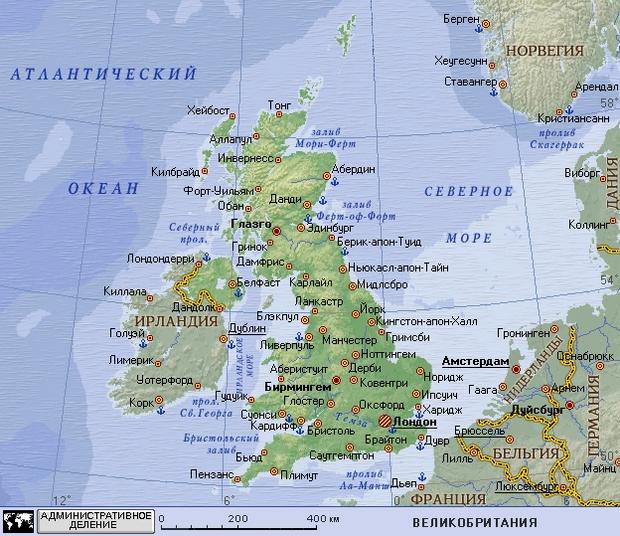
Great Britain is located in the north-west of the continent of Europe and is washed on all sides by the cold waters of two seas, an ocean and several straits. The British Isles can boast of a fairly advantageous position in terms of military strategy. That is why throughout its existence, right up to the 18th century, many fought for the territory of the country. European states. Today, the UK economy ranks second in European rankings, right after Germany, and sixth in the world ranking. Thanks to this and a number of other significant factors, despite the finicky climate, the country remains attractive today for tourists and emigrants from less developed countries. Get to Foggy Albion possible only through the North and Irish Seas, the Atlantic Ocean or the straits.
Atlantic ocean
The United Kingdom of Great Britain is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, which is the second largest in the world after the Pacific. The British Isles are one of the largest in the Atlantic waters, which also includes Bermuda, Malta, Sicily, Cyprus, Cuba, Haiti, Jamaica and others.
Northern sea
The North Sea Shelf is part of the Atlantic Ocean and washes the shores of western continental Europe and the UK. It is considered shallow - its deepest point is only 725 meters. Temperature sea shores Great Britain does not rise above 13-17°C even in the hottest months of the year. At the same time, in winter time near the sea it is significantly warmer than in other regions of the country. The legendary River Thames flows into the North Sea, and among the most major ports listed as the port of London.
Coast North Sea in England is a great place to relax both alone and with the whole family. The calm, peaceful landscapes and long sandy beaches of the resort towns of Bridlington, Whitby, Scarborough or Seahouses will not leave any tourist indifferent. Those who love an active pastime will be able to play traditional English golf on the seashore, go sailing or go fishing.
Irish sea
This sea is located between the islands of Ireland in the west and Great Britain in the east. Its waters connect with Atlantic Ocean through the North and St. George Straits. The Irish Sea itself is not deep - the most impressive depth is only 175 meters. But even at this depth, the water temperature in the sea is not high. For example, in summer it reaches +16°C, and in winter - +5°C. Also in winter, especially in January and February, residents of coastal cities have to contend with severe storms. On the eastern coast of the sea there is the most big port United Kingdom - Liverpool, and on west bank stands the port of Dublin, through which a significant share of Ireland's trade passes.
Great Britain located in northwestern Europe, in the British Isles. It occupies the island of Great Britain (England, Scotland and Wales) and part of the island of Ireland, as well as independent administrative units - the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands. Great Britain is washed by the Atlantic Ocean in the north and west, the North Sea in the east and the Irish Sea in the west, and is separated from the mainland in the south by the English Channel and Pas-de-Calais.
Total area of the country: 244.1 thousand km²
Coastline length: more than 10 thousand km
Political system
: a constitutional monarchy
Capital: London
Population: 60 million people
Language: Official language- English. The use of 'national' languages is maintained in the province.
Religion: About 70% of the population professes Anglicanism, 16% is Catholic, 2% is Muslim.
Currency unit: GBP/GBP (1 GBP = 100 pence)
Time: 3 hours behind Moscow
Geographical location and nature.
The territory of the United Kingdom is divided into two main areas based on relief features. The Highlands of Britain (including Northern Ireland), located in the north and west of the country, are underlain by resistant ancient bedrock and consist mostly of highly dissected uplands and much less widespread lowlands. To the south and east lies Low Britain, characterized by rolling terrain, low elevations and several mountainous areas; younger sedimentary rocks lie at its base. The border between High and Low Britain runs approximately in a south-westerly direction from Newcastle at the mouth of the Tyne to Exeter at the mouth of the Exe in south Devon. This boundary is not always clearly defined, and often the transitions between High and Low Britain are smoothed out. In general, the country's topography is so diverse that, driving in one direction for more than an hour, you cross several different landscapes.
Climate.
The climate in Great Britain is temperate oceanic. In the western part of Great Britain the climate is wetter than in the eastern part due to the prevailing westerly winds from the Atlantic Ocean. In the mountains of Scotland, Wales and Northern Scotland weather more severe.
The oceanic nature of the country's climate is reflected in the prevalence of unstable weather with gusty winds and dense fogs throughout the year. It is no coincidence that Great Britain is called “Foggy Albion”. Big influence provides warm current The Gulf Stream means that British winters are very wet and mild, with temperatures rarely falling below freezing.
The coldest month is January (from +2°C to +7°C), the warmest month is July (from +11°C to +17°C). The weather is very changeable, so even in summer it is necessary to carry light woolen clothes with you in case of cool weather.
Population.
The majority of residents are English (81.5%), Scots - 9.6%, Irish - 2.4%, Welsh - 1.9%, Indians, Pakistanis, Arabs, Chinese, and Africans also live in the country.
State structure.
