Answer the question which rivers belong to the basin Atlantic Ocean, you can list huge amount rivers of Europe, Russia and North America. But since it's too much big list, we will indicate only water streams flowing through our country.
The rivers of the Atlantic Ocean basin in Russia are also very numerous, there are more than 3 dozen of them. Most have a small volume of flow, and among the significant water arteries are the Kuban, Don and Neva. Further in the article we will tell you which rivers belong to the Atlantic Ocean basin, the largest in Russia, and give them a detailed description.
Mighty River Don
If you look at the map of Eurasia, you can easily answer the question of which river belongs to the Atlantic Ocean basin, and at the same time is the largest among the others.
Don originates from Tula region, in the northern part of the vast Central Russian Upland. For a long time, the question of the source of this mighty river remained open. Some geographers believed that the river originates in Lake Ivan, others - in the Novomoskovsk reservoir. Currently, researchers have concluded that the source of the Don is the Urvanka River, which flows not far from Novomoskovsk.
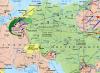
The river crosses the territory of twelve Russian regions(Kursk, Belgorod, Oryol, Tula, Ryazan, Tambov, Penza, Saratov, Volgograd, Lipetsk, Voronezh, Rostov region) as well as three Ukrainian ones (Kharkiv, Donetsk, Lugansk regions).
General characteristics
The length of the river is about 1,870 km, and the basin area is 420,000 km². The Don crosses the steppe and forest-steppe zones, and the nature of its flow along almost its entire length is slow and leisurely, highly winding.
About 5,200 hectares of water flow into this water artery. big rivers, as well as a huge number of streams. Among the main tributaries we can name such rivers of the Atlantic Ocean as Seversky Donets, Voronezh, Quiet and Bystryasny Sosny, Manych, Aksai, Nepryadva, Bear, Black Kalitva, Beautiful Mecha, Bityug, Chir, Ilovlya, Osered, Sal, etc.
The Don flows into the Sea of Azov in the Sea of Azov region, in turn, through the Black and Mediterranean Seas, through straits, it flows into the Atlantic Ocean.
The right bank of the Don, composed mainly of rocky and chalk deposits, is steep and steep. The left bank, on the contrary, is gentle and flat. Left side The river basin has a large number of lakes as well as wetlands. Forests are predominantly broad-leaved, coniferous or mixed. In the steppe zone there are meadow grasses.
Sections of the river
The Don is divided into three main sections - Upper, Middle and Lower. Upper part extends from the source to the mouth of Tikhaya Sosny. In this place there is the fastest current, there are riffles and whirlpools. The depth of the river is small - up to 1.5 m, but there are also deeper places. In this part, three large right tributaries (Sosna, Nepryadva) and one left tributary (Voronezh) flow into the Don.

The middle part of the Don continues all the way to the Tsimlyanskoye reservoir. Here the current is slower, the average depth is about 1.5 m. In the deepest places it reaches 15 m. In this zone, two large right tributaries (Chernaya Kalitva and Bogucharka) and four left ones (Bityug, Medveditsa, Khoper, Ilovlya) flow into it ). The eighty-kilometer Volga-Don Canal is also located here, connecting two large Russian rivers.
The lower part of the Don is the deepest. The depth of the pools here reaches 17 m. After the city of Rostov-on-Don, the river delta begins. In this part it is divided into many ducts. The largest of them are ( right side), as well as Sal, Manych ( left side). Immediately the Don flows into the Sea of Azov.
Water regime, ichthyofauna
The river is fed mainly by snow. The snow contribution is about seventy percent, the rest is represented by ground and rain nutrition. The river is covered with ice from early December to March/early April. During the rest of the year, the Middle and Lower Don are navigable (the total length of the navigable part is about 1.6 thousand km).
The ichthyofauna of the Don is very abundant. Here in significant amount There are such species of fish as bream, rudd, carp, roach, crucian carp, bleak, pike perch, sabrefish, pike, burbot, perch, catfish, ide, etc. During the spawning period, the river is visited by sterlet, and before the construction of the Tsimlyanskoye reservoir, even beluga was found. There is no industrial fishing, and fishing is mainly done by the local population.
Kuban
The Kuban River is born at the confluence of two rapid mountain streams - Uskulan and Ullukan. Its upper reaches are fed by Elbrus glaciers. Total length The Kuban is about 0.87 thousand km long, and it also flows into the Sea of Azov.
