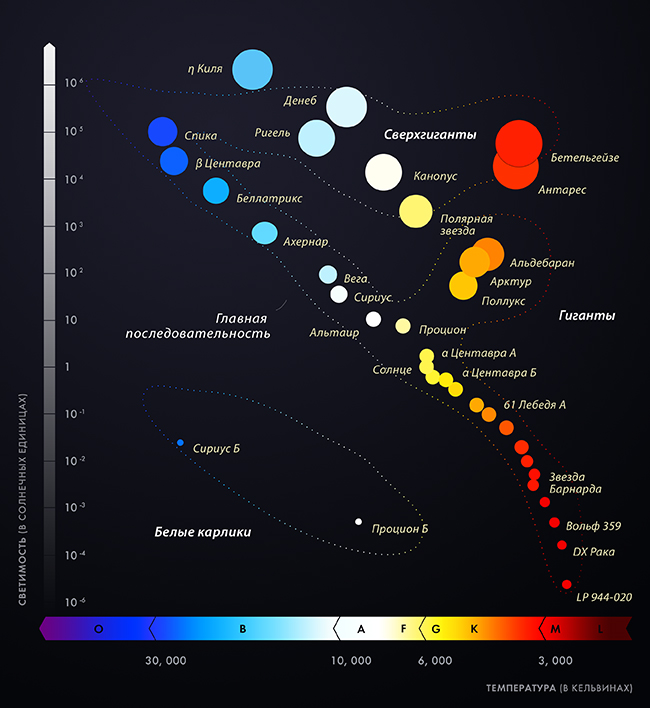
In summer and autumn, in the night sky, in the northern hemisphere of the celestial sphere, the so-called Great Summer Triangle can be distinguished. This is one of the most famous asterisms. At the top point of the Triangulum is Vega, a bright star. blue color, which is the main one in.
The name Vega is translated from Arabic like a falling eagle. Its other name is Alpha Lyrae (α Lyrae / α Lyr) official name, mentioned in scientific literature. In terms of brightness for Russian residents, Vega is the third star after Arcturus. The distance from the Sun to Vega is 25.3 light years, which is considered relatively close.
How Vega helped astronomers
Vega played vital role in the development of astrophysics. It served as the starting point for the development of a photometric system for determining the color and brightness of UVB stars. That is, its brightness was taken as 0 (the reference point).
This is the first star photographed since, and also one of the first, the distance to which was determined by the parallax method. AND, interesting fact, in the 12th century BC. she was (a star pointing to North Pole) and it will happen again in 12,000 years!
Some properties of Vega

Star Vega - spectral class A0V, that is white star main sequence. This means that the source of energy for it is the reaction thermonuclear fusion helium from hydrogen. Vega is more than 2 times heavier than the Sun, and its luminosity is 37 times greater than the Sun. Because of large mass this blue sun will exist as a white star for 1 billion years, or 1/10 of the life of the Sun. Vega is 386-510 million years old and is now in the middle of its life, just like our Sun. It will then turn into an M-type red giant, and subsequently become a white dwarf.
Options
Its radius was measured to be 2.73 ± 0.01 solar radii, but this fact contradicted theoretical calculations of the star's size. The explanation for this probably lies in the speed of rotation of the object, this fact was confirmed by observations in 2005. Indeed, Vega rotates so quickly that its shape is an ellipse. Vega's rotation speed reaches 274 km/sec. Its equatorial diameter is 23% larger than the polar one.

In astronomy, any element heavier than helium is called a metal; Vega contains few such metals, only 32% of the same solar indicator.
The reason for this is still unclear. The speed of stars relative to the Earth is calculated using the displacement of their spectrum. If the color shifts towards the red part of the spectrum, then the celestial object is moving away from the Earth. For Vega, this displacement is − 13.9 ± 0.9 km/s, the minus sign means that the “falling eagle” is approaching us.
Movement
The star also has its own speed of motion. It is equal to 202.03 ±0.63 milliseconds of arc in right ascension and 278.47 ±0.54 milliseconds of arc in declination. By celestial sphere Vega moves by 1 degree in 11,000 years. Relative to neighboring stars, the blue star moves at approximately the same speed as the Sun, or 19 km/sec.
Astronomers also studied other stars similar to Vega, and as a result it was classified as a member of the Castor group. This group includes 16 stars; in space they move parallel to each other with at equal speeds. Scientists' guess is that the stellar objects of this group were formed at one time and in one place, but then became gravitationally independent.

