Everyone knows that planet Earth has round shape. But few people can say what size the planet is. What is the circumference of the earth along the equatorial line or along the meridian? What is the diameter of the Earth? We will try to answer these questions in as much detail as possible.
First of all, let's look at the basic concepts, which we will encounter when answering the question about the circumference of the Earth.
What is the equator called? This is a circular line encircling the planet and passing through its center. The equator is perpendicular to the axis earth's rotation. It is equally distant from one and the other pole. The equator divides the planet into two hemispheres called the Northern and Southern. It plays a big role in determining the climate zones on the planet. The closer to the equator, the hotter the climate, because these areas receive more sunlight.
What are meridians? These are the lines that divide everything globe . There are 360 of them, that is, each fraction between them is equal to one degree. Meridians run through the poles of the planet. They count according to meridians geographic longitude. The countdown starts from the prime meridian, which is also called the Greenwich meridian, since it runs through the Greenwich Observatory in England. Longitude is called eastern or western, depending on the direction in which the count is taken.
In ancient times
The circumference of the Earth was first measured in Ancient Greece. It was the mathematician Eratosthenes from the city of Siena. At that time it was already known that the planet has a spherical shape. Eratosthenes observed the Sun and noticed that the luminary at the same time of day, when observed from Syene, was located exactly at the zenith, but in Alexandria it had a deviation angle.
These measurements were made by Eratosthenes on the day of the solstice in summer period. The scientist measured the angle and found that its value was 1/50 of the whole circle, equal to 360 degrees. Knowing the chord of an angle of one degree, it needs to be multiplied by 360. Then Eratosthenes took the interval between two cities (Syena and Alexandria) as the length of the chord, assumed that they were on the same meridian, made calculations and named the figure 252 thousand stadia. This number meant the circumference of the Earth.

For that time, such measurements were considered accurate, because there were no ways to measure the circumference of the Earth more accurately. Modern scientists admit that the value calculated by Eratosthenes turned out to be quite accurate, despite the fact that:
- these two cities - Siena and Alexandria are not located on the same meridian;
- the ancient scientist obtained the figure based on the days of travel of camels, but they did not walk in a perfectly straight line;
- it is unknown what instrument the scientist used to measure angles;
- it is not clear what the stage used by Eratosthenes was equal to.
However, scientists still maintain an opinion about the accuracy and uniqueness of the method of Eratosthenes, who first measured the diameter of the Earth.
In the Middle Ages
In the 17th century, a Dutch scientist named Sibelius invented a method for calculating distances using theodolites. These are special instruments for measuring angles, used in geodesy. Sibelius's method was called triangulation; it consisted of constructing triangles and measuring their bases.
Triangulation is still practiced today. Scientists have conventionally divided the entire surface of the globe into triangular areas.
Russian studies
Scientists from Russia in the 19th century also contributed to the issue of measuring the length of the equator. The research was carried out at the Pulkovo Observatory. The process was led by V. I Struve.
If previously the Earth was considered a ball perfect shape, then later facts accumulated according to which the force gravity decreased from the equator to the poles. Scientists have tried to explain this phenomenon. There were several theories. The most popular of them was considered the theory about the compression of the Earth from both poles.
To test the validity of the hypothesis, French Academy organized expeditions in 1735 and 1736. As a result, scientists measured the length of the equatorial and polar degrees at two points on the globe - in Peru and Lapland. It turned out that at the equator the degree has a shorter length. Thus, it was found that the polar circumference of the Earth is 21.4 kilometers smaller than the equator circumference.
Nowadays, after error-free and accurate research, it has been established that the circumference of the Earth at the equator is 40075.7 km, and along the meridian - 40008.55 km.
It is also known that:
- The semimajor axis of the Earth (the radius of the planet at the equator) is 6378245 meters;
- the polar radius, that is, the semiminor axis, is 6356863 meters.
Scientists have calculated the surface area of the Earth and determined the figure of 510 million square meters. km. Land occupies 29% of this area. The volume of the blue planet is 1083 billion cubic meters. km. The mass of the planet is determined by the figure 6x10^21 tons. The share of water in this value is 7%.
Video
Look interesting experiment, demonstrating how Eratosthenes was able to calculate the circumference of the Earth.
A. Sokolovsky
Geometry (Ancient Greek: Geo - “earth”, -Metron “dimension”) the original meaning of the word was - measurement of the Earth. Today, geometry has more broad meaning: It is a branch of mathematics dealing with questions of shape, size, relative position in space and properties of space. Geometry arose independently in a number of early cultures as a discipline practical knowledge, relating to length, area, volume, with elements of formal mathematical science.
Modern units of length
Modern units of measurement related to the size of our planet.
