The Big Bang theory has always been an interesting and mysterious topic of conversation for scientists around the world. The TBW was basically an attempt made by astronomers to explain how our universe came into being.
So what does the word universe really mean?
So, let's try to describe the Big Bang Theory in simple terms.
The universe includes everything that we call matter. Its "composition" includes the sun, moon, stars, galaxies, atoms, molecules.
As a result of research, scientists have found that there are about 100 billion galaxies in the Universe. But surprisingly, the universe is only 10% matter and 90% dark space.
"Dark space refers to a mass that neither emits nor absorbs electromagnetic radiation"
So how did the universe come into being and how does it exist to this day?
According to the Big Bang Theory, it all started about 14 billion years ago. The Universe existed as a small material object with a diameter of several millimeters, consisting of very small particles (like an atom). In scientific language, such a state is called a cosmological singularity. It had a very high temperature and was very dense - it had an infinite mass, and, as a result, an infinite gravitational force.
Scientists claim that this object was so hot that at a certain point in time it exploded, creating space for the creation of the universe, while others believe that there was not an “explosion”, but an “expansion” from a tiny size to the size of the universe where we live. today. Moreover, the expansion to the size of the solar system occurred at an incredible speed - comparable to the speed of light (300,000 m/s). It is claimed that this expansion is still taking place. Let's try to find proof of this. 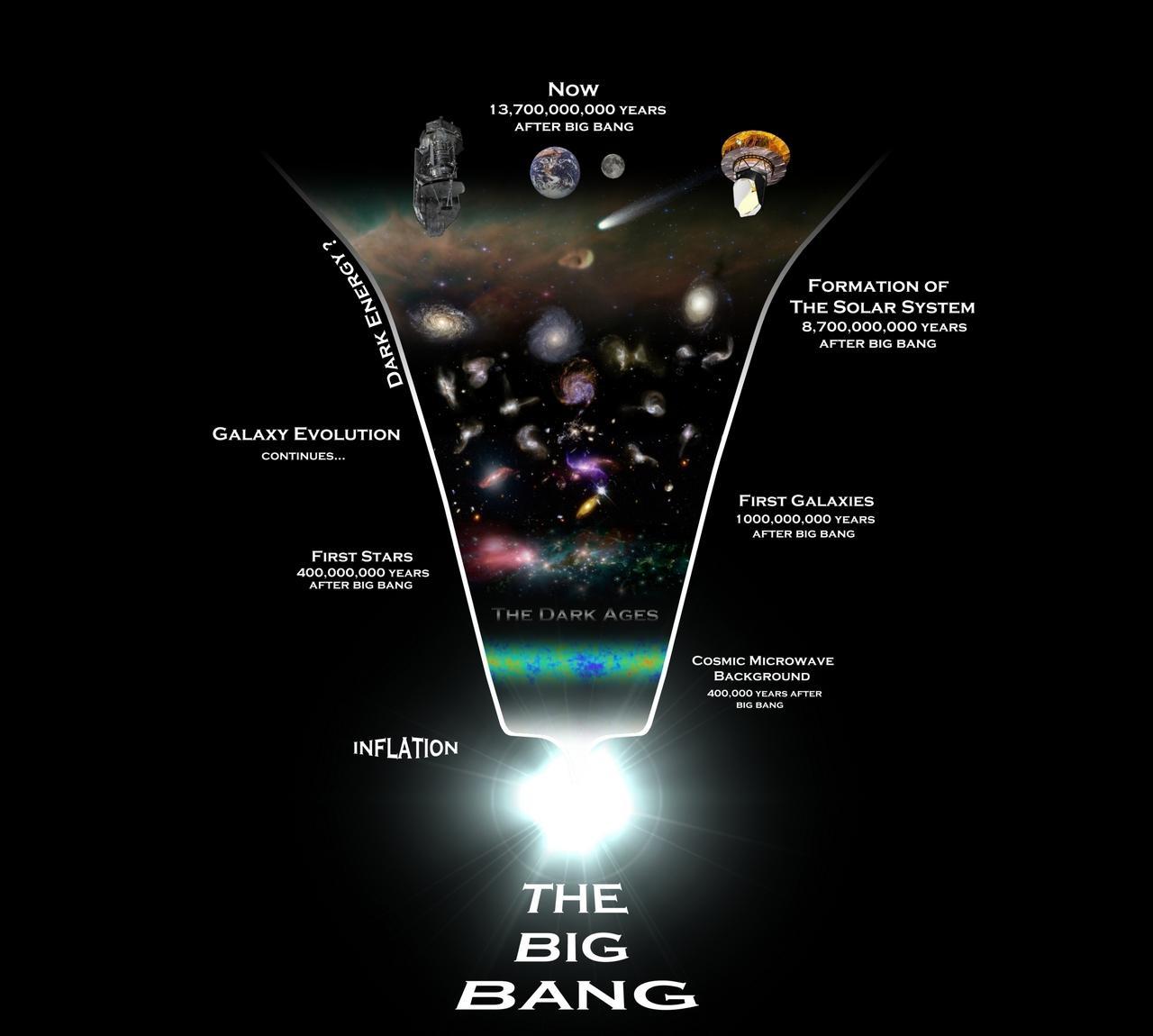
Stars were born a few hundred million years after the Big Bang. The smallest particles formed as a result of the explosion under the influence of gravitational forces began to shrink, twist, forming various substances, galaxies and stars. A gigantic collection of stars, gas and dust makes up any galaxy today. That is why there are billions of galaxies in the universe.
According to the Big Bang Theory, there is a huge black hole at the center of every galaxy. By the way,