A dust disk around the planet, imaged by the Spitzer telescope at a wavelength of 24 (left) and 70 microns
Currently, the question of whether Vega has an exoplanet (or exoplanets), as well as planets, is being studied terrestrial group. But for now the question remains open. On at the moment, only a dust disk was discovered around Vega.
Journey to Vega
The mythical role of the blue sun
Thanks to its brightness, Vega has undoubtedly attracted the attention of many people since ancient times. That's why she is the heroine of myths and legends different nations peace.
The Chinese, for example, believed that the earthly incarnation of Altair, a young man named Nu-Lan, on the advice of his old ox, goes to the Silver River, where he finds a girl named Zhi-nyu (Vega), the granddaughter of Tian-di (heavenly ruler) and marries on her. They have a son and daughter (β and γ Orla), but the heavenly ruler took his daughter, Zhi-nyu, to heaven, and allowed the spouses to see each other once a year. This day, the 7th of the 7th moon, is considered by the Chinese to be the day when lovers meet.
Briefly about Vega
List of the brightest stars
| № | Name | Distance, St. years | Apparent value | Absolute value | Spectral class | Celestial hemisphere |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0,0000158 | −26,72 | 4,8 | G2V | ||
| 1 | 8,6 | −1,46 | 1,4 | A1Vm | South | |
| 2 | 310 | −0,72 | −5,53 | A9II | South | |
| 3 | 4,3 | −0,27 | 4,06 | G2V+K1V | South | |
| 4 | 34 | −0,04 | −0,3 | K1.5IIIp | Northern | |
| 5 | 25 | 0.03 (variable) | 0,6 | A0Va | Northern | |
| 6 | 41 | 0,08 | −0,5 | G6III + G2III | Northern | |
| 7 | ~870 | 0.12 (variable) | −7 | B8Iae | South | |
| 8 | 11,4 | 0,38 | 2,6 | F5IV-V | Northern | |
| 9 | 69 | 0,46 | −1,3 | B3Vnp | South | |
| 10 | ~530 | 0.50 (variable) | −5,14 | M2Iab | Northern | |
| 11 | ~400 | 0.61 (variable) | −4,4 | B1III | South | |
| 12 | 16 | 0,77 | 2,3 | A7Vn | Northern | |
| 13 | ~330 | 0,79 | −4,6 | B0.5Iv + B1Vn | South | |
| 14 | 60 | 0.85 (variable) | −0,3 | K5III | Northern | |
| 15 |
With the naked eye, in a clear night sky, a person can see stars from the first to the sixth magnitude, therefore, in the vastness of the Universe, numerous dim objects are hidden from our eyes, visible only with the help of astronomical instruments. And among them, scientists have discovered many interesting cosmic bodies of 11 magnitude - red dwarfs. Despite the fact that red dwarfs are the most common stars in the Galaxy, they are also the least studied. Astronomers face difficulties in studying the properties of stellar pygmies due to their low luminosity.
However, general information Scientists have known about red dwarfs for a long time. The mass of a red dwarf may be less than one tenth the mass of the Sun. The largest representative of the small celestial centenarians weighs just over half ours celestial body. Red dwarfs are cool stars. Their temperature ranges from 2000 K to 3800 K.
If we talk about the high prevalence of red dwarfs, then here, for example, is an interesting fact: 80% of stars Milky Way- these are red dwarfs, which are numerically is about 300 billion stars. In biology, the number of organisms is inversely proportional to the size of the individuals: the smaller, the more. The stars also follow the same rule. If in living nature this situation can be explained by the fact that small individuals are food for large ones, therefore there are more of them, then in space giant stars cannot in any way eat red dwarfs. How can we explain the analogy with biological objects?
On the question of the long lifespan of red dwarfs
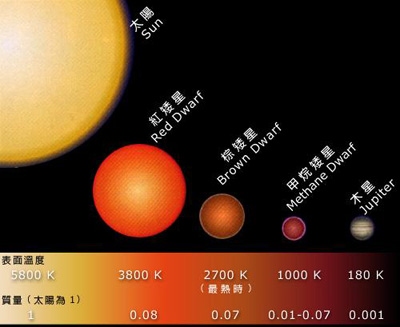
(The picture shows the types of stars and their surface temperatures (K) in comparison with the planet Jupiter)
It is known that what more mass stellar object, the more unstable its state, the faster it flows in its center thermonuclear reaction and the higher its temperature. Continuous nuclear reactions inside red dwarfs begin to go after billions of years. This is due weak gravity due to the low mass of cool stars. Thus, the evolution of red dwarfs is noticeably slower than their heavy counterparts; the true age of small cold stars is many times greater than that of massive celestial bodies.