The river bed changes its character from the upper reaches to the lower reaches. In the upper part of the Kuban there is a typical mountain river, with all the attributes - rocky gorges, steep, sometimes sheer slopes, a deep valley, rifts and rapid currents.

After the city of Cherkessk, its character changes, the valley expands, and the flow becomes calmer and more measured. The slopes become more gentle. In the middle and lower parts, the Kuban channel is very winding. There are many oxbow lakes in the river valley. The largest of them is Lake Staraya Kuban.
A hundred kilometers from its confluence with the Sea of Azov, the river divides, forming three main branches - Protok, Kazachiy Erik and Petrushin Rukav.
Water regime of Kuban
During the year, the river experiences 7-8 floods, the most abundant of which are spring and summer, and the summer flood is stronger than the spring. This is due to the melting of seasonal snows and glaciers in the Caucasus.

With a relatively short length (only about 74 km), the river’s catchment area is 28 thousand square kilometers, since it is the only one flowing from Lake Ladoga. The total drop is 5.1 m.
The river basin is complex hydrological network, With a large number lakes and reservoirs. IN total The Neva's drainage area includes over 48 thousand rivers and more than 26 thousand lakes. At the same time, 26 tributaries flow directly into the river.
These are also rivers of the Atlantic Ocean basin, the largest of which on the left bank are the Staro- and Novo-Ladoga canals, Mga, Izhora, Tosna, Slavyanka, and on the right bank are the Chernaya and Okhta rivers. In the delta it is divided into several channels connected by canals.
With a length of 74 km, the discharge of the Neva is 78.9 cubic kilometers per year, which puts it among the ten largest rivers in Europe. The average width is 400-600 m, and the average depth is 8-11 m.

Rivers of the Atlantic Ocean basin (list)
Now let’s list all the rivers included in the Atlantic Ocean basin:
- Don and tributaries: Seversky Donets, Voronezh, Quiet and Bystraya Sosny, Manych, Aksai, Nepryadva, Medveditsa, Black Kalitva, Krasnaya Mecha, Bityug, Chir, Ilovlya, Osered, Sal.
- Kuban and tributaries: Bolshoy and Maly Zelenchuk, Teberdya, Laba, Urup, Pshish, Belaya, Afips, Psekups (left bank), Mara, Dzheguta, Gorkaya (right bank).
- Neva and tributaries: Old and New Ladoga canals, Mga, Izhora, Tosna, Slavyanka, and on the right are the Chernaya and Okhta.
Telling which rivers belong to the Atlantic Ocean basin, in general it can be said that all of them are fed predominantly by snow. Their current is calm, and for the most part they are quite deep. Although in our country, by the way, they are not the largest, as in Eurasia. The deepest rivers are the rivers of the Arctic Ocean.
Now, we hope, it will not be difficult for you to answer the question of which rivers belong to the Atlantic Ocean basin in Russia.
The very name of the Atlantic Ocean comes either from the Atlas Mountains in northern Africa, or from the name of the legendary continent of Atlantis, which supposedly existed in ancient times and died as a result of a terrible flood. Disputes and searches are still going on regarding the location of Atlantis.
The Atlantic is generally rich in myths, legends and mysterious stories. For example, one of the oldest geographical descriptions- about the voyage of a certain Greek Pytheas from Massilia (present-day Marseille) in the 4th century. BC e. to the north Atlantic, where Thule is supposedly located, the land of legendary cold and fog. Until now, the exact location of Thule, like Atlantis, has not been determined.
Some enthusiasts claim that even before Columbus, Egyptians, Phoenicians, Greeks, the disappeared fleet of Alexander the Great, Arab sailors, Templars, etc. could have sailed along the Atlantic to the shores of America. These legends of the Atlantic have not yet been confirmed. But the primacy of Scandinavian navigators in the discovery of America has been absolutely proven. Archaeological excavations showed that the Vikings in the 10th century. They discovered not only Greenland, where they then lived for several centuries, but also reached the coast of the mainland. Remains of their settlements have been found on the Newfoundland peninsula.
But the Atlantic Ocean became the most important ocean for all mankind in the era of the Great geographical discoveries, in the XV-XVII centuries, when across the Atlantic European civilization I discovered how huge our world is. The Atlantic Ocean was the first to test the strength of the skills of European shipbuilders, and practical experience expeditions suggested how to create new technologies, how to improve cartography and navigation tools.
However, when humanity decided that it had already achieved perfection in conquering the elements, the Atlantic Ocean taught a harsh lesson.