Meter
The meter was originally designed to be one ten-millionth (1/10.000000) of a quadrant, the distance between the equator and the North Pole. In other words, the meter was defined as 1/10.000000 of the distance from the Earth's equator to North Pole measured along the surface of the circumference (ellipsoid) of the Earth through the longitude of Paris.
Using this value, the circle is ideal round earth must be exactly 40,000,000 meters (or 40,000 km). But since the shape of the Earth is not an ideal circle but is more like an ellipsoid, today the official circumference of the Earth along the line of longitude is 40,007.86 km.
Nautical mile
The nautical mile is the basis of the circumference of planet Earth. If you divide the Earth's circumference into 360 degrees and then divide each degree by 60 minutes, you get 21,600 arc minutes.
1 nautical mile is defined as 1 minute of arc (circumference of the Earth). This unit of measurement is used by all countries for air and sea transport. Using 40,007.86 km according to the official circumference of our planet, we get the value nautical miles in kilometers: 1,852 km (40,007.86 / 21600)
Ancient units of measurement show that our ancestors were able to measure the size of our planet with perfect accuracy...
Measuring the Earth's Circumference
Here's a simple way to measure the circumference (and diameter) of the Earth that was most likely used ancient astronomers.
This method is based on the understanding that the Earth, like the Sun and Moon, is also round in shape and that the stars are very far from our planet (with the exception of the Sun), and they revolve around a certain point above the northern horizon (North Pole).

Long exposure photographs show the apparent movement of stars around the north pole.
The measurement process should be carried out in places with good visibility of the sky, for example, desert areas, away from populated areas.
One night, 2 astronomers in two different places (A and B), separated known distance(so it will be easy to measure the circumference of the Earth knowing the distance between points located hundreds of kilometers from each other), they will measure the angle above the horizon (using an astrolabe with a plumb line giving a vertical line) of a certain star to its location in the night sky above the horizon.
The ideal choice would be Star, which is close to the celestial axis of the North Pole (indicating the center of the Earth's rotation axis). These days the North Star will be best choice, however, thousands of years ago, due to precession (the rotation of the Earth's axis), the North Star was not in the area of the North Pole (see image below).
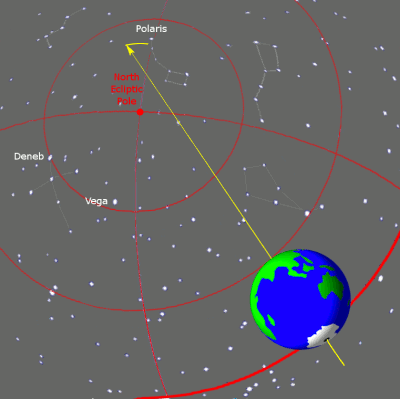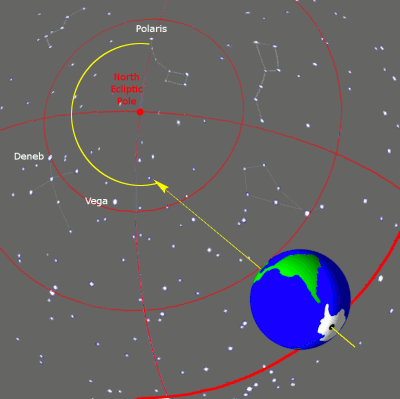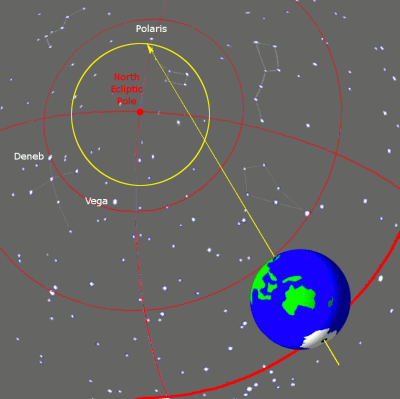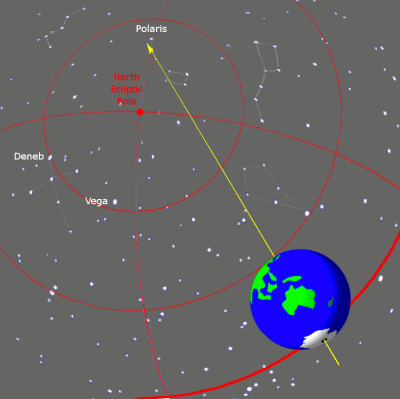
Precession is the rotation of the Earth's axis over a period of 26,000 years.