Full name - United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland(abbreviated Great Britain). The government system is a constitutional monarchy. The United Kingdom includes England, Scotland, Wales, Northern Ireland - a total of 47 counties, 7 capital districts, 26 districts, 9 regions and 3 islands. England consists of 39 counties, 7 capital districts, Scotland - of 9 regions and 3 islands, Wales - of 8 districts, Northern Ireland - of 26 districts. In addition, the country includes dependent territories: the island of Anguilla, Bermuda, British Territory Indian Ocean, British Virgin Islands, Gibraltar, Cayman Islands, Isle of Man, Montserrat Island, Pitcairn Islands, St. Helena Island, Terke and Caicos Islands, Falkland Islands, South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands.
The UK does not have a constitution; the fundamental law is replaced by parliamentary legislative acts adopted by a bicameral parliament, which consists of the House of Lords (upper house) and the House of Commons (lower house). National holiday(The Queen's Birthday) is celebrated on the second Saturday in June. The head of state is the Queen of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. Real executive power belongs to the Prime Minister, who forms the Cabinet of Ministers.
Transport communications.
Public transport in London is quite well developed - you can get to any point in the city by underground, famous double-decker buses, express buses (green) or minibuses. The cost of travel for all types of transport depends on the distance. In the metro, tickets are checked at the exit. It is profitable to buy a daily or weekly ticket (a photograph is required for a weekly ticket). In addition to the main subway, there is another small private line - the `Docklands Light Railway`. Single tickets on this line are your own, but citywide passes are valid everywhere. Travel cards `travelcard` are valid for almost all buses, metro and trains within the city. `Travelcard` is not valid on buses that take passengers to Heathrow airport and on overnight flights, but weekly passes are valid there. In addition, it is worth paying attention to the fact that some passes are valid only after 9.30 am. Taxi - two types. The famous 'black cabs' are relatively expensive. They operate on a meter basis: $3 per landing and $1.2 per 1 kilometer. Cheaper cars are called `minicab` (they can take not 5 passengers, like real `cabs`, but only 4). They only accept orders by phone and operate without meters, so it’s worth inquiring about the tariff in advance.
Currency exchange.
Widely used credit cards and traveler's checks from the world's leading payment systems. Automated teller machines (ATMs) are very widespread, but the unreliability of street ATMs has already become a proverb - cases of erroneous blocking of credit cards are quite common, and the operation of unblocking an account is quite lengthy, so it is recommended to use ATMs in institutions.
You can change money at any bank branch (commission 0.5-1%), in evening time- V exchange offices large department stores and some travel agencies. At airports, exchange offices operate 24 hours a day. A passport is required to exchange cash.
Banks are open from 9.00 to 15.30 without breaks on weekdays. Weekends are Saturday and Sunday. Large banks may be open an extra hour and are usually open on Saturday. Most high rate exchange at American Express banks, which does not charge fees for currency exchange. Commission fees in other banks, as a rule, range from 0.5 to 1%; You must have your passport with you. There is also a good rate at street exchange offices, especially in places where they are concentrated (for example, near Padington station).
Story.
Inhabited by Celtic tribes, what is now Britain became the Roman colony of Britannia in 43 AD under Emperor Claudius. Started at the end of the 3rd century. raids on Britain by Scandinavian tribes, and then by Germanic ones - the Angles and Saxons - put an end to Roman rule in 411. Having pushed the Celts to the west of the country, the Angles and Saxons formed during the 5th-9th centuries. seven kingdoms that adopted Christianity from the 6th to the 8th centuries.
In the 9th century Britain began to be subject to raids by the Vikings, who gradually subjugated all the Saxon kingdoms except Wessex, which became the first English kingdom. The Saxon king Edward restored the influence of the Saxon dynasty, but the Saxon troops led by his son Harold were defeated at Hastings in 1066 by the Norman commander William the Conqueror. The Normans had a huge impact on the life of English society, which underwent a serious reorganization - administrative, legal, financial, in addition, French, spoken by the Norman conquerors, left a serious imprint on Saxon culture.
William's descendant Henry I, who became king of England in 1154, founded the Plantagenet dynasty. Dispute English kings with the French for lands on the continent led to the Hundred Years' War between England and France (1330-1435). Defeat in the war and the weakness of King Henry VI led in 1455 to a civil war known as the War of the Roses, which ended in 1485 with the victory of Henry Tudor (Henry VII). During the reign last representative The Tudor dynasty - Elizabeth I - England reached an unprecedented prosperity, turning into a powerful maritime power.
In 1603, James VI of the Scottish Stuart dynasty became king of England. In 1649, an outbreak broke out in England Civil War, which divided the country into supporters of the king and parliament and ended in 1649 with the proclamation of a republic led by Oliver Cromwell. The monarchy was restored in 1660, when the son of Charles I, Charles II, ascended the English throne. In 1707, the Act of Union of England and Scotland was signed, which led to the formation of the United Kingdom of Great Britain with a common parliament, which played an increasingly important role important role in the life of the country.
At the end of the 17th century. formed in England political parties-Tory and Whig (which in the 19th century transformed, respectively, into the Conservative and Labor parties). After the death of Anne Stuart, Elector of Hanover George (George I) was invited from Germany to the English throne. In 1783, Great Britain lost some of its colonies in North America(US War of Independence).