Our earth is in a galaxy called the Milky Way and the movement of other galaxies away from our Milky Way at considerable speed proves that the expansion is continuing. In addition, the expansion of the universe as a result of the Big Bang is explained by the action of the blast wave. Every hour the universe expands by a billion miles in every direction. 
In 1963, two American scientists, Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson, discovered that microwave radiation hits the earth from space. These radiations also support the big bang theory. Let's say radiation comes with a finite speed from space to the Earth. In fact, its source was active far in the past. For example, it was found that the CMB was emitted 13.7 billion years ago. Thus, by studying the detailed physical properties of radiation, we can learn about the conditions in the universe at very early times, since the radiation we see today actually traveled an enormous distance and its source may no longer exist. 
And now the most interesting. According to scientists, sooner or later the expansion of the universe under the influence of the blast wave will end. At that moment, the entire universe will experience a state of some kind of balance. But the fact is that the force of attraction of black holes located in the centers of galaxies will not stop its action. That is, black holes will pull surrounding particles into themselves with increasing force. Due to this, the universe will begin to shrink back, until sooner or later it turns into a small object with a critical mass and gravitational force (everything is like at the very beginning). These two parameters will also continue to grow, which will undoubtedly lead to a new big bang. Scientists also do not deny the fact that the entire universe consists of a large number of such objects, contracting and expanding indefinitely. How many times this can go on is a mystery to everyone. 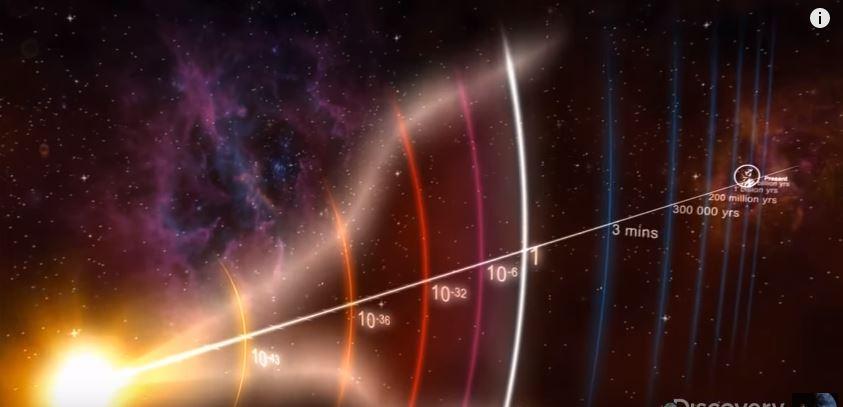
So, in a nutshell, briefly, we tried to describe the Big Bang Theory in simple words. I hope you liked the article, write your questions and corrections in the comments. And finally, the video "The Big Bang Theory in simple words."







