Chemistry refers to natural sciences. She studies the composition, structure, properties and transformations of substances, as well as the phenomena accompanying these transformations.
Substance is one of the main forms of existence of matter. Substance as a form of matter consists of individual particles varying degrees of complexity and has its own mass, the so-called
rest mass.
Simple and complex substances. Allotropy.
All substances can be divided into simple And complex .
Simple substances consist of atoms of one chemical element, complex - from atoms of several chemical elements.
Chemical element - this is a certain type of atom with the same nuclear charge. Hence, atom is the smallest particle of a chemical element.
Concept simple substance cannot be identified with the concept
chemical element . A chemical element is characterized by a certain positive charge of the atomic nucleus, isotopic composition, and chemical properties. The properties of elements relate to its individual atoms. A simple substance is characterized by a certain density, solubility, melting and boiling points, etc. These properties relate to a collection of atoms and are different for different simple substances.
Simple substance - this is the form of existence of a chemical element in a free state. Many chemical elements form several simple substances, different in structure and properties. This phenomenon is called allotropy , and the forming substances are allotropic modifications . Thus, the oxygen element forms two allotropic modifications - oxygen and ozone, the carbon element - diamond, graphite, carbyne, fullerene.
The phenomenon of allotropy is caused by two reasons: a different number of atoms in the molecule (for example, oxygen ABOUT 2 and azon ABOUT 3 ) or the formation of various crystalline forms (for example, carbon forms the following allotropic modifications: diamond, graphite, carbine, fullerene), carbine was discovered in 1968 (A. Sladkov, Russia), and fullerene was discovered theoretically in 1973 (D. Bochvar, Russia) , and in 1985 - experimentally (G. Kroto and R. Smalley, USA).
Complex substances They consist not of simple substances, but of chemical elements. Thus, hydrogen and oxygen, which are part of water, are contained in water not in the form of gaseous hydrogen and oxygen with their characteristic properties, but in the form elements - hydrogen and oxygen.
The smallest particle of substances having a molecular structure is a molecule that retains chemical properties of this substance. According to modern concepts, molecules consist mainly of substances in liquid and gaseous states. Most solids (mostly inorganic) do not consist of molecules, but of other particles (ions, atoms). Salts, metal oxides, diamond, metals, etc. do not have a molecular structure.
Relative atomic mass
Modern research methods make it possible to determine extremely small atomic masses with greater accuracy. For example, the mass of a hydrogen atom is 1,674 10 -27 kg, carbon – 1,993 10 -26 kg.
In chemistry, not absolute values of atomic masses are traditionally used, but relative ones. In 1961, the unit of atomic mass was adopted atomic mass unit (abbreviated a.u.m.), which is 1/12 part of the mass of a carbon isotope atom 12 WITH.
Most chemical elements have atoms with different masses (isotopes). That's why relative atomic mass (or just atomic mass) A r of a chemical element is a quantity equal to the ratio average weight atom of element k 1/12 carbon atom mass 12 WITH.
The atomic masses of the elements are A r, where index r– initial letter English word relative – relative. Posts A r (H), A r (O) A r (C) mean: relative atomic mass hydrogen, relative atomic mass of oxygen, relative atomic mass of carbon.
Relative atomic mass is one of the main characteristics of a chemical element.
When studying the material in the previous paragraphs, you have already become acquainted with some substances. For example, a molecule of hydrogen gas consists of two atoms of the chemical element hydrogen - H + H = H2.
Simple substances- substances that contain atoms of the same type
Simple substances known to you include: oxygen, graphite, sulfur, nitrogen, all metals: iron, copper, aluminum, gold, etc. Sulfur consists only of atoms of the chemical element sulfur, while graphite consists of atoms of the chemical element carbon.
It is necessary to clearly distinguish between concepts "chemical element" And "simple matter". For example, diamond and carbon are not the same thing. Carbon is a chemical element, and diamond is a simple substance formed by the chemical element carbon. IN in this case a chemical element (carbon) and a simple substance (diamond) are called differently. Often a chemical element and its corresponding simple substance are named the same. For example, the element oxygen corresponds to a simple substance - oxygen.
It is necessary to learn how to distinguish between where we are talking about an element and where about a substance! For example, when they say that oxygen is part of water - we're talking about about the element oxygen. When they say that oxygen is a gas necessary for breathing, we are talking about the simple substance oxygen.
Simple substances of chemical elements are divided into two groups - metals and non-metals.
Metals and non-metals radically different in their physical properties. All metals at normal conditions solids, with the exception of mercury - the only liquid metal. Metals are opaque and have a characteristic metallic luster. Metals are ductile and conduct heat and electricity well.

