A cylinder is a figure consisting of cylindrical surface and two circles located parallel. Calculating the area of a cylinder is a task geometric section mathematics, which is solved quite simply. There are several methods for solving it, which in the end always come down to one formula.
How to find the area of a cylinder - calculation rules
- To find out the area of the cylinder, you need to add the two areas of the base with the area of the side surface: S = Sside + 2Sbase. In a more detailed version, this formula looks like this: S= 2 π rh+ 2 π r2= 2 π r(h+ r).
- The lateral surface area of a given geometric body can be calculated if its height and the radius of the circle lying at its base are known. IN in this case one can express the radius from the circumference of a circle, if given. The height can be found if the value of the generator is specified in the condition. In this case, the generatrix will be equal to the height. The formula for the lateral surface of this body looks like this: S= 2 π rh.
- The area of the base is calculated using the formula for finding the area of a circle: S osn= π r 2 . In some problems, the radius may not be given, but the circumference may be given. With this formula, the radius is expressed quite easily. С=2π r, r= С/2π. You must also remember that the radius is half the diameter.
- When performing all these calculations, the number π usually does not translate into 3.14159... It just needs to be added next to numerical value, which was obtained as a result of calculations.
- Next, you just need to multiply the found area of the base by 2 and add to the resulting number the calculated area of the lateral surface of the figure.
- If the problem indicates that the cylinder contains axial section and this is a rectangle, then the solution will be slightly different. In this case, the width of the rectangle will be the diameter of the circle lying at the base of the body. The length of the figure will be equal to the generatrix or height of the cylinder. Need to calculate required values and substitute it into the already known formula. In this case, the width of the rectangle must be divided by two to find the area of the base. To find the lateral surface, the length is multiplied by two radii and the number π.
- You can calculate the area of a given geometric body through its volume. To do this, you need to derive the missing value from the formula V=π r 2 h.
- There is nothing complicated in calculating the area of a cylinder. You just need to know the formulas and be able to derive from them the quantities necessary to carry out calculations.
Surface area of the pyramid. In this article we will look at problems with regular pyramids. Let me remind you that a regular pyramid is a pyramid whose base is a regular polygon, the top of the pyramid is projected into the center of this polygon.
The side face of such a pyramid is an isosceles triangle.The height of this triangle drawn from the vertex regular pyramid, called apothem, SF – apothem:
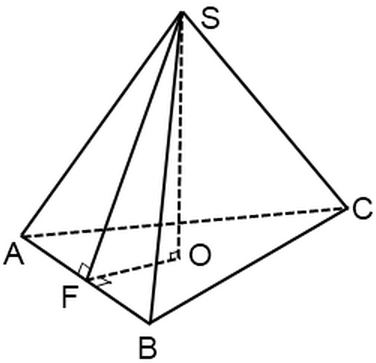
In the type of problem presented below, you need to find the surface area of the entire pyramid or the area of its lateral surface. The blog has already discussed several problems with regular pyramids, where the question of finding elements (height, base edge, side edge) was raised.
IN Unified State Exam assignments As a rule, regular triangular, quadrangular and hexagonal pyramids are considered. I haven’t seen any problems with regular pentagonal and heptagonal pyramids.
The formula for the area of the entire surface is simple - you need to find the sum of the area of the base of the pyramid and the area of its lateral surface:
![]()
Let's consider the tasks:
The sides of the base are correct quadrangular pyramid are equal to 72, lateral ribs are equal to 164. Find the surface area of this pyramid.

The surface area of the pyramid is equal to the sum of the areas of the lateral surface and the base:
*The lateral surface consists of four triangles of equal area. The base of the pyramid is a square.
We can calculate the area of the side of the pyramid using:
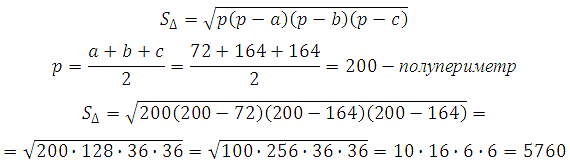
Thus, the surface area of the pyramid is:
Answer: 28224
The sides of the base are correct hexagonal pyramid are 22, side edges are 61. Find the lateral surface area of this pyramid.