In 1801, Ireland became part of the United Kingdom. After the defeat Napoleonic army At the Battle of Waterloo, Great Britain became one of the leading European powers. The Victorian era, named after Queen Victoria (1837-1901), was characterized by the expansion colonial possessions UK (India, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa) and carrying out deep reforms (governance, law, education, army) within the country. After the end of the First World War, the Irish question again became acute in the country. After Ireland declared independence in 1921, only Northern part islands. Great Britain entered the war against fascist Germany in September 1939, becoming one of the main participants anti-Hitler coalition. W. Churchill, who proved himself outstanding politician during the Second World War, lost in the 1945 elections to the representative of the Labor Party K. Attlee. IN
50s and 60s Almost all of Britain's colonies became independent states, some of them remained in the British Commonwealth formed in 1931. One of the most prominent British politicians in post-war years became M. Thatcher (Prime Minister of Great Britain in 1979-1990), who defeated the trade unions that declared a general strike in 1979, and in 1982 sent troops to the Falkland Islands, which Argentina intended to occupy. Serious political problem The conflict in Northern Ireland between Catholics and Protestants remains before the British government. After years of armed clashes between warring parties in the 90s The process of negotiations has begun, but the British and Irish governments are prevented from reaching an agreement by the periodic resumption of terrorist activities of the Irish Republican Army.
Attractions.
LONDON. Tower, Buckingham Palace, famous all over the world Big Ban, Houses of Parliament, St Paul's Cathedral, patron saint of London, gothic Bridge Tower, Trafalgar Square , Westminster Abbey and Cathedral with Henry VII Chapel, National Gallery and British Museum, Covent Garden Transport Museum, Museum decorative arts Victoria and Albert, Tate Gallery and Courtauld Institute - largest collections of paintings and sculptures.
London's parks are magnificent: the most famous of the royal parks Hyde Park, the oldest - St. James park and one of the most elegant - Regents Park, located next to Madame Tussauds.
LINCOLN. City with the oldest fortress in England.
BAT. The city with those there Roman baths.
CHESTER. A city founded by the Romans 2000 years ago.
YORK. One of the most beautiful medieval cities England with magnificent Ministerial Council mountainous area of the Lake District with picturesque lakes and medieval villages, turned into picturesque national park, legendary Stonehenge(dated to approximately 3100 - 1800 BC).
Lake District in Lancashire national parks and stalactite caves of Dan ir Igof and etc.
SCOTLAND. Palace of Holyroodhouse in Edinburgh, Kelvingrove Museum in Glasgow, National Nature Museum Snowdonia with Bryn Bras castle and a park with waterfalls. The place is also called the edge of waterfalls Vale of Neath, near National Park Brecon Beacons. Loch Ness Monster Museum.
WALES. Lock Harlech, perched on a cliff in central Wales, Conwy Castle, Boumaris Castle on o. Anglesey and impressive Caernarfon Castle, Castell Coch Castle with the current drawbridge, 12th century cathedral in the town of St. David's, where the relics of St. David, the patron saint of Wales, are kept.
Kitchen.
English cuisine is characterized by fairly conservative cooking with virtually no use of sauces or hot spices. Fish and vegetable dishes, as well as fried dishes, are very popular. in various forms meat. The national drink is tea, usually drunk with milk and sugar. Welsh (Welsh) and Scottish cuisines are somewhat different from English - more “bright” and spicy. It is highly recommended to try lamb chops with lemon, coriander, yoghurt and mint sauce, the famous British steaks and steaks, a wide variety of smoked fish, hot buttered pancakes and scones and, of course, countless types of puddings. Muffins, biscuits, cookies and saffron buns are especially good.
Spirits are also quite traditional - beer, whiskey and gin of all kinds, as well as the famous ale and cider.
The quality of UK beaches has improved fourfold over the past 10 years. In 1997, the Society for the Protection of the Sea recommended only 127 British beaches for recreation, and in 2007 - 494 (out of 787 surveyed). All recommended beaches meet European water quality standardsHampshire
Newport
Newport is located on the border of England and Wales, which gives it a special flavor. The Port of Newport is one of the main industrial ports in Britain. Situated in the English Channel on the Isle of Wight, Newport is famous for its mild winters and cool summers. Patients with anemia and those suffering from catarrh of the upper respiratory tract come here for treatment.
The beach is small pebbles, aquatic species sports: sailing training, traditional English rowing, yachts and catamarans.
Sussex
Eastbourne
The elegant seaside resort of Eastbourne is located on the English Channel, south of London. The beaches are sandy and well maintained. The water temperature in August rises to +19 C. In the beach administration premises you can rent beach umbrellas and sun loungers, as well as buy the necessary accessories: sunscreen, towels, robes, swimming boards and so on. Some beaches have private bathing cabins that can be rented all year round. Each has a shower, tap, dressing room and wardrobes for storing clothes and personal belongings.
The 6-kilometer promenade leading along the beaches is rich in sights and architectural monuments. On the beaches there is a specially equipped “green theater”, where various musical groups perform from May to September.
Eastbourne is home to Britain's largest chalk cliff, Beachy Head (162m), rising above the water at most picturesque place coast.
Brighton
The small fishing village of Brighton came to the attention of the Crown in 1724, when most of the houses were washed away by a powerful storm and the orphaned residents turned to the government for help. Money was allocated, and new buildings were erected on the embankments. And in 1750, Brighton was “discovered” again by Dr. Richard Russell. He informed Britain that sea air was good for health, and, according to the doctor, it was the air of Brighton that had especially healing properties. So almost overnight, Brighton transformed from a provincial town into a fashionable resort for high society.
During the residence of Prince George (the future George IV) in Brighton, the city was equipped with special “bathing machines” that delivered “beachers” to the coast. In addition, several unique buildings in Chinese and Indian styles were erected for the prince. You can still admire them to this day.
Brighton is home to the unique West Pier, one of only two piers in the UK to be listed as a number one listed building. Its proportions, style and shape are exceptional. Built in 1866 by Eugene Birch, the Pier was originally just a promenade. Then gazebos, a theater, and then concert hall for 1400 people. In the 1920s, Pierce even had his own orchestra. The pier was closed in 1975, and in 2003 it was severely damaged by fire. Now the British government is thinking about restoring its property.
Another Brighton attraction is the pub. Bertie and Belcher's Brighton Brewing Company offers a taste of beer at the Hedgehog and Cask in Hove of all places. For a name of such length, the pub is included in the Guinness Book of Records.