Nonmetals are not similar to each other in physical properties. So, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen are gases, silicon, sulfur, phosphorus are solids. The only liquid non-metal is bromine, a brownish-red liquid.

If you draw a conventional line from the chemical element boron to the chemical element astatine, then in the long version of the Periodic System there are non-metallic elements above the line, and below it - metal. IN short version The Periodic Table contains non-metallic elements below this line, and both metallic and non-metallic elements above it. This means that it is more convenient to determine whether an element is metallic or non-metallic using the long version of the Periodic Table. This division is conditional, since all elements in one way or another exhibit both metallic and non-metallic properties, but in most cases this distribution corresponds to reality.

Complex substances and their classification
If simple substances contain only one type of atom, it is easy to guess that complex substances will contain several types different atoms, at least two. An example of a complex substance is water; you know its chemical formula - H2O. Water molecules are made up of two types of atoms: hydrogen and oxygen.
Complex substances- substances containing atoms of various types
Let's conduct the following experiment. Mix sulfur and zinc powders. Place the mixture on a metal sheet and set it on fire using a wooden torch. The mixture ignites and quickly burns with a bright flame. After the completion of the chemical reaction, a new substance was formed, which included sulfur and zinc atoms. The properties of this substance are completely different from those starting materials– sulfur and zinc.

Complex substances are usually divided into two groups: inorganic substances and their derivatives and organic substances and their derivatives. For example, rock salt is an inorganic substance, and the starch contained in potatoes is an organic substance.

Types of structure of substances
Based on the type of particles that make up the substances, substances are divided into substances molecular and not molecular structure.
The substance may contain various structural particles, such as atoms, molecules, ions. Consequently, there are three types of substances: substances of atomic, ionic and molecular structure. Substances of different types of structure will have various properties.
Substances of atomic structure
Example of substances atomic structure there may be substances formed by the element carbon: graphite and diamond. These substances contain only carbon atoms, but the properties of these substances are very different. Graphite– a fragile, easily exfoliating substance of gray-black color. Diamond– transparent, one of the hardest minerals on the planet. Why do substances consisting of the same type of atom have different properties? It's all about the structure of these substances. Carbon atoms in graphite and diamond combine in different ways. Substances of atomic structure have high temperatures boiling and melting, as a rule, insoluble in water, non-volatile.
Crystal lattice – an auxiliary geometric image introduced to analyze the structure of a crystal
Substances of molecular structure
Substances of molecular structure- these are almost all liquids and most gaseous substances. There are also crystalline substances whose crystal lattice includes molecules. Water is a substance of molecular structure. Ice also has a molecular structure, but unlike liquid water, has a crystal lattice where all molecules are strictly ordered. Substances of molecular structure have low boiling and melting points, are usually fragile, and do not conduct electricity.
Substances of ionic structure
Substances of ionic structure are solid crystalline substances. Example of a substance ionic compound maybe table salt. Its chemical formula is NaCl. As we can see, NaCl consists of ions Na+ and Cl⎺, alternating in certain places (nodes) of the crystal lattice. Substances with an ionic structure have high melting and boiling points, are fragile, are usually highly soluble in water, and do not conduct electric current.
The concepts of “atom”, “chemical element” and “simple substance” should not be confused.
- "Atom" – concrete concept, since atoms really exist.
- "Chemical element"- this is a collective abstract concept; in nature, a chemical element exists in the form of free or chemically bonded atoms, that is, simple and complex substances.
The names of chemical elements and the corresponding simple substances are the same in most cases.
When we talk about a material or component of a mixture - for example, a flask is filled chlorine gas, aqueous solution bromine, let's take a piece of phosphorus - we are talking about a simple substance. If we say that a chlorine atom contains 17 electrons, the substance contains phosphorus, the molecule consists of two bromine atoms, then we mean a chemical element.
It is necessary to distinguish between the properties (characteristics) of a simple substance (a collection of particles) and the properties (characteristics) of a chemical element (isolated atom a certain type), see table below:
Complex substances must be distinguished from mixtures, which also consist of different elements.
The quantitative ratio of the mixture components can be variable, and chemical compounds have a constant composition.
For example, in a glass of tea you can add one spoon of sugar, or several, and sucrose molecules С12Н22О11 contains exactly 12 carbon atoms, 22 hydrogen atoms and 11 oxygen atoms.
Thus, the composition of the compounds can be described by one chemical formula, and the composition no mixture.
The components of the mixture retain their physical and chemical properties. For example, if you mix iron powder with sulfur, a mixture of two substances is formed. Both sulfur and iron in this mixture retain their properties: iron is attracted by a magnet, and sulfur is not wetted by water and floats on its surface.
If sulfur and iron react with each other, a new compound is formed with the formula FeS, which has neither the properties of iron nor sulfur, but has a set own properties. In connection FeS iron and sulfur are bound to each other, and it is impossible to separate them using the methods used to separate mixtures.
Thus, substances can be classified according to several parameters:

Conclusions from an article on the topic Simple and complex substances
- Simple substances- substances that contain atoms of the same type
- Simple substances are divided into metals and non-metals
- Complex substances- substances containing atoms of various types
- Complex substances are divided into organic and inorganic
- There are substances of atomic, molecular and ionic structure, their properties are different
- Crystal lattice– an auxiliary geometric image introduced to analyze the crystal structure
About atoms and chemical elements
There is nothing else in nature
neither here nor there, in the depths of space:
everything - from small grains of sand to planets -
consists of unified elements.
S. P. Shchipachev, “Reading Mendeleev.”
In chemistry, except for terms "atom" And "molecule" the concept is often used "element". What do these concepts have in common and how do they differ?
Chemical element – these are atoms of the same type . So, for example, all hydrogen atoms are the element hydrogen; all oxygen and mercury atoms are the elements oxygen and mercury, respectively.
Currently, more than 107 types of atoms are known, that is, more than 107 chemical elements. It is necessary to distinguish between the concepts of “chemical element”, “atom” and “simple substance”
Simple and complex substances
According to their elemental composition they are distinguished simple substances, consisting of atoms of one element (H 2, O 2, Cl 2, P 4, Na, Cu, Au), and complex substances, consisting of atoms of different elements (H 2 O, NH 3, OF 2, H 2 SO 4, MgCl 2, K 2 SO 4).
Currently, 115 chemical elements are known, which form about 500 simple substances.
Native gold is a simple substance.
The ability of one element to exist in the form of various simple substances differing in properties is called allotropy For example, the element oxygen O has two allotropic forms - dioxygen O 2 and ozone O 3 with different numbers of atoms in the molecules.
Allotropic forms of the element carbon C - diamond and graphite - differ in the structure of their crystals. There are other reasons for allotropy.
chemical compounds, for example, mercury(II) oxide HgO (obtained by combining atoms of simple substances - mercury Hg and oxygen O 2), sodium bromide (obtained by combining atoms of simple substances - sodium Na and bromine Br 2).
So, let's summarize the above. There are two types of molecules of matter:
1. Simple– the molecules of such substances consist of atoms of the same type. In chemical reactions they cannot decompose to form several simpler substances.
2. Complex- molecules of such substances consist of atoms different types. In chemical reactions they can decompose to form simpler substances.
The difference between the concepts of “chemical element” and “simple substance”
Distinguish between concepts “chemical element” And “simple substance” possible by comparing the properties of simple and complex substances. For example, a simple substance - oxygen– a colorless gas necessary for breathing and supporting combustion. smallest particle The simple substance oxygen is a molecule that consists of two atoms. Oxygen is also included in carbon monoxide ( carbon monoxide) and water. However, water and carbon monoxide contain chemically bound oxygen, which does not have the properties of a simple substance; in particular, it cannot be used for respiration. Fish, for example, do not breathe chemically bound oxygen, which is part of the water molecule, but free oxygen dissolved in it. Therefore, when we talk about the composition of any chemical compounds, it should be understood that these compounds do not contain simple substances, but atoms of a certain type, that is, the corresponding elements.
When complex substances decompose, atoms can be released in a free state and combine to form simple substances. Simple substances consist of atoms of one element. The difference between the concepts of “chemical element” and “simple substance” is also confirmed by the fact that the same element can form several simple substances. For example, atoms of the element oxygen can form diatomic oxygen molecules and triatomic ozone molecules. Oxygen and ozone are completely different simple substances. This explains the fact that much more simple substances are known than chemical elements.
Using the concept of “chemical element”, we can give the following definition to simple and complex substances:
Simple substances are those that consist of atoms of one chemical element.
Complex substances are those that consist of atoms of different chemical elements.
The difference between the concepts of “mixture” and “chemical compound”
Complex substances are often called chemical compounds.
Try to answer the questions:
1. How do mixtures differ in composition from chemical compounds?
2. Compare the properties of mixtures and chemical compounds?
3. In what ways can you separate the components of a mixture and a chemical compound?
4. Is it possible to judge by external signs about the formation of a mixture and a chemical compound?
Comparative characteristics of mixtures and chemicals
|
Questions to match mixtures to chemical compounds |
Comparison |
|
|
Mixtures |
Chemical compounds |
|
|
How do mixtures differ in composition from chemical compounds? |
Substances can be mixed in any ratio, i.e. variable composition of mixtures |
The composition of chemical compounds is constant. |
|
Compare the properties of mixtures and chemical compounds? |
Substances in mixtures retain their properties |
Substances that form compounds do not retain their properties, since chemical compounds with other properties are formed |
|
In what ways can a mixture and a chemical compound be separated into its constituent components? |
Substances can be separated by physical means |