The base of a regular hexagonal pyramid is a regular hexagon.
The lateral surface area of this pyramid consists of six areas of equal triangles with sides 61,61 and 22:
Let's find the area of the triangle using Heron's formula:

Thus, the lateral surface area is:
![]()
Answer: 3240
*In the problems presented above, the area of the side face could be found using another triangle formula, but for this you need to calculate the apothem.
27155. Find the surface area of a regular quadrangular pyramid whose base sides are 6 and whose height is 4.

In order to find the surface area of the pyramid, we need to know the area of the base and the area of the lateral surface:
The area of the base is 36 since it is a square with side 6.
The lateral surface consists of four faces, which are equal triangles. In order to find the area of such a triangle, you need to know its base and height (apothem):
*The area of a triangle is equal to half the product of the base and the height drawn to this base.
The base is known, it is equal to six. Let's find the height. Consider a right triangle (highlighted in yellow):

One leg is equal to 4, since this is the height of the pyramid, the other is equal to 3, since it is equal to half base ribs. We can find the hypotenuse using the Pythagorean theorem:
![]()
This means that the area of the lateral surface of the pyramid is:

Thus, the surface area of the entire pyramid is:
Answer: 96
27069. The sides of the base of a regular quadrangular pyramid are equal to 10, the side edges are equal to 13. Find the surface area of this pyramid.
27070. The sides of the base of a regular hexagonal pyramid are equal to 10, the side edges are equal to 13. Find the lateral surface area of this pyramid.
There are also formulas for the lateral surface area of a regular pyramid. In a regular pyramid, the base is orthogonal projection lateral surface, therefore:
P- base perimeter, l- apothem of the pyramid
*This formula is based on the formula for the area of a triangle.
If you want to learn more about how these formulas are derived, don’t miss it, follow the publication of articles.That's all. Good luck to you!
Sincerely, Alexander Krutitskikh.
P.S: I would be grateful if you tell me about the site on social networks.
Pyramid- one of the varieties of a polyhedron formed from polygons and triangles that lie at the base and are its faces.
Moreover, at the top of the pyramid (i.e. at one point) all the faces are united.
In order to calculate the area of a pyramid, it is worth determining that its lateral surface consists of several triangles. And we can easily find their areas using
various formulas. Depending on what data we know about the triangles, we look for their area.
We list some formulas that can be used to find the area of triangles:
- S = (a*h)/2 . In this case, we know the height of the triangle h , which is lowered to the side a .
- S = a*b*sinβ . Here are the sides of the triangle a , b , and the angle between them is β .
- S = (r*(a + b + c))/2 . Here are the sides of the triangle a, b, c . The radius of a circle that is inscribed in a triangle is r .
- S = (a*b*c)/4*R . The radius of a circumscribed circle around a triangle is R .
- S = (a*b)/2 = r² + 2*r*R . This formula should only be used when the triangle is a right triangle.
- S = (a²*√3)/4 . We apply this formula to an equilateral triangle.
Only after we calculate the areas of all the triangles that are the faces of our pyramid, can we calculate the area of its lateral surface. To do this, we will use the above formulas.
In order to calculate the area of the lateral surface of a pyramid, no difficulties arise: you need to find out the sum of the areas of all triangles. Let's express this with the formula:
Sp = ΣSi
Here Si is the area of the first triangle, and S n - area of the lateral surface of the pyramid.
Let's look at an example. Given a regular pyramid, its lateral faces are formed by several equilateral triangles,
« Geometry is the most powerful tool for sharpening our mental abilities».
Galileo Galilei.
and the square is the base of the pyramid. Moreover, the edge of the pyramid has a length of 17 cm. Let's find the area lateral surface of this pyramid.
We reason like this: we know that the faces of the pyramid are triangles, they are equilateral. We also know what the edge length of this pyramid is. It follows that all triangles have equal sides, their length is 17 cm.