Municipal beaches are pebbly and sandy, and their cleanliness is monitored almost fanatically. The beaches are free. The fee for the use of umbrellas and sunbeds is indicated at the entrance to the beach. The money is collected by an employee walking around the area.
But swimming itself is not the main entertainment of Brighton. The road from the beaches to the Old Town is a real exhibition of works of folk craftsmen. Here you can buy a variety of souvenirs and trinkets, visit the Fisherman's Museum, and sit in cozy cafes and bars.
The coast provides a varied range of water activities - yachts, catamarans, fishing, tourist boat trips. On the embankment you can rent skateboards, play petanque, run kite or just have a romantic picnic. There is also a wonderful marine aquarium here.
Possibilities organized holiday provides Brighton Marina - a seaside entertainment complex, a city within a city with a bowling alley, cinema, swimming pools, shops, many restaurants and pubs, with picturesque views of the harbour. The marina is home to more than a thousand ships. Elegant yachts of millionaires coexist here with salty "hard workers" who have just committed circumnavigation. If you are a diving enthusiast, you will be offered a dive to the wreck sites of military ships.
Every May, Brighton hosts Britain's largest arts festival (since 1967). Brighton is also known as one of the largest and most vibrant gay resorts in the south of Great Britain.
Devonshire
Torbay
Torbay's history goes back many thousands of years. In the vicinity of the city, remains of Paleolithic settlements have been found in caves. Torbay became a resort in Victorian era, whose legacy includes magnificent gardens, elegant terraces and white villas.
Torbay is called the English Riviera. The resort area consists of 20 landscaped beaches stretching along the coast for 35 km - from Torquay (previously a separate resort, but now part of Torbay) to Brixham. The coast is distinguished by its enviable diversity and provides discerning tourists with almost all recreational options: there are sandy beaches, ruined fortresses, bird sanctuaries, golf courses, climbing cliffs, picturesque parks by the sea, fishing, and sailing. Moreover, the English Riviera boasts real palm trees. The first trees were planted here in 1820, and today the sandy beaches are lined with literally thousands of classic Southern plants. And, of course, there are bars and restaurants with sea views everywhere.
Torbay is composed of former cities Torquay, Brixham and Paignton. Paignton is best suited for families: long sandy beaches, a vibrant atmosphere, calm seas friendly to inexperienced swimmers and plenty of attractions and entertainment.
Life in Brixham is centered around the harbour. It is one of Britain's busiest fishing ports. The favorite pastimes of tourists here are strolling through the numerous small shops in the port area, watching the unloading of the day's catch, and also looking at the works of artists exhibited on the embankment. Here you can buy the freshest fish and seafood or try it already ready meals in a restaurant or pub. On the beaches you can rent chalets and bungalows.
Torbay has two ancient canals built over 200 years ago to transport goods to the sea. The canals themselves are historical sites, plus along their banks there are buildings included in international catalogs of historical and architectural monuments. Outside the city limits, it is pleasant to stroll along the canals on foot or by bicycle. The roads are well maintained and there are plenty of wild flowers, birds and small animals around. Torbay's parks are also a Crown National Treasure and offer hundreds of kilometers of walking trails.
England is surrounded on all sides by water, because the main part of the country is located on the island of Great Britain, and also covers the northeast of the island of Ireland and several islands located nearby. Two seas, an ocean and several straits - water wealth England. The country's position is considered very advantageous from the point of view of military strategy.
The poetic name "Foggy Albion" comes from the weather conditions prevailing in this territory. A large number of precipitation and frequent fogs have become business card England. Western and northern shores countries are at the mercy of the Atlantic Ocean. From the east, England is washed by the North Sea, and from the west by the Irish Sea. The English Channel and Pas de Calais straits separate the island part from the mainland by south direction. The length of the total coastline is approximately 12,429 km.
North Sea

The waters of the North Sea are part of the Atlantic Ocean. If you trace the location of the sea on a map, it will become clear that it washes the British Isles from the west, East Coast belongs to Norway and Denmark, and Germany, Holland, Belgium and France divided South coast, from Baltic Sea The northern one is separated by six straits and borders the Norwegian Sea and the English Channel.
The depth of the sea is about 94 meters. It should be taken into account that the topography of the seabed is quite heterogeneous. In the northern direction there is a decrease, there are several faults and depressions. Dogger Bank crosses the seabed in east direction. The depth above it will decrease to 13 meters. Experts believe that it is a remnant of glacial moraines that reached East Anglia and Northern Germany. Off the coast of Britain there is a second large bank - Goodmin Sand.
Above the sea surface, average annual temperature fluctuations are insignificant - within 8-9 degrees.
In winter, the number of storms increases.
Irish sea

This sea is also considered part of the Atlantic Ocean. Relatively shallow average fluctuates around 50 m, and the deepest point reaches 175 m. The bottom topography is quite uniform. The boundaries of the sea lie mainly along the coasts of Ireland and Great Britain. The sea brings warm waters of the North Atlantic Current to the shores of the British Isles.
The Irish Sea dates back 1.6 million years of existence.
There are several islands in the Irish Sea. The Isle of Man, one of the largest, belongs to British crown. Moreover, it has an independent form of self-government, but questions foreign policy supervised by Great Britain. The second of the islands, Anglesey, also belongs to Great Britain. The shores of the island are broken by bays and shallow bays.
Due to westerly winds, the number of storms increases in winter. The Irish Sea is rich in fish, and several large ports have been built on its shores. The most famous of them is Liverpool, which belongs to the United Kingdom.
The seas and Atlantic Ocean surrounding England create a temperate and humid climate.
The national flag of Great Britain.