Chemical compounds can only be broken down through chemical reactions |
|
Is it possible to judge by external signs the formation of a mixture and a chemical compound? |
Mechanical mixing is not accompanied by the release of heat or other signs of chemical reactions |
The formation of a chemical compound can be judged by the signs of chemical reactions |
Tasks for consolidation
I. Work with simulators
II. Solve the problem
NaCl, H 2 SO 4, K, S 8, CO 2, O 3, H 3 PO 4, N 2, Fe.
Explain your choice in each case.
III. Answer the questions
№1
How many simple substances are written in a series of formulas:
H 2 O, N 2, O 3, HNO 3, P 2 O 5, S, Fe, CO 2, KOH.
№2
Both substances are complex:
A) C (coal) and S (sulfur);
B) CO 2 (carbon dioxide) and H 2 O (water);
B) Fe (iron) and CH 4 (methane);
D) H 2 SO 4 (sulfuric acid) and H 2 (hydrogen).
№3
Choose the correct statement:
Simple substances consist of atoms of the same type.
A) Correct
B) Incorrect
№4
What is typical for mixtures is that
A) They have a constant composition;
B) Substances in the “mixture” do not retain their individual properties;
C) Substances in “mixtures” can be separated by physical properties;
D) Substances in “mixtures” can be separated using a chemical reaction.
№5
The following are typical for “chemical compounds”:
A) Variable composition;
B) Substances contained in a “chemical compound” can be separated by physical means;
C) The formation of a chemical compound can be judged by the signs of chemical reactions;
D) Permanent composition.
№6
In what case are we talking about gland how about chemical element?
A) Iron is a metal that is attracted by a magnet;
B) Iron is part of rust;
C) Iron is characterized by a metallic luster;
D) Iron sulfide contains one iron atom.
№7
In what case are we talking about oxygen as a simple substance?
A) Oxygen is a gas that supports respiration and combustion;
B) Fish breathe oxygen dissolved in water;
C) The oxygen atom is part of the water molecule;
D) Oxygen is part of air.
IN previous chapter it was said that not only atoms of the same chemical element can form bonds with each other, but also atoms of different elements. Substances formed by atoms of one chemical element are called simple substances, and substances formed by atoms of different chemical elements are called complex substances. Some simple substances have a molecular structure, i.e. consist of molecules. For example, substances such as oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine have a molecular structure. Each of these substances is formed by diatomic molecules, so their formulas can be written as O 2, N 2, H 2, F 2, Cl 2, Br 2 and I 2, respectively. As you can see, simple substances can have the same name as the elements that form them. Therefore, one should clearly distinguish between situations when we are talking about a chemical element and when about a simple substance.
Often simple substances have not a molecular, but an atomic structure. In such substances, atoms can form bonds with each other various types, which will be discussed in detail a little later. Substances of a similar structure are all metals, for example, iron, copper, nickel, as well as some non-metals - diamond, silicon, graphite, etc. These substances are usually characterized not only by the coincidence of the name of the chemical element with the name of the substance formed by it, but also by the identical recording of the formula of the substance and the designation of the chemical element. For example, the chemical elements iron, copper and silicon, designated Fe, Cu and Si, form simple substances whose formulas are Fe, Cu and Si, respectively. There is also a small group of simple substances consisting of isolated atoms that are not connected in any way. Such substances are gases, which are called noble gases due to their extremely low chemical activity. These include helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), radon (Rn).
Since there are only about 500 known simple substances, the logical conclusion follows that many chemical elements are characterized by a phenomenon called allotropy.
Allotropy is a phenomenon when one chemical element can form several simple substances. Different chemical substances formed by one chemical element are called allotropic modifications or allotropes.
So, for example, the chemical element oxygen can form two simple substances, one of which has the name of the chemical element - oxygen. Oxygen as a substance consists of diatomic molecules, i.e. its formula is O 2. It is this compound that is part of the air we need for life. Another allotropic modification of oxygen is the triatomic gas ozone, whose formula is O 3 . Despite the fact that both ozone and oxygen are formed by the same chemical element, they chemical behavior very different: ozone is much more active than oxygen in reactions with the same substances. In addition, these substances differ from each other in physical properties, at least due to the fact that molecular weight ozone is 1.5 times greater than oxygen. This leads to the fact that its density is gaseous state also 1.5 times more.
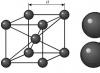
Many chemical elements tend to form allotropic modifications that differ from each other in the structural features of the crystal lattice. So, for example, in Figure 5, you can see schematic images of fragments crystal lattices diamond and graphite, which are allotropic modifications of carbon.
Figure 5. Fragments of crystal lattices of diamond (a) and graphite (b)
In addition, carbon can also have a molecular structure: such a structure is observed in a type of substance such as fullerenes. Substances of this type formed by spherical carbon molecules. Figure 6 shows 3D models of a c60 fullerene molecule and a soccer ball for comparison. Notice their interesting similarities.