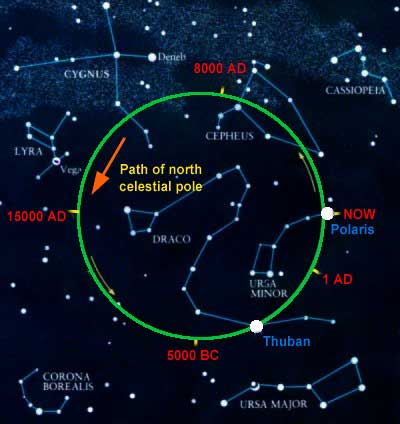
Despite the fact that the North Star is located within the north pole in half a circle celestial sphere, this was not always the case. The Earth's rotation axis undergoes a slow oscillation over 26,000 years, known as precession, around a perpendicular to its orbit around the Sun, causing the position of the celestial rotation pole around which all stars move to constantly change. Around the time of the Greek poet Homer, the star Kochab was the star of the north pole. Before it, the north pole star was the star Thuban, which was almost exactly at the pole in 2700 BC. It occupied a better, near-ideal position than the star Kochab until about 1900 BC, and was therefore the North Star during ancient Egyptians. Other bright stars, including Alderamin, were at one time polar stars, and will be again in the distant future. The star that is currently closest to South Pole is Sigma Octantis, which is barely visible to the naked eye and lies 1º3′ from the pole (though it was closer, at 45′ just a century ago). [Encyclopedia of Science]
Careful observation of the night sky will allow you to choose bright star with the most appropriate parameters to compare the location of a star with the measured parameters of the same star from another location.
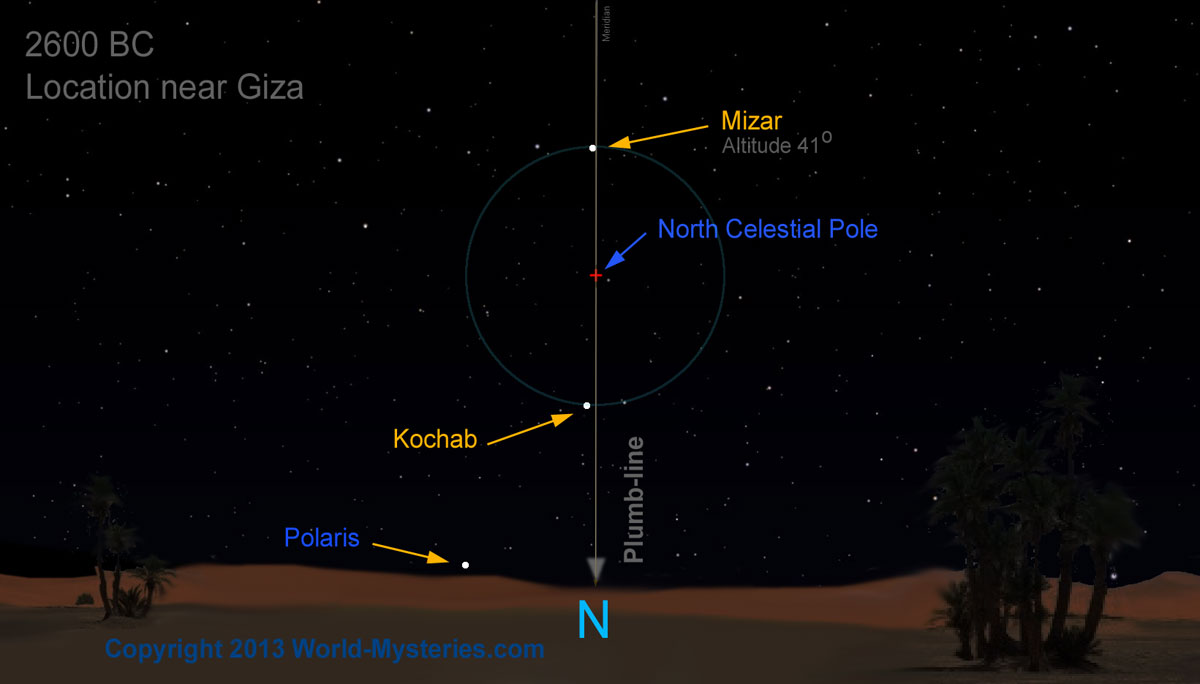
Click to enlarge
For example, in 2600 B.C. (see image above) in Egypt near the Giza Plateau when the stars Mizar and Kochab (which orbit the North Pole every night) will align with vertical line(marked by a plumb line), the star Mizar (easy to measure height) would be an ideal star to compare its height in different points(A and B).