Great Britain ( Great Britain, United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland) - a state in Western Europe; consists of four historical areas: England (39 counties and 7 metropolitan counties), Wales (8 counties), Scotland (9 districts) and Northern Ireland (26 counties). A special regime has been established for the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands. Great Britain heads the Commonwealth of Nations (called the British Commonwealth of Nations until 1947), created in 1931. Great Britain is a constitutional monarchy. The head of state (and also the head of the Commonwealth) is Queen Elizabeth II. Legislative power in the country belongs to the monarch (purely formally) and parliament, consisting of the House of Commons and the House of Lords; actual power is concentrated in the hands of the government, headed by the prime minister. Two parties are actually fighting for power - Conservatives and Labor.
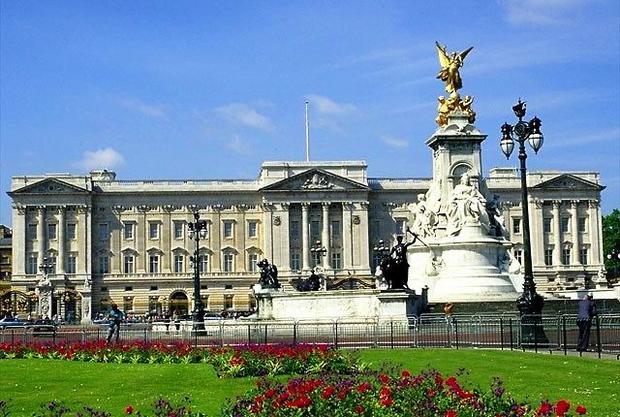

London. Buckingham Palace is the main residence of British monarchs; was built according to the design of the architect John Nash. First half of the 19th century. The first monarch to live in the palace was Queen Victoria.
The population of Great Britain is 60.7 million people, predominantly English (80%), as well as Scots, Welsh (indigenous residents of Wales), and Irish. The stability and prosperity of the country attract numerous immigrants from different parts Sveta. In the majority major cities there are neighborhoods inhabited by Indians and Pakistanis, Chinese, people from Arab countries. Most of population is concentrated in the most industrialized southern and central regions of England, where Largest cities- London (agglomeration called Greater London), Portsmouth, Southampton, Birmingham, Liverpool, Manchester, Leeds, Sheffield. The UK is one of the highly urbanized countries. Most English people belong to the Anglican Established Church (one of the largest branches of Protestant Christianity), and there are also many Catholics and Methodists in Wales.

Queen of Great Britain Elizabeth II Windsor.
Geography
Great Britain is located in the north-west of Europe, on the British Isles (the island of Great Britain is the largest, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Channel Islands, numerous small ones: the Hebrides, Shetland, Orkney, etc.). Great Britain is washed by the Atlantic Ocean, the North and Irish seas, the English Channel (locally called the English Channel), Pas-de-Calais, North and St. George. Coastline strongly dissected by numerous bays (fjords in the north and river estuaries in the south), forms large peninsulas Wales and Cornwall.
Parts of the country differ significantly in topography and climate. Predominant in the north and west mountainous terrain- North Scottish Highlands (the highest peak in Great Britain is Ben Nevis, its height is 1343 m), South Scottish Highlands, Pennine and Cambrian mountains. These mountain systems have plateau-like peaks and gentle slopes covered with vegetation. The eastern and southern parts of the country are occupied by hilly plains framed by rocky ridges (cuestas). The mountains are dominated by peat bogs, heathland and meadows used for pasture. Forests consisting of oak, beech and birch occupy about 8% of the country's territory.
In Great Britain - big number rivers, many of which are navigable and connected by canals. Among largest rivers- Thames, Severn, Trent. The north of the country is replete with lakes, the largest being Lough Neagh in Northern Ireland, Loch Ness and Loch Lomond in Scotland. Near the north-western spurs of the Pennines lies the vast Lake District. Great Britain, especially Scotland, is called the land of fog and rain.
Island position and warm Atlantic current The Gulf Stream determines the climate of Great Britain: mild and humid, oceanic. Negative temperatures are rare even in winter. The wettest cities are Liverpool and Manchester; it rains here 220–230 days a year. In London rainy days also a lot - 180 a year, but this does not mean that it rains from morning to evening. In spring and summer, the weather is changeable, and rain clouds quickly give way to sparkling sunshine.
In the mountains, especially in the north - in Scotland - frosts are common in winter, and snow on many slopes lies from November to April-May. On the peaks and slopes of mountains facing the sea, in many places along the coast, the cold is aggravated by constant winds. Scotland would lose some of its flavor without the cloudy low skies and biting winds.
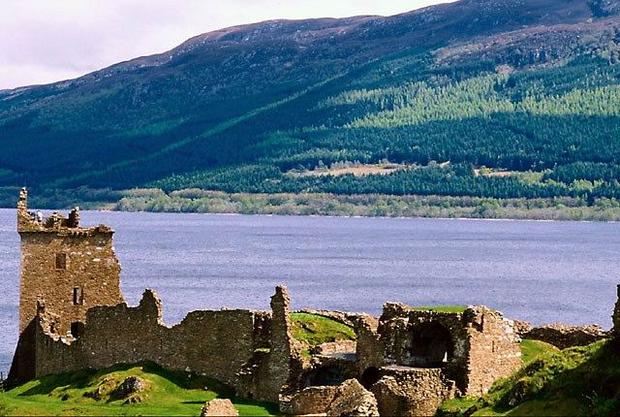

Scotland. Loch Ness.
Loch Ness in Scotland is famous primarily as the abode of Nessie - a semi-mythical monster (either a descendant of dinosaurs, or even a fabulous beast), which, according to legend, lives in the depths of the lake, sometimes appearing on the surface.