Figure 6. C60 fullerene molecule (a) and soccer ball (b)
Complex substances are substances that consist of atoms of different elements. They, just like simple substances, can have molecular and non-molecular structure. The non-molecular type of structure of complex substances can be more diverse than that of simple ones. Any complex chemical substances can be obtained either by direct interaction of simple substances or by a sequence of their interactions with each other. It is important to realize one fact, which is that the properties of complex substances, both physical and chemical, are very different from the properties of the simple substances from which they are obtained. For example, table salt, which has NaCl forum and is colorless clear crystals, can be obtained by the interaction of sodium, which is a metal with properties characteristic of metals (brilliance and electrical conductivity), with chlorine Cl 2, a yellow-green gas.
Sulfuric acid H 2 SO 4 can be formed by a series of successive transformations from simple substances - hydrogen H 2, sulfur S and oxygen O 2. Hydrogen is a lighter-than-air gas that forms explosive mixtures with air; sulfur is a solid. yellow, capable of burning, and oxygen is a gas slightly heavier than air in which many substances can burn. Sulfuric acid, which can be obtained from these simple substances, is a heavy oily liquid with strong water-removing properties, due to which it chars many substances of organic origin.
It is obvious that in addition to individual chemicals, there are also mixtures of them. The world around us is formed primarily by mixtures of various substances: metal alloys, food products, drinks, various materials, of which the objects around us are made.
For example, the air we breathe consists mainly of nitrogen N2 (78%), oxygen (21%), which is vital for us, and the remaining 1% is made up of impurities of other gases (carbon dioxide, noble gases etc.).
Mixtures of substances are divided into homogeneous and heterogeneous. Homogeneous mixtures are those mixtures that do not have phase boundaries. Homogeneous mixtures are a mixture of alcohol and water, metal alloys, a solution of salt and sugar in water, mixtures of gases, etc. Heterogeneous mixtures are those mixtures that have a phase boundary. Mixtures of this type include a mixture of sand and water, sugar and salt, a mixture of oil and water, etc.
The substances that make up mixtures are called components.
Mixtures of simple substances, unlike chemical compounds that can be obtained from these simple substances, retain the properties of each component.
Organic and inorganic substances;
> recognize metals and non-metals;
> identify metallic and non-metallic elements by their location in periodic table D. I. Mendeleev; understand why all metals have similar properties.
Atoms under ordinary conditions cannot exist alone for long. They are able to combine with the same or other atoms, which causes a wide variety of substances in the world.
A substance formed by one chemical element is called simple, and a substance formed by several elements is called a complex or chemical compound.
Simple substances
Simple substances are divided into metals and non-metals. This classification of simple substances was proposed by the outstanding French scientist A.L. Lavoisier in late XVIII V. The chemical elements from which metals come are called metallic, and those that form non-metals are called
non-metallic. In the long version of D.I. Mendeleev’s system (endpaper II), they are delimited by a broken line. Metal elements are to the left of it; there are significantly more of them than non-metallic ones.
This is interesting
Simple substances of 13 elements - Au, Ag, Cu, Hg, Pb, Fe, Sn, Pt, S, C, Zn, Sb and As were known in ancient times.
Each of you can, without hesitation, name several metals (Fig. 36). They differ from other substances by a special “metallic” luster. These substances have a lot general properties.
Rice. 36. Metals
Metals under normal conditions are solids(only mercury is a liquid), conduct electric current and heat well, have generally high temperature melting (over 500 °C).