Astronomers are confident that when all generations of bright white and yellow stars die, lonely red dwarfs will burn here and there as dim sparks in the darkness of the Universe.
Perhaps this only partially explains such an advantage in the number of red dwarfs over other celestial bodies. Astronomers are still conducting research in this direction.
Flare stars

(The picture shows a flare star of the UV Ceti type, a red dwarf 2MASS J06045215-3433360, located quite close to us, of course, by astronomical standards)
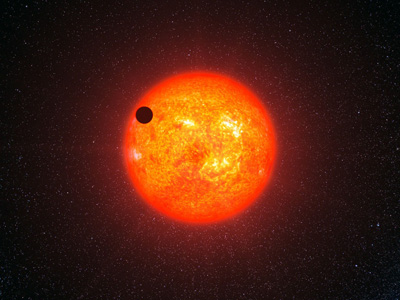
Among dim red dwarfs there are flare stars. Not too many of them have been discovered due to their ultra-low luminosity. Astronomers call exploding red dwarfs stars like UV Ceti or variable stars, whose luminosity increases sharply. The brightness of a star can increase sharply in just a few seconds, but its decay occurs much more slowly. Scientists have not discovered the periodicity of outbreaks; this process is spontaneous character. Similar flares occur on the Sun, but they are much weaker.
Do red stars have planets?

Astronomers have discovered many planets orbiting red dwarfs. There are significantly fewer of them than planets belonging to yellow dwarfs - stars similar to our Sun. If we consider the probability of life on planets, scientists admit this possibility. True, due to a certain pattern in the movement of planets in red dwarf systems, the prospect of detecting the development biological organisms small.
The fact is that due to the small mass and low temperature of the star, life is possible on planets whose orbital period is several days. Only on such close planets can water be present? liquid state. But with such closeness to the star, according to the law of gravity, the planet will always face one side towards the star, therefore, the optimal place for the possible existence of living organisms is the twilight zone near the terminator. That is, the conditions for development biological species are far from optimal. However, due to the prevalence of red dwarfs in the Universe, scientists do not exclude the possibility that one day life will be discovered on some planet in the system of a small star.
IN outer space stars live various types, which differ from each other in their structure, in the strength of radiation, in the color they create around themselves, as well as in a number of other characteristics. Based on this, they were compiled individual characteristics for each type of celestial body. Fortunately, there weren’t too many of them, and all of them can fit in our article. Therefore, below we will look at how to identify the difference in stars by color, what this generally means and how it affects the environment.
What is a star?
In fact, any star is a huge ball of hot plasma. It consists of components such as hydrogen and helium, which, when in contact with each other, form enormous flows of heat and light. After the state of these two components around the star returns to normal, planets begin to surround it. They are formed from space rocks, from asteroids, comets, or in other, more complex reasons. But here it is worth noting that it is the difference in star color that gives us the opportunity to understand whether planets can form around a particular celestial body. As a rule, such satellites appear around stars that have an average glow and heat transfer. So we will talk about what color stars are characterized by certain features below.
Class "O" celestial bodies
Such space objects are considered one of the brightest in the universe. Blue stars are the largest in radius, mass and luminosity. They got their name due to the fact that they emit such a bluish tint that is visible at great distances, even by cosmic standards. There is a chemical explanation for this - in this plasma ball, elements such as helium, nitrogen, carbon and others are very strongly ionized, resulting in an ultraviolet glow. Blue stars, despite their power and gigantic size, live very short lives. On average, their existence lasts for 1 million years, after which the star explodes. Planets theoretically suitable for life are formed extremely rarely around such celestial bodies. A bright representative of this type is the star Garnib. 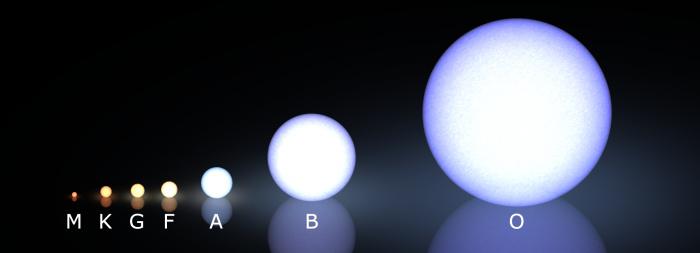
A little less light - category "B"
Now we will look at the category of blue-white cosmic luminaries, which are slightly behind their predecessors in all respects. Since the name and color of stars in astronomy always coincide, we will not describe them appearance. The cosmic body receives its characteristic shade due to the fact that hydrogen is ionized in the plasma, while helium reaches an almost neutral state. It is the last element that creates a white shell around them, which is most often presented in the form of stripes. Such stars live for 10-15 million years, and the likelihood that planets suitable for habitation can form around them is very high. You can find it in the sky in the constellation Virgo. They are called Spica. 