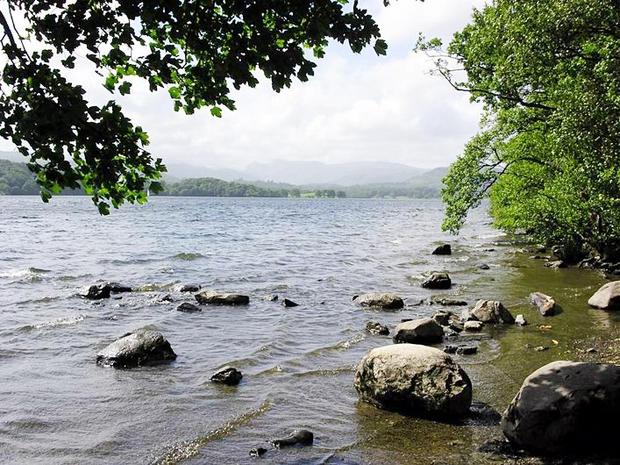

Great Britain. Lake District. Lake Windermere.
Lovers of lakes and water recreation should visit the Lake District (Lancashire and Cumbria), where England's largest national park is located. The steep coastal cliffs of the Hebrides Islands, cut by fjords, are attractive, the most beautiful of them is the island of Iona. The Orkney Islands are well worth a visit, including the bird sanctuary on the "bird island" of Bass Rock.
Lovers mountain tourism, skiing and rock climbing will be attracted by the mountains of Scotland: the Ilond Hills (a favorite place for walks of Walter Scott), the Cairngorms, the Pennines, especially the Peak District at their southern tip on the border of England and Wales.
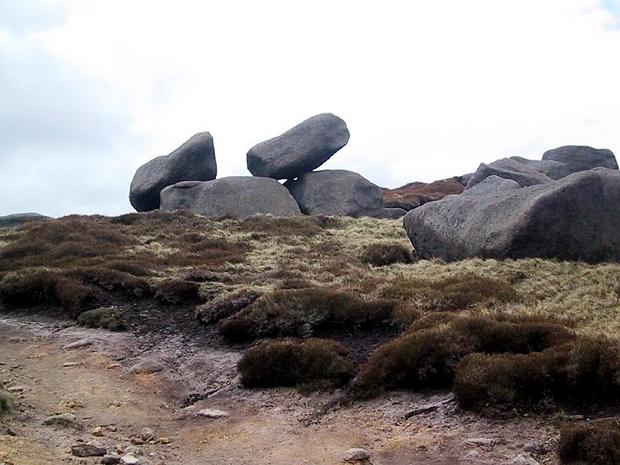

The mountains and coasts of Wales are extremely beautiful - especially in its northern part, where the most high mountain England and Wales - Snowdon (1085 m), the surrounding Snowdonia National Park is overflowing with numerous mountain streams, waterfalls, and wooded valleys. In southwest Wales there are sulfur, salt and other mineral springs.

Fans of paleontology will undoubtedly be interested in seeing the Devonian limestone deposits, where ancient fossil organisms have been found. Thanks to the discoveries made in its depths, an entire geological era began to be named after this county!
Story
The British Isles have been inhabited since antiquity. Tin has been mined here since prehistoric times; the Phoenicians and Greeks called them the Tin Islands. Archaeological excavations parking lots discovered ancient man Paleolithic (40,000–10,000 BC) in Wales and Derbyshire, Neolithic monuments (3400–1600 BC) in barrows on the chalk hills of southern and eastern England, in South Wales, Gloucestershire, Norfolk and many other places, remains of settlements , defensive structures of the Bronze and Iron Ages (up to 450 BC) throughout the country. The most amazing and famous monument is Stonehenge.
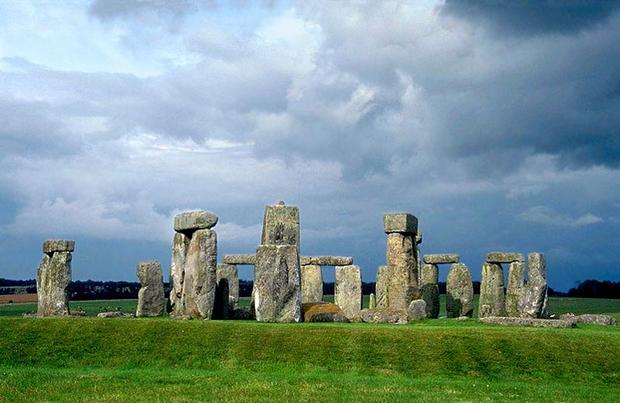

Salisbury. Cromlech. Stonehenge.
The builders of Stonehenge did not leave their name to their descendants. We know the name of their successors - the Celts. The Celts came here in the second half of the 1st millennium BC. e. We know about them mainly from the descriptions of Julius Caesar, who conquered Britain. The Romans established themselves here very precariously, and there were frequent uprisings. However, it was the Romans who founded many cities, including the capital - London, then Londinium. The Romans failed to conquer all the islands (and they didn’t need relatively cold northern lands). To keep out the barbarians from the north, they built a series of fortifications, the most famous of which survives is Hadrian's Wall, separating England from Scotland (built by Emperor Hadrian in 122–130). The city gates in Lincoln, the gates in Colchester, the baths in Bath, and numerous ruins of Roman military fortifications have survived to this day.

Great Britain. Andrianov Val.
The Romans brought Christianity to the Celts and merged with local population. After the collapse of the Roman Empire, the Celts arose their own kingdoms. One of the kings, Arthur from the Pendragon dynasty, became famous not so much as a real historical figure, but as a hero of later legends. Until now, researchers are looking for historical truth in the legends of the Arthurian cycle. Associated with Arthur memorable places in Cornwall, his supposed grave (looted in the Middle Ages) is at Glastonbury. The Celts succumbed in the 6th century. to the conquerors the Angles and Saxons - the peoples of the Germanic group. The Anglo-Saxons (in the north of the country they were also joined by the Jutes) were soon baptized. And not from the Celts, but from Augustine sent from Rome. Augustine became the first Archbishop of Canterbury and under him the construction of the main cathedral began. And to this day the Archbishop of Canterbury is the primate of the Anglican Church.
