fused remains of meteorites and lunar rocks destroyed by them.
When you look at the sky, you can see the Earth hanging motionless and always in the same place. A beautiful, but almost never changing picture is due to the synchronization of the moon's rotation around our planet and its own axis. This is one of the most wonderful sights that the astronauts who landed on the surface of the Earth's satellite for the first time had a chance to see. 
famous
There are periods when the Moon is the "star" not only of scientific conferences and publications, but also of all kinds of media. Of great interest to a large number of people are some rather rare phenomena associated with the satellite. One of them is a supermoon. It occurs on those days when the night luminary is at the smallest distance from the planet, and in the phase of the full moon or new moon. At the same time, the night luminary becomes visually 14% larger and 30% brighter. In the second half of 2015, the supermoon will be observed on August 29, September 28 (on this day the supermoon will be the most impressive) and October 27.
Another curious phenomenon is associated with the periodic hit of the night star in the earth's shadow. At the same time, the satellite does not disappear from the sky, but acquires a red color. The astronomical event is called the Blood Moon. This phenomenon is quite rare, but modern space lovers are lucky again. Blood Moons will rise over the Earth several times in 2015. The last of them will appear in September and coincide with the total eclipse of the night star. This is definitely worth seeing!
The night light has always attracted people to itself. The moon and the full moon are central images in many poetic essays. With the development of scientific knowledge and methods of astronomy, the satellite of our planet became of interest not only to astrologers and romantics. Many facts from the time of the first attempts to explain the lunar "behavior" have become clear, a large number of the secrets of the satellite have been revealed. However, the night luminary, like all objects of space, is not as simple as it might seem.

Even the American expedition could not answer all the questions put to it. At the same time, every day scientists learn something new about the Moon, although often the data obtained gives rise to even more doubts about existing theories. So it was with the hypotheses of the origin of the moon. All three main concepts that were recognized in the 60-70s were refuted by the results of the American expedition. Soon the hypothesis of a giant collision became the leader. Most likely, in the future we will have many amazing discoveries related to the night star.