On April 14, 1912, the world's largest passenger liner, the Titanic, collided with an iceberg and sank on its maiden voyage. 1502 people died, this tragedy was a shock for the whole world. Atlantic demanded to be taken seriously, and this lesson was remembered for a long time. The sinking of the Titanic has become a legend; many books have been written about it and many films have been made.
There is no point in hoping that someday we, people, will manage the Atlantic like we do in our own kitchen. Even in the 21st century, having much more advanced technology than it was at the time of the Titanic, experienced captains are seriously wary of many places in the ocean that have earned a bad reputation. What is one worth? Bermuda Triangle, where people and ships continue to disappear.
Geography of the Atlantic Ocean
Almost everything passes through the Atlantic Ocean climatic zones Earth, its length is about 20,000 km. Among the many seas belonging to the Atlantic Ocean, the Sargasso Sea deserves special mention. Because this is the only sea in the world that does not have continental shores, and its waters are replete with sargassum (brown seaweed).
The Atlantic Ocean is shaped like Latin letter S. It extends from Greenland in the north to Antarctica in the south. Fresh water from most of the land flows into this huge water basin.
Second largest in the world after Pacific Ocean, The Atlantic Ocean has its characteristic features. Its coastline is highly indented and has relatively small quantity islands, rivers flowing into the Atlantic Ocean or its marginal seas, have largest area swimming pools.
The Atlantic Ocean is also characterized by the complexity of its bottom topography. The Mid-Atlantic Ridge rises above the ocean floor to a height of 2 km. Individual peaks of the ridge form islands, the largest of which is Iceland. It doesn't stop in this area volcanic activity and frequent earthquakes occur.
Another feature of the Atlantic is icebergs - huge mountains of ice floating on the surface of the ocean. They periodically break off from the ice surface of Greenland and Antarctica. These beautiful ocean wanderers are still - big threat for sea vessels.
For Europeans, the concept of the Atlantic is strongly associated with the current, which has the most serious impact on the weather of the continent. It is thanks to the Gulf Stream, which carries its waters from the Bahamas (where the Florida Current joins the Antilles Current, forming the Gulf Stream), that the countries of Europe adjacent to the Atlantic Ocean can enjoy a climate milder than that observed at the same latitude, but away from the Gulf Stream. Suffice it to say that the thermal power of the Gulf Stream is equal to the power of a million nuclear power plants. In the ocean, the Gulf Stream moves at a speed of 6-10 km/h, the thickness of its stream is 700-800 m.
The Atlantic Ocean is the most intensively used ocean by humans and therefore the most susceptible to contamination and other anthropogenic (human-involved) impacts. Suffice it to say that fishing in the Atlantic is regularly the subject of dispute between different countries- it is very difficult to agree on quotas. Overfishing regularly leads to population declines and the need for new restrictions. Availability of many major cities and developed countries on the Atlantic coast leads to discharge into its waters large quantity pollutants.
It is believed that approximately 200 million years ago there was no Atlantic Ocean. And there was a huge continent of Pangea, which 160-180 million years ago, again approximately (in paleogeography exact dates almost never occur), split. Further splits and divergences lithospheric plates Earth led to the fact that about 5-10 million years ago the Atlantic Ocean acquired almost modern look. Many scientists tend to consider the Atlantic Ocean to be the youngest ocean existing on Earth.

General information of the ATLANTIC
The International Hydrographic Organization has established the boundaries of the Atlantic Ocean: in the north - along the border of the Labrador Sea (Atlantic) with Davis Strait (), the Atlantic Ocean with (Arctic Ocean) and the Norwegian Sea (Arctic Ocean) and the North Sea (Atlantic) with the Norwegian Sea (Arctic Ocean); in the south - from Southern Ocean(surrounding Antarctica); in the southwest - with the Pacific Ocean along the Strait of Magellan (belongs to the Pacific Ocean); in the southeast - with the Indian Ocean. Largest sea: Weddell Sea.
The largest rivers flowing into the Atlantic Ocean: Amazon, Nile, Congo, Niger, Mississippi, La Plata.
The most important currents: Gulf Stream, North Atlantic, Canary, Northern Trade Wind, Labrador, Southern Trade Wind, Brazilian, Antarctic Circumpolar, Bengal, Guiana, Falklands Equatorial Countercurrent.
Numbers
Length (from north to south): about 20,000 km.Smallest width (from east to west): 2800 km.
Maximum width: 13,500 km.
Area: 91.4 million km 2 (including continental seas).
Greatest depth: 8742 m - Puerto Rico Trench.
Average depth: 3600 m.
