Our planet is in constant motion, it rotates around the Sun and its own axis. The Earth's axis is an imaginary line drawn from the North to the South Pole (they remain motionless during rotation) at an angle of 66 0 33 ꞌ relative to the plane of the Earth. People cannot notice the moment of rotation, because all objects move in parallel, their speed is the same. It would look exactly the same as if we were sailing on a ship and did not notice the movement of objects and objects on it.
A full revolution around the axis is completed within one sidereal day, consisting of 23 hours 56 minutes and 4 seconds. During this period, first one or the other side of the planet turns towards the Sun, receiving different amounts of heat and light from it. In addition, the rotation of the Earth around its axis affects its shape (flattened poles are the result of the planet’s rotation around its axis) and the deviation when bodies move in the horizontal plane (rivers, currents and winds of the Southern Hemisphere deviate to the left, of the Northern Hemisphere to the right).
Linear and angular rotation speed

(Earth Rotation)
The linear speed of rotation of the Earth around its axis is 465 m/s or 1674 km/h in the equator zone; as you move away from it, the speed gradually slows down, at the North and South Poles it is zero. For example, for citizens of the equatorial city of Quito (the capital of Ecuador in South America), the rotation speed is exactly 465 m/s, and for Muscovites living at the 55th parallel north of the equator, it is 260 m/s (almost half as much) .
Every year, the speed of rotation around the axis decreases by 4 milliseconds, which is due to the influence of the Moon on the strength of sea and ocean tides. The Moon's gravity "pulls" the water in the opposite direction to the Earth's axial rotation, creating a slight frictional force that slows the rotation speed by 4 milliseconds. The speed of angular rotation remains the same everywhere, its value is 15 degrees per hour.
Why does day give way to night?
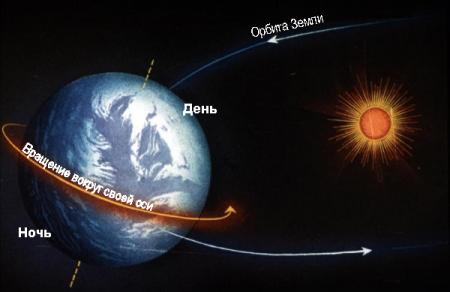
(The change of night and day)
The time for a complete revolution of the Earth around its axis is one sidereal day (23 hours 56 minutes 4 seconds), during this time period the side illuminated by the Sun is first “in the power” of the day, the shadow side is under the control of the night, and then vice versa.
If the Earth rotated differently and one side of it was constantly turned towards the Sun, then there would be a high temperature (up to 100 degrees Celsius) and all the water would evaporate; on the other side, on the contrary, frost would rage and the water would be under a thick layer of ice. Both the first and second conditions would be unacceptable for the development of life and the existence of the human species.
Why do the seasons change?
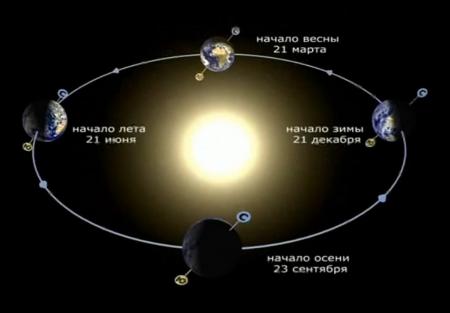
(Change of seasons on Earth)
Due to the fact that the axis is tilted relative to the earth's surface at a certain angle, its parts receive different amounts of heat and light at different times, which causes the change of seasons. According to the astronomical parameters necessary to determine the time of year, certain points in time are taken as reference points: for summer and winter these are the Solstice Days (June 21 and December 22), for spring and autumn - the Equinoxes (March 20 and September 23). From September to March, the Northern Hemisphere faces the Sun for less time and, accordingly, receives less heat and light, hello winter-winter, the Southern Hemisphere at this time receives a lot of heat and light, long live summer! 6 months pass and the Earth moves to the opposite point of its orbit and the Northern Hemisphere receives more heat and light, the days become longer, the Sun rises higher - summer comes.
If the Earth were located in relation to the Sun in an exclusively vertical position, then the seasons would not exist at all, because all points on the half illuminated by the Sun would receive the same and uniform amount of heat and light.