To calculate the area of each of these triangles, you can use the following formula:
S = (17²*√3)/4 = (289*1.732)/4 = 125.137 cm²
So, since we know that the square lies at the base of the pyramid, it turns out that we have four equilateral triangles. This means that the area of the lateral surface of the pyramid can be easily calculated using the following formula: 125.137 cm² * 4 = 500.548 cm²
Our answer is as follows: 500.548 cm² - this is the area of the lateral surface of this pyramid.
Instructions
First of all, it is worth understanding that the lateral surface of the pyramid is represented by several triangles, the areas of which can be found using the most various formulas, depending on known data:
S = (a*h)/2, where h is the height lowered to side a;
S = a*b*sinβ, where a, b are the sides of the triangle, and β is the angle between these sides;
S = (r*(a + b + c))/2, where a, b, c are the sides of the triangle, and r is the radius of the circle inscribed in this triangle;
S = (a*b*c)/4*R, where R is the radius of the triangle circumscribed around the circle;
S = (a*b)/2 = r² + 2*r*R (if the triangle is right-angled);
S = S = (a²*√3)/4 (if the triangle is equilateral).
In fact, these are only the most basic of known formulas to find the area of a triangle.
Having calculated the areas of all triangles that are the faces of the pyramid using the above formulas, you can begin to calculate the area of this pyramid. This is done extremely simply: you need to add up the areas of all the triangles that form lateral surface pyramids. This can be expressed by the formula:
Sp = ΣSi, where Sp is the area of the lateral surface, Si is the area of the i-th triangle, which is part of its lateral surface.
For greater clarity, we can consider a small example: given a regular pyramid, the side faces of which are formed by equilateral triangles, and at its base lies a square. The length of the edge of this pyramid is 17 cm. It is required to find the area of the lateral surface of this pyramid.
Solution: the length of the edge of this pyramid is known, it is known that its faces are equilateral triangles. Thus, we can say that all sides of all triangles on the lateral surface are equal to 17 cm. Therefore, in order to calculate the area of any of these triangles, you will need to apply the formula:
S = (17²*√3)/4 = (289*1.732)/4 = 125.137 cm²
It is known that at the base of the pyramid lies a square. Thus, it is clear that the data equilateral triangles four. Then the area of the lateral surface of the pyramid is calculated as follows:
125.137 cm² * 4 = 500.548 cm²
Answer: The lateral surface area of the pyramid is 500.548 cm²
First, let's calculate the area of the lateral surface of the pyramid. The lateral surface is the sum of the areas of all lateral faces. If you are dealing with a regular pyramid (that is, one that has a regular polygon at its base, and the vertex is projected into the center of this polygon), then to calculate the entire lateral surface it is enough to multiply the perimeter of the base (that is, the sum of the lengths of all sides of the polygon lying at the base pyramid) by the height of the side face (otherwise called the apothem) and divide the resulting value by 2: Sb = 1/2P*h, where Sb is the area of the side surface, P is the perimeter of the base, h is the height of the side face (apothem).
If you have an arbitrary pyramid in front of you, you will have to separately calculate the areas of all the faces and then add them up. Since the side faces of the pyramid are triangles, use the formula for the area of a triangle: S=1/2b*h, where b is the base of the triangle, and h is the height. When the areas of all the faces have been calculated, all that remains is to add them up to get the area of the lateral surface of the pyramid.
Then you need to calculate the area of the base of the pyramid. The choice of formula for calculation depends on which polygon lies at the base of the pyramid: regular (that is, one with all sides of the same length) or irregular. Square regular polygon can be calculated by multiplying the perimeter by the radius of the circle inscribed in the polygon and dividing the resulting value by 2: Sn=1/2P*r, where Sn is the area of the polygon, P is the perimeter, and r is the radius of the circle inscribed in the polygon.