Volume: 329.7 million km 3 .
Average annual water salinity: 35%.
Economy
The main meaning is transport, northern part Atlantic - most used today sea route. Subsea oil and gas production, many offshore mineral deposits.Usage biological resources- more than half of the world's production of cod, tuna, herring, etc.
Climate and weather
All climate zones are represented.Most of the Atlantic Ocean is between 40º N. w. and 42º S. w. - found in the equatorial, subequatorial, tropical and subtropical zones, Where all year round positive temperatures. In tropical latitudes the average temperature is +20ºС with heavy rainfall. In subequatorial regions - from +10ºС in winter and +20ºС in summer, precipitation mainly in summer. Tropical hurricanes are a common occurrence. In the subtropics, the temperature of the coldest month of the year drops to +10ºС, and winter is characterized by heavy rainfall. In temperate latitudes, north of 40º N. w. and south of 42º S. sh., precipitation most often falls evenly throughout the year (within 1000 mm), reaching a maximum in the autumn-winter period. Strong storms are typical, temperatures range from +10...15ºС in summer to -10ºС in winter. The most severe climate is in the southernmost part of the Atlantic, in subantarctic and Antarctic latitudes. However, the Atlantic Ocean in subarctic and arctic latitudes can be considered “warmer” only conditionally.
Attractions
■ Beautiful beaches on the shores of all continents washed by the Atlantic Ocean;■ Madeira Island;
■ Azores;
■ Cape Verde Islands;
■ Canary and Antilles.
■ Bermuda.
Curious facts
■ American pilot Charles Lindbergh was the first to fly non-stop across the Atlantic Ocean in 1927.■ The most remote island in the world is Bouvet Island in South Atlantic, located 1600 km from the cape Good Hope. And the largest island in the world is Greenland in the North Atlantic Ocean.
■ Proven oil reserves in the Gulf of Mexico are believed to be 4 billion tons.
■ In the center of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, which runs in the central part of the Atlantic Ocean floor, a volcanic process is constantly underway. Emissions of molten rock - magma - put pressure on the layers earth's crust. As a result, America and Europe are becoming 2 cm further apart every year.
The Atlantic Ocean basin includes over thirty Russian rivers and their tributaries. Most of these rivers are quite shallow, with slow flows and shallow depths. The Don River, glorified by many writers and poets of Russia, is considered the largest and most significant river flowing into the Atlantic. The Don River originates in the Tula region. For a long time, there were heated debates regarding the source […]
The waters of the World Ocean are never at rest. Movements occur not only in surface water masses, but also in depths, down to the bottom layers. Water particles perform both oscillatory and forward movements, usually combined, but with a noticeable predominance of one of them. Wave movements (or disturbances) - predominantly oscillatory movements. They represent fluctuations [...]
The Arctic Ocean is the most small ocean of our planet. Its area is only 14.78 million km2. For this reason, sometimes foreign literature this water body considered as an inland sea of the Atlantic Ocean. However, in Russian classical geography it has always been considered an independent ocean. The Arctic Ocean is also the shallowest. It is located in the center of the Arctic and [...]
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest ocean after the Pacific. Its area is much smaller and amounts to 91.6 million km2. About a quarter of this area is in shelf seas. Coastline It is very rugged, primarily in the Northern Hemisphere; in the Southern Hemisphere it is relatively flat. The ocean washes all continents except Australia. Islands located in the ocean are located near continents. […]
Russia has significant reserves fresh water. Most widely in national economy are used river waters. There are about 3 million rivers within Russia total length almost 10 million km. In terms of total river flow, Russia is in second place in the world after Brazil. The average long-term flow of all rivers is 4290 km3 per year, which is 13% […]
They are the most numerous. There are six of them: Beloe, Barents, Kara, Laptev, East Siberian and Chukotka. The farthest sea in the west is the Barents Sea. It is named after the Dutch navigator Barents, who in the 16th century led three expeditions across the Arctic Ocean in search of a northeast passage from the Atlantic to the Pacific Ocean. The Barents Sea is very different from others northern seas: most […]
The western and southwestern outskirts of Russia are washed by the seas of the Atlantic Ocean. The Baltic Sea forms bays off the coast of the country, on the shores of which there are major ports. St. Petersburg is located in the Gulf of Finland, and Kaliningrad is located on the Pregola River, which flows into the Vistula Lagoon. In the southwest there is Chernoe and Sea of Azov, where there are also large bays. In the Black Sea - Karakinitsky Bay and [...]