Rice. 37. Simplified model internal structure metal
They are plastic; they can be forged and wire drawn from them.
Thanks to their properties, metals have confidently entered people's lives. About them of great importance the names indicate historical eras: copper age, Bronze 1st Age, Iron Age.
The similarity of metals is due to their internal structure.
Structure of metals. Metals are crystalline substances. Crystals in metals are much smaller than sugar crystals or table salt, and it is impossible to see them with the naked eye.
Molecule - an electrically neutral particle consisting of two or more connected atoms.
In each molecule, the atoms are connected to each other quite strongly, but the molecules to each other in the substance are very weakly connected. Therefore, substances of molecular structure have low melting and boiling points.
Oxygen and ozone are molecular substances. These are simple oxygen substances. An oxygen molecule contains two Oxygen atoms, and an ozone molecule contains three (Fig. 39).

Rice. 39. Models of molecules
Not only oxygen, but also many other elements form two or more simple substances. Therefore, there are several times more simple substances than chemical elements.
Names of simple substances.
Most simple substances are named after the corresponding elements. If the names are different, then they are given in the periodic table, with the name of the simple substance located below the name
element (Fig. 40).
Name the simple substances of the elements Hydrogen, Lithium, Magnesium, Nitrogen.
1 The term "molecule" comes from Latin word moles (mass), diminutive suffix cula and translated means “small mass”.
The names of simple substances are written inside the sentence with a small letter.

Rice. 40. Cell of the periodic table
Complex substances (chemical compounds)
The combination of atoms of different chemical elements gives rise to many complex substances(there are tens of thousands of times more of them than simple ones).
There are complex substances with molecular, atomic and ionic structure. Therefore, their properties are very different.
Molecular compounds are mostly volatile and often have an odor. Their melting and boiling points are significantly lower than those of compounds with an atomic or ionic structure.
The molecular substance is water. A water molecule consists of two Hydrogen atoms and one Oxygen atom (Fig. 41).