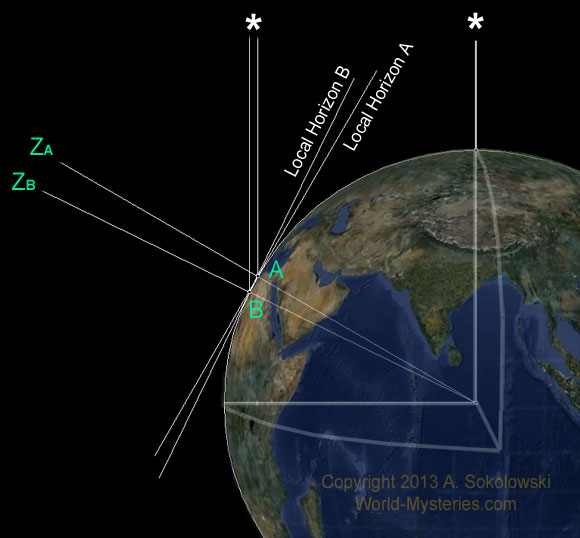
Since the stars are in space are too far from the Earth, using the parallax effect, you can, knowing the distance between the observation points D (base) and the displacement angle α in radians, determine the distance to the object:
for small angles:
parallax effect: (a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object considered from two different viewing points), the only cause of change in the measured angle north star is the curvature of the Earth's circumference.
The angular diameter of the Moon and the Sun is almost the same: 0.5 degrees.
Our ancient astronomers/ Priests, priests / could measure the position of the northern star with an accuracy of 1 degree. Using such an angle measuring instrument (astrolabe), calibrated in degrees, he could obtain fairly accurate results (perhaps with a 0.25% degree of accuracy).
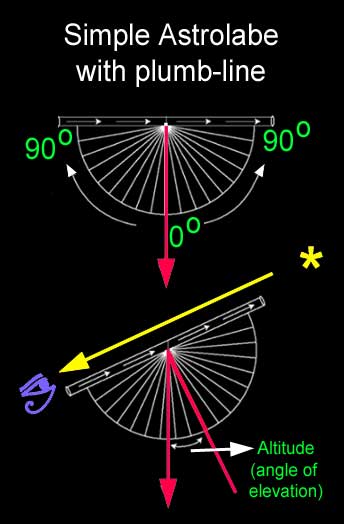
If one of our astronomers made this measurement from a location at point (A) near Giza (30 0 C), the star Mizar should have appeared about 41 degrees above local horizon. If the second astronomer were located 120 nautical miles south of *point (A) (*measured in ancient units of length, of course), he would notice that the height of the same object (star) is 39 degrees (2 degrees lower, than the height measured at the location).
These 2 simple measurements would have allowed ancient astronomers to calculate the circumference of the Earth with fairly high accuracy:
(360/2) * 120 nautical miles = 21600 nautical miles, from which the diameter of the Earth can be estimated as: 21600 nautical miles / (22/7) (ancient Egyptian estimates of Pi) = = 6873 nautical miles = 12728 km
Note: modern and accurate data: Circumference of the Earth between the North and South Poles:
21,602.6 nautical miles = 24,859.82 miles (40008 km) Diameter of the Earth at the equator: 6,887.7 nautical miles = 7,926.28 km (12,756.1 km)
The equator is an imaginary circular line that encircles the entire globe and passes through the center of the Earth.
The equator line is perpendicular to the axis of rotation of our planet and is located at equal distance from both poles.
Equator: what is it and why is it needed?
So, the equator is an imaginary line. Why did serious scientists need to imagine some lines outlining the Earth? Because the equator, like meridians, parallels and other dividers of the planet, which exist only in the imagination and on paper, make it possible to make calculations, navigate in the sea, on land and in the air, determine the location various objects etc.
The equator divides the Earth into North and Southern Hemisphere and serves as the starting point geographical latitude: The latitude of the equator is 0 degrees. It helps you navigate climatic zones planets. The equatorial part of the Earth receives the most large number sun rays. Accordingly, the further the territories are located from the equatorial line and the closer they are to the poles, the less sun they get it.
The equatorial region is an eternal summer, where the air is always hot and very humid due to constant evaporation. At the equator, day is always equal to night. The sun is at its zenith - it shines vertically downwards - only at the equator and only twice a year (on those days on which the equinoxes occur in most geographic zones of the Earth).

The equator passes through 14 countries. Cities located directly on the line: Macapa (Brazil), Quito (Ecuador), Nakuru and Kisumu (Kenya), Pontinac (Kalimanta island, Indonesia), Mbandaka (Republic of the Congo), Kampala (capital of Uganda).
Equator length
The equator is the longest parallel to the Earth. Its length is 40.075 km. The first who was able to approximately calculate the extent of the equator was Eratosthenes, an ancient Greek astronomer and mathematician. To do this, he measured the time during which sun rays reached the bottom deep well. This helped him calculate the length of the radius of the Earth and, accordingly, the equator thanks to the formula for circumference.
It should be noted that the Earth is not a perfect circle, so its radius is different parts a little different. For example, the radius at the equator is 6378.25 km, and the radius at the poles is 6356.86 km. Therefore, to solve problems of calculating the length of the equator, the radius is taken equal to 6371 km.
The length of the equator is one of the key metric characteristics of our planet. It is used for calculations not only in geography and geodesy, but in astronomy and astrology.