Answers to GIA tickets on geography The largest rivers in North America are the Mississippi with a tributary of the Missouri (the largest long river mainland - 6420 km), the St. Lawrence River, Rio Grande, belonging to the Atlantic Ocean basin, Mackenzie, flowing into the Arctic Ocean, Yukon, Columbia, Colorado, belonging to the Pacific Ocean basin. The internal drainage basin occupies a small area and does not have large [...]
Central part Arctic region The Earth is occupied by the Arctic Ocean, almost all of which is framed by land. Geographical remoteness of the main economic centers, sparse population and harsh natural conditions significantly reduce it economic importance and increase costs for economic development. The economic potential of the USA, Canada, Russia, Norway, Greenland (possession of Denmark), Iceland, whose coastal areas overlook the Arctic Ocean, […]
Within the Atlantic Ocean, all physiographic zones are clearly represented, except for the North Polar. The northern subpolar (subarctic) belt covers the waters off the island of Greenland and the Labrador Peninsula. In winter, the air temperature drops to - 20°, water temperature to - 1 °C and below. The ocean is partially covered with ice in winter. Ice formation causes an additional increase in the salinity of water and its immersion to depth. In spring […]
The climatic conditions of the Atlantic Ocean determine the features of its hydrological regime. Waves in the Atlantic Ocean Wave formation in the Atlantic Ocean depends on the nature of the prevailing winds over certain areas. The area of most frequent storms extends north of 40° N. w. and south of 40° S. w. Wave heights during long and very strong storms can reach 20-26 m. But […]
The climate of the Atlantic Ocean is determined by its enormous meridional extent, the nature of atmospheric circulation and the ability water surface significantly equalize the annual temperature range. The oceanic climate is generally characterized by slight fluctuations in air temperature. In the Atlantic Ocean at the equator they are less than 1 °C, in subtropical latitudes 5 °C, and at 60 ° N. w. and Yu. w. - 10 °C. Only […]
A significant feature of the underwater margin of North America is a wide shelf zone, occupying 10.3% of the total area of the ocean floor. The shelf has a significant distribution in the northwest - off the coast of Greenland, the Labrador Peninsula, Nova Scotia, where its width reaches 300-400 km. The shelf in this area is characterized by the development of relict forms glacial relief, deep-sea trenches, canyons, raised banks, which are giant […]
Inland waters are that part of the hydrosphere that is located inside a territory. Inland waters include rivers, lakes, groundwater, swamps, artificial reservoirs, etc. Russia's inland waters are rich and diverse. The rivers of Russia belong to the basins of the Arctic, Pacific, Atlantic oceans and the internal drainage basin (drainless Aral-Caspian region). The main features of rivers are related to their regime and [...]
To the South Seas Russian Federation include the Caspian, Azov and Black Sea. These seas are combined into one group because they have a close geographical location and are located relatively close to each other. These seas are of tectonic origin and are “descendants” of the Tethys Ocean, which currently no longer exists. South Seas formed as a result of periodic [...]
North America is rich in inland waters. Rivers and lakes are distributed unevenly across the continent, which is due to the diversity of its climate and topography. The rivers and lakes of the mainland belong to the basins of three oceans - the Atlantic, Pacific and Arctic. The endorheic region is small and occupies the Great Cordillera Basin and the northern Mexican Highlands. Rivers of North America The Atlantic Ocean river basin is the most [...]
Area: 8.5 million km2 Population: 201 million Capital: Brasilia Geographical location Brazil Brazil - tropical country, stretching for 4 thousand km from west to east and 4.3 thousand km from north to south. It occupies almost half of the continent, bordering almost all countries of the mainland, with the exception of Chile and Ecuador. The territory in the north and east […]
South America is the richest water resources continent. River flow the mainland is twice as large average flow rivers globe. Main source Rivers are fed by rainfall. Rivers are glacially fed only in the southern Andes. The role of snow nutrition is small. The mainland is characterized by large river systems. Their formation is facilitated by the flat terrain of the eastern part and the high mountain ranges of the mainland, large […]
The geographical position and evenness of the relief contributed to the location of the geographical zones of Africa (equatorial, subequatorial, tropical and subtropical) and natural areas twice on both sides of the equator. With decreasing humidity north and south of the equator, the vegetation cover becomes thinner and the vegetation more xerophytic. In the north there are many Mediterranean plant species. In the center and south the most ancient […]
Rivers The river network is distributed unevenly on the mainland. The hot and contrasting climate of Africa affects the river network and river regime. In humid climates river network the densest, and the rivers are fed mainly by rain. About 1/3 of the surface of the continent has no flow into the ocean and belongs to the area of internal flow (most of the Sahara, Lake Chad basin, […]
The longest river in the world is the Nile
Nile- the longest river in the world, its length is 6,690 km from the source of the Luvironza River in Burundi, in Central Africa, to its mouth at the confluence with the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile flows from south to north and its basin is about 2,850,000 square meters. km, which is approximately equal to one tenth of the area of Africa, including the territories of Egypt, Sudan, Ethiopia, Eritrea, South Sudan, Kenya, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Tanzania, and Congo (Kinshasa). Its waters support virtually everything agriculture in the most densely populated parts of Egypt, providing a source of irrigation for almost all of Sudan's food crops, and are widely used throughout the basin for navigation and hydroelectric power.