Category "A" stars
Stars white are among the most popular in space. The intensity of the glow is great, but at the same time, huge flows of radiation and other radiations do not interfere with other comic bodies that are located around them. normal life. Space objects included in this category are exclusively white in color due to the fact that hydrogen in them reaches the most neutral state. This turns it, in synthesis with other components, into a snow-white mass that emits countless Kelvins, which are converted into heat and light. White stars are also called “stripes”, since it is hydrogen that appears on their surface in the form of stripes. The lifespan of such a star ranges from 400 million to 2 billion years. We meet similar celestial bodies in the constellations Canis Major(Sirius), as well as Lyra (Vega). 
Group of stars coded "F"
By the fact that the name and color of the stars always coincide with each other, we are obliged chemical processes that are happening there. Therefore, now we will look at cosmic plasma giants, which are included in the “white-yellow” category and have a characteristic glow. Hydrogen in such heavenly bodies is no longer contained in that a huge number, as in the above cases. Here, on the contrary, other metals predominate - iron, titanium, and calcium. They ionize, giving the melting plasma a slightly yellowish tint. Since the star is not too large in size, this color is a salvation for it. It is visible for billions of light years, so astronomers can see such space objects in their telescopes, even if they are very far from Earth. Such stars live for 4 billion years or more, and often gather around themselves where life can arise. Representatives of this group are the luminaries Porcyon and Ropagi. 
A star called the Sun... consider class "G"
Next on our list are the colors, the brightest representative of which for us is the Sun. Such cosmic bodies filled with various metals, the main place among which is calcium. They are very strongly ionized, as a result of which they acquire a rich yellow tint. Others give it more intensity heavy metals, which also melt under enormous temperatures. The stripes of hydrogen are completely invisible here, and this substance itself is contained in yellow stars in very small quantities. The lifespan of such luminaries is approximately 10 billion years. This allows you not only to gather a certain number of planets around you, but also to keep them in their orbits for a fairly long (by cosmic standards) period of time. For example, take a look at our Solar System. 
Star category "K"
Since the difference in color between stars is officially recognized astronomical system worldwide, we move to the penultimate category, which is called “orange”. As part of the data celestial bodies Hydrogen is already contained in a very small state, so it manifests itself little. White lines practically do not appear on the surface, but the results of the melting of other metals that make up the star are very noticeable. There is aluminum, titanium, iron, and, most importantly, calcium. Moreover, the melting point of all these elements is not too high. Because of this, the lilac train, which can be seen for more bright stars(categories O, A, etc.), is completely absent here. However, despite the low temperatures and small magnitude, orange stars can gather small ones around themselves. planetary systems. Life does not always arise on them, but they exist until the orange “sun” itself disappears from space. His life is measured at 60 billion years. Representative stars of this category are Yavin, Aldebaran and Arcturus. 
Smallest stars - group "M"
Red stars are characterized by very cold temperatures and weakened metal melting processes. They also have very small parameters compared to their giant counterparts, low mass and radiation strength. The reddish glow around the star is no longer created due to the fact that various metals are melted here, but because the degree of their oxidation reaches its maximum, and the molecules simply absorb each other. It is very rare for habitable planets to form around such red dwarfs. Betelgeuse is the brightest representative of this category, whose age is estimated in tens of trillions of years.
Atypical celestial bodies
We have just looked at how stars are distinguished by color, but we have not mentioned the fact that there are certain anomalous categories of such celestial bodies. Well, in fact, there are category C stars in space. This can be said to be a synthesis of an orange and red star, which contains maximum quantity different metals. Main feature categories - there are atoms here that absorb carbohydrates and hydrogen, which makes the star even colder and fainter. Much more anomalous is the S class star. It is very similar to orange, but instead large quantity titanium, it contains the same amount of zirconium.
Conclusion
As it turns out, it is their appearance that can tell us what color the stars are and how to classify them. The glow and its shade are created thanks to the materials that melt there and form certain mixtures. They are released at a specific degree, spreading into space not only light, but also heat, which can heat or burn all nearby objects.