A truncated pyramid is a polyhedron that is formed by a pyramid and its cross section, parallel to the base. Finding the lateral surface area of the pyramid is not difficult at all. Its very simple: the area is equal to the product of half the sum of the bases by . Let's consider an example of calculating the lateral surface area. Suppose we are given a regular pyramid. The lengths of the base are b = 5 cm, c = 3 cm. Apothem a = 4 cm. To find the area of the lateral surface of the pyramid, you must first find the perimeter of the bases. In a large base it will be equal to p1=4b=4*5=20 cm. smaller base the formula will be as follows: p2=4c=4*3=12 cm. Therefore, the area will be equal to: s=1/2(20+12)*4=32/2*4=64 cm.
If there is an irregular polygon at the base of the pyramid, to calculate the area of the entire figure, you will first need to break the polygon into triangles, calculate the area of each, and then add them. In other cases, to find the side surface of the pyramid, you need to find the area of each of its side faces and add up the results. In some cases, the task of finding the side surface of the pyramid can be made easier. If one side face is perpendicular to the base or two adjacent side faces are perpendicular to the base, then the base of the pyramid is considered an orthogonal projection of part of its side surface, and they are related by formulas.
To complete the calculation of the surface area of the pyramid, add the areas of the side surface and the base of the pyramid.
A pyramid is a polyhedron, one of whose faces (base) is an arbitrary polygon, and the remaining faces (sides) are triangles having . According to the number of angles, the bases of the pyramid are triangular (tetrahedron), quadrangular, and so on.
A pyramid is a polyhedron with a base in the form of a polygon, and the remaining faces are triangles with a common vertex. An apothem is the height of the side face of a regular pyramid, which is drawn from its vertex.
A pyramid is a polyhedron, the base of which is a polygon, and the side faces are triangles that have one common vertex. Square surfaces pyramids equal to the sum of the areas of the lateral surfaces and grounds pyramids.
You will need
- Paper, pen, calculator
Instructions
First we calculate the area of the side surfaces . By lateral surface we mean the sum of all lateral faces. If you are dealing with a regular pyramid (that is, one in which a regular polygon lies, and the vertex is projected to the center of this polygon), then to calculate the entire lateral surfaces it is enough to multiply the perimeter of the base (that is, the sum of the lengths of all sides of the polygon lying at the base pyramids) by the height of the side face (otherwise called) and divide the resulting value by 2: Sb=1/2P*h, where Sb is the area of the side surfaces, P - perimeter of the base, h - height of the side face (apothem).
If you have an arbitrary pyramid in front of you, you will have to calculate the areas of all the faces and then add them up. Since the side faces pyramids are, use the formula for the area of a triangle: S=1/2b*h, where b is the base of the triangle, and h is the height. When the areas of all the faces have been calculated, all that remains is to add them up to get the area of the side surfaces pyramids.
Then you need to calculate the area of the base pyramids. The choice for calculation depends on whether the polygon lies at the base of the pyramid: regular (that is, one whose sides are all the same length) or. Square of a regular polygon can be calculated by multiplying the perimeter by the radius of the inscribed circle in the polygon and dividing the resulting value by 2: Sn = 1/2P*r, where Sn is the area of the polygon, P is the perimeter, and r is the radius of the inscribed circle in the polygon.
If at the base pyramids lies an irregular polygon, then to calculate the area of the entire figure you will again have to divide the polygon into triangles, calculate the area of each, and then add them.
To complete the area calculation surfaces pyramids, fold the square side surfaces and grounds pyramids.
Video on the topic
The polygon represents geometric figure, constructed by closing a broken line. There are several types of polygon, which differ depending on the number of vertices. The area is calculated for each type of polygon in certain ways.