The Aglo-Saxons founded several kingdoms, sometimes uniting with each other, sometimes at war. Their boundaries generally coincide with the boundaries of the historical counties. Aglo-Saxon is the basis of modern English. Among the Saxon legends is the legend of King Lear, later used by Shakespeare. The epic Beowulf has also been preserved from the Saxons. In Scotland, Ireland, Wales and partly in Cornwall, Celtic populations remained.
For a long time, the Angos-Saxons paid tribute to the Vikings - “Danish money”. King Alfred the Great (c. 849-900) unified the country and stopped paying tribute. However, after his death, King Canute I the Mighty united England with the countries of Scandinavia. Close relations with the Vikings persisted later. After the death of the childless King Edward the Confessor (1066), three claimants claimed the right to the throne: from the Anglo-Saxons - Harold, from the Vikings from Norway - also Harold (who, by the way, was married to one of the daughters of Yaroslav the Wise), from Normandy - William. William's troops, having crossed the English Channel, fought with the Anglo-Saxons and England began to be ruled by the Plantagenet dynasty. These kings spoke French and English language a lot penetrated French words. Even the famous Richard Lion Heart didn't speak English.
English literary language born at the end of the 14th century with the publication of The Canterbury Tales by J. Chaucer. At this time the country was experiencing Hundred Years' War, in which success was largely on the side of England, but ultimately it lost, losing its continental possessions. The Plantegenet dynasty was replaced by the Tudors as a result of the Wars of the Roses. In the same war, almost the entire old nobility was killed; the new gentry nobles became the support of the new dynasty. To the board Henry VIII(1491-1547) two great things began that had a huge impact on the history of the country: the enclosures that drove the peasants off the land and the Reformation, the formation of the Anglican Church. Henry's daughter Elizabeth I (1533-1603) with her wise and cautious policy made England great power. She Special attention devoted to the development of the fleet and sent her people to found colonies.
Her reign is a golden age English culture, whose decoration was the work of Shakespeare. Elizabeth was childless and left the throne to her relative James Stuart, the son of Mary Stuart, Queen of Scots. Elizabeth executed Mary, accusing her of attempting to assassinate herself, and thereby created a precedent for regicide in Europe. The reign of the Stuarts united England and Scotland. James (James) I's son, King Charles I, was executed during the Revolution in 1649. England was a republic for almost two decades. Here religious strife broke out between different branches of Protestantism. Despite their slight difference in faith, the Puritans and Independents destroyed each other, and many others along the way. With the restoration of the monarchy (Charles II, on the throne since 1660), religious disputes were stopped and many customs that the Puritans had prohibited were restored. Hence the British love for the holiday of Christmas, which was banned during the revolution.
The Stuart dynasty was not particularly popular and was replaced by another, the Hanoverian. Already in the 18th century in England began Industrial Revolution. The first steam engine, J. Watt, was created here, and the world's first spinning machines and weaving machines appeared. Although the discovery of porcelain was made in England even later than in Russia, England became the birthplace of the original "stone masses", varieties of ceramics, the center of production of which was and remains the historical county of Staffordshire. In the 18th century Britain lost its colonies in North America, which split off to form the United States (but Canada remained), but began to populate Australia and conquer India. During the reign of Queen Victoria (1819-1901), the country became Great Britain, creating an empire on which the sun never set. Victorian age became a period of prosperity for English culture. And the names of cultural figures are not so striking with their greatness or deep psychologism, but with their inimitable ability to captivate the reader with a plot, create surprisingly believable images of heroes, scare, make them laugh and warm them with descriptions of home comfort.
The Victorians are Charles Dickens, William Thackeray, Arthur Conan Doyle. Under Queen Victoria, the basic rule of British state life: The queen reigns, but does not rule. There is no constitution in the country, but its role is played by a whole set of laws, starting with the famous “Habeas Corpus” and the “Bill of Rights”. The leading role belongs to the parliament; the party that wins the parliamentary elections forms its own government headed by the prime minister. During the reign of Queen Victoria, Whigs (liberals) and Tories (conservatives) fought for power. At the beginning of the 20th century, a new political force- Labor (Workers) Party. Under the influence of impressions from October revolution 1917, changes were made to legislation in order to improve the situation of workers and employees. If the London “bottom” of the 19th century. was considered a gathering place for criminals and beggars, then from the beginning of the 20th century. it is gradually being put in order.
Two world wars contributed to the collapse colonial system. After experiencing a period of stagnation (especially in the 1950s), the UK became a founding member of the European Coal and Steel Union, from which the European Union has now grown.
Architecture and landmarks
English architectural styles are distinctive. The Romanesque style of the Anglo-Saxons, which dominated architecture until the mid-11th century, was distinguished by the simplicity of architectural and construction techniques: simple semicircular arches, gable roofs, borrowed from the usual wooden architecture. The Norman Romanesque style that replaced it lasted until the end of the 12th century. It was distinguished by an abundance of identical powerful columns, round decorated window openings and ceiling vaults, narrow windows, and not very powerful buttresses.
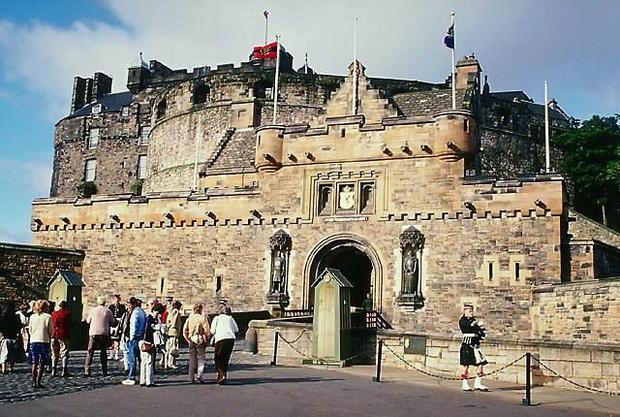

Edinburgh. Lock.