The deepest river in the world is the Amazon
River Amazon the second longest river in the world by extent. Its length is about 6,296 km, it is formed by the junction in the northern Peruvian Andes of two main sources - the Ucayali and the shorter Maranon. The Amazon River flows through northern Brazil and empties into the Atlantic Ocean near the city of Belem. The Amazon is the deepest river in the world (carries more water than any other river in the world). The basin with tributaries is huge and amounts to 6,475,000 square meters. km, which is approximately 35% of the territory of South America. The Amazon draws water from both hemispheres and flows not only through Brazil, but also through parts of Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, and Venezuela. The average depth of the river over its greater length is 50 m. The slope of the river is very small: Manaus, 1,610 km upstream, is only 30 m higher than Belem near the river delta. Marine vessels with a landing of 4 m can reach Iquitos in Peru, which is 3,700 km from the Atlantic Ocean. Peru, Ecuador, and Colombia have international ports on the Amazon.
The following table shows the largest rivers in the world, including their name, source, where they flow and their length:
|
Name |
Source |
Mainland |
Where |
Length, |
|
|
Tributaries of Lake Victoria |
Mediterranean Sea |
||||
|
Amazon |
Glacial lake, Peru |
South America |
Atlantic Ocean |
||
|
Mississippi-Missouri |
Red Rock River, Montana, USA |
North America |
|||
|
Yangtze |
Tibetan plateau, China |
China Sea |
|||
|
Altai, Russia |
Ob Bay, bay Kara Sea |
||||
|
Yellow River |
Eastern part Kunlun Mountains, China |
Bohai Bay of the Yellow Sea |
|||
|
Yenisei |
Tannu-Ola mountains, south of Tuva, Russia |
Arctic Ocean |
|||
|
Parana |
confluence of the Paranaiba and Rio Grande rivers, Brazil |
South America |
La Plata Bay of the Atlantic Ocean |
||
|
Irtysh |
Altai, Russia |
||||
|
Zaire (Congo) |
confluence of the Lualaba and Luapula rivers |
Atlantic Ocean |
|||
|
Amur |
confluence of the Shilka and Argun rivers |
Strait of Tartary Sea of Okhotsk |
|||
|
Lena |
Lake Baikal, Russia |
Arctic Ocean |
|||
|
Mackenzie |
Head of the Finlay River, British Columbia, Canada |
North America |
Beaufort Sea |
||
|
Niger |
Fouta Djallon, Guinea |
Gulf of Guinea Atlantic Ocean |
|||
|
Mekong |
Tibetan plateau |
South China Sea |
|||
|
Mississippi |
Lake Itasca, Minnesota, USA |
North America |
Gulf of Mexico |
||
|
Missouri |
Confluence of the Jefferson, Gallatin and Madison Rivers, Montana, USA |
North America |
mississippi river |
||
|
Volga |
Valdai Hills, Russia |
Caspian Sea |
|||
|
Madeira |
Confluence of the Beni and Mamore rivers, border of Bolivia and Brazil |
South America |
Amazon River |
||
|
Purus |
Peruvian Andes |
South America |
Amazon River |
Thus, the Nile is the longest river in the world, with a length of approximately 6,690 kilometers, and is also the largest river in Africa. The second largest river in the world, the Amazon, is also the longest river in South America. The third largest river, the Mississippi River, together with the Missouri River, is the most... big river North America. The fourth largest river, the Yangtze River is the longest river in Asia. And, being only the eighteenth largest in the world, the Volga is the longest river in Europe.
So, we looked at the 20 largest rivers in the world, eight of which flow in Asia, eight in America, three in Africa, and only one of the 20 largest large rivers peace - in Europe.