Rice. 41. Water molecule model
The molecular structure is carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide. gases, sugar, starch, alcohol, acetic acid etc. The number of atoms in the molecules of complex substances can be different - from two atoms to hundreds and even thousands.
Some compounds have an atomic structure.
One of them is the mineral quartz, the main component of sand. It contains Silicium and Oxygen atoms (Fig. 42).

Rice. 42. Model of compound of atomic structure (quartz)
There are also ionic compounds. These are table salt, chalk, soda, lime, gypsum and many others. Table salt crystals consist of positively charged Sodium ions and negatively charged Chlorine ions (Fig. 43). Each such ion is formed from the corresponding atom (§ 6).

Rice. 43. Model of an ionic compound (table salt)
This is interesting
In molecules organic compounds In addition to Carbon atoms, as a rule, there are also Hydrogen atoms, often Oxygen atoms, and sometimes some other elements.
The mutual attraction of many oppositely charged ions causes the existence of ionic compounds.
An ion formed from one atom is called simple, and an ion formed from several atoms is called complex.
Positively charged simple ions exist for metal elements, and negatively charged - for non-metallic elements.
Names of complex substances.
The textbook has so far provided technical or household names complex substances. In addition, substances also have chemical names. For example, chemical name table salt is sodium chloride, and chalk is calcium carbonate. Each such name consists of two words. The first word is the name of one of the elements that form the substance (it is written with a small letter), and the second comes from the name of another element.
Organic and inorganic substances.
Previously, organic substances were those substances that are found in living organisms. These are proteins, fats, sugar, starch, vitamins, compounds that give color, smell, taste to vegetables and fruits, etc. Over time, scientists began to obtain in laboratories substances similar in composition and properties that do not exist in nature. Nowadays, organic substances are called carbon compounds (with the exception of carbon dioxide and carbon dioxide, chalk, soda, and some others).
Most organic compounds are capable of burning, and when heated in the absence of air, they become charred (coal consists almost entirely of carbon atoms).
K not organic matter belong to the remaining complex substances, as well as all simple ones. They form the basis of the mineral world, i.e. they are found in soil, minerals, rocks, air, natural water. In addition, inorganic substances are also found in living organisms.
The material in this paragraph is summarized in Diagram 6.

Laboratory experiment No. 2
Introduction to different types of substances
You have been given the following substances (the option will be indicated by the teacher):
option I - sugar, calcium carbonate (chalk), graphite, copper;
option II - paraffin, aluminum, sulfur, sodium chloride (table salt).
The substances are in jars with labels.
Carefully examine the substances, pay attention to their names. Identify among them simple (metals, non-metals) and complex substances, as well as organic and inorganic.
Enter the name of each substance in the table and indicate its type by writing a “+” sign in the appropriate columns.
Conclusions
Substances can be simple and complex, organic and inorganic.
Simple substances are divided into metals and nonmetals, and chemical elements are divided into metallic and nonmetallic.
Metals have many common properties due to the similarity of their internal structure.
Nonmetals are made up of atoms or molecules and have different properties from metals.
Complex substances (chemical compounds) have an atomic, molecular or ionic structure.
Almost all Carbon compounds belong to organic substances, and the remaining compounds and simple substances belong to inorganic substances.
?
56. Which substance is called simple and which is complex? What types of simple substances exist and what are the names of the corresponding elements?
57. By what physical properties can a metal be distinguished from a non-metal?
58. Define a molecule. How does a molecule of a simple substance differ from a molecule of a complex substance?
59. Fill in the blanks by inserting the words “Nitrogen” or “nitrogen” in the appropriate cases and explain your choice:
a) ... - the gas that contains the largest amount in the air;
b) a molecule... consists of two atoms...;
c) compounds... enter plants from the soil;
d)... is poorly soluble in water.
60. Fill in the blanks by inserting the words “element”, “atom” or “molecule” in the appropriate case and number:
A)... white phosphorus contains four... Phosphorus;
b) there is... carbon dioxide in the air;
c) gold is a simple substance... Aurum.