Instructions
Multiply the lengths of the sides if you need to calculate the area of a square or rectangle. If you need to know the area right triangle, build it to a rectangle, calculate its area and divide it by two.
Use the following method to calculate the area if the figure does not have more than 180 degrees (a convex polygon), while all its vertices are in the coordinate grid, and does not intersect itself.
Draw a rectangle around such a polygon so that its sides are parallel to the grid lines (coordinate axes). In this case, at least one of the vertices of the polygon must be the vertex of a rectangle.
Only a truncated one can have two bases pyramids. In this case, the second base is formed by a section parallel to the larger base pyramids. Find one of reasons possible if it is known or linear elements second.

You will need
- - properties of the pyramid;
- - trigonometric functions;
- - similarity of figures;
- - finding the areas of polygons.
Instructions
If the base is regular triangle, find it square by multiplying the square of the side by the square root of 3 divided by 4. If the base is a square, raise its side to the second power. IN general case, for any regular polygon, apply the formula S=(n/4) a² ctg(180º/n), where n is the number of sides of the regular polygon, a is the length of its side.
Find the side of the smaller base using the formula b=2 (a/(2 tg(180º/n))-h/tg(α)) tg(180º/n). Here a – larger base, h – height of the truncated pyramids, α – dihedral angle at its base, n – number of sides reasons(it's the same). Find the area of the second base similarly to the first, using in the formula the length of its side S=(n/4) b² ctg(180º/n).
If the bases are other types of polygons, all sides of one of them are known reasons, and one of the sides of the other, then calculate the remaining sides as similar. For example, the sides of the larger base are 4, 6, 8 cm. Big side smaller base wound 4 cm. Calculate the coefficient of proportionality, 4/8 = 2 (take the sides in each of reasons), and calculate the other sides 6/2=3 cm, 4/2=2 cm. We get sides 2, 3, 4 cm at the smaller base of the side. Now calculate them as the areas of the triangles.
If the ratio of the corresponding elements in the truncated one is known, then the ratio of the areas reasons will be equal to the ratio of the squares of these elements. For example, if the relevant parties are known reasons a and a1, then a²/a1²=S/S1.
Under area pyramids usually refers to the area of its lateral or full surface. At the base of this geometric body lies a polygon. Side faces have triangular shape. They have common vertex, which is also the top pyramids.

You will need
- - a sheet of paper;
- - pen;
- - calculator;
- - a pyramid with given parameters.
Instructions
Consider the pyramid given in the task. Determine whether the polygon is regular or irregular at its base. The correct one has all sides equal. The area in this case is equal to half the product of the perimeter and the radius. Find the perimeter by multiplying the length of the side l by the number of sides n, that is, P=l*n. The area of the base can be expressed by the formula So=1/2P*r, where P is the perimeter, and r is the radius of the inscribed circle.
The perimeter and area of an irregular polygon are calculated differently. The sides have different lengths. To
A parallelepiped is a quadrangular prism with a parallelogram at its base. There are ready-made formulas for calculating lateral and full area surfaces of a figure, for which only the lengths of three dimensions of the parallelepiped are needed.
How to find the lateral surface area of a rectangular parallelepiped
It is necessary to distinguish between a rectangular and a straight parallelepiped. The base of a straight figure can be any parallelogram. The area of such a figure must be calculated using other formulas.
The sum S of the lateral faces of a rectangular parallelepiped is calculated using the simple formula P*h, where P is the perimeter and h is the height. The figure shows that a rectangular parallelepiped opposite faces are equal, and the height h coincides with the length of the edges perpendicular to the base.
Surface area of a cuboid
The total area of the figure consists of the side and the area of 2 bases. How to find the area of a rectangular parallelepiped:
Where a, b and c are the dimensions of the geometric body.
The described formulas are easy to understand and useful in solving many geometry problems. Example typical task presented in the following image.

When solving problems of this kind, it should be remembered that the basis quadrangular prism is chosen randomly. If we take the face with dimensions x and 3 as the base, then the values of Sside will be different, and Stotal will remain 94 cm2.
Surface area of a cube
Cube is cuboid, in which all 3 dimensions are equal to each other. In this regard, the formulas for the total and lateral area of a cube differ from the standard ones.

The perimeter of the cube is 4a, therefore, Sside = 4*a*a = 4*a2. These expressions are not required for memorization, but significantly speed up the solution of tasks.