Outstanding Norman castle buildings are Hedingham in Essex and Conisbrough in Yorkshire. Part of the buildings of Edinburgh Castle in Scotland is made in the same style. Early Gothic is typical for buildings of the 13th century, their general form is determined by its significant height and vastness, long windows reaching the base of the building (the facade of Lincoln Cathedral, fragments of the cathedrals in Ely and Peterborough).
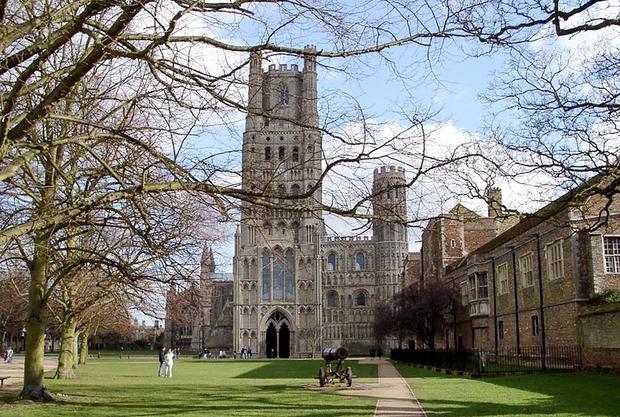

Or. Gothic cathedral. 14th century
In the 14th century, English Gothic, otherwise called decorative, replaced the early Gothic - in such architecture a characteristic emphasis was placed on individual elements ornaments: huge lancet windows with complex openwork stone carvings, heavy buttresses, pillars with tightly connected ribs, sculptures entwined with leaves, cornices, floral ornaments. This style is best represented by the cathedrals of York, Norwich and Lincoln, and individual elements of Westminster Abbey.
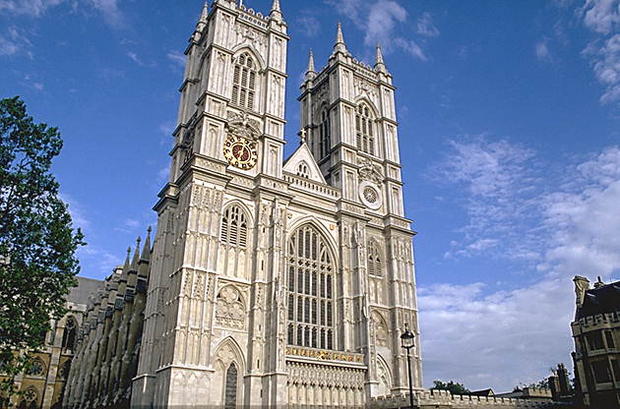

London. Westminster Abbey. Gothic church 1245-1745, chapel of Henry VII - 1503-1519. The site of the coronation of English kings since William the Conqueror. Since the 13th century, Westminster Abbey has housed the tomb of English kings (the last of them was George II, 1760; since then burials have been made in Windsor Castle), statesmen, famous people. Legends attribute the founding of the abbey to the Saxon king Sibert (7th century), the first Christian Saxon.
The richest ornamentation reached perfection in the building art of the late Gothic, or "perpendicular" style (late 14th century - 15th century), characterized by a special predilection for vertical planes (King's College in Cambridge, St. George's Chapel in Windsor Castle and Henry VII's Chapel in Westminster Abbey ). In the 16th and early 18th centuries, Renaissance and Baroque styles dominated Britain, and their elements were often mixed in the same building. The most important monument style called "English Baroque" is Cathedral St. Paul's in London, built in the last third of the 17th century according to the design of Sir Christopher Wren, one of the largest English architects. In appearance This building contains spatial scope, unity, and fluidity of complex curvilinear forms.
In the 19th century, the monumental Georgian style was replaced by Victorian. One of the world's most famous buildings, Buckingham Palace, was built in this style. Having withstood the trials of fate (September 9, 1940 german bomb fell on the palace, three days later it was attacked again), it appears before us in all its grandeur and beauty. Later styles - from proto-Byzantine (Westminster Cathedral in London) to Art Nouveau and Constructivism did not change the prevailing architectural appearance most cities in Great Britain, although they have added a sometimes irresistible charm to their urban development. New
National characteristics
The British people's commitment to tradition is manifested not only in politics, but literally at every step, in everything everyday life: the British adhere to their system of weights and measures (in a pub - an English beer bar - you will always be served a pint of beer, not half a liter), left-hand traffic(when crossing the street, look right, then left). Of course, many purely “nutritious traditions” remained only in wonderful novels and films based on them. Bacon and eggs breakfast is not as popular due to non-compliance with the rules " healthy eating”, puddings and meat pies survive only in a few “points” with local cuisine. Many are even sounding the alarm about the onset of varied continental (French, Mediterranean) cuisine and inexpensive catering establishments with Indian, Chinese, Thai and other Asian cuisine.
Tea with milk has long been the national drink of the British, their indispensable everyday “five o’clock tea” - “five o’clock” - is not just a strictly established meal time, but, above all, a reason for communicating with relatives, friends, and colleagues. This famous English tradition has spread to Europe and the USA. Nowadays, tribute to tradition is not just decoration. If near Edinburgh Castle you see a guard in an operetta-like Scottish skirt, in the eyes of a modern European, then the carbine in his hands, you can rest assured, is not a toy at all. And the Scots Guardsman himself is not an actor hired to entertain tourists, but a member of the guard company military service the young man is necessarily from the ancient Gordon family, who has long been granted the privilege of guarding the castle of the kings of Scotland. Old-fashioned cabs and omnibuses on the streets of London are just as functional, and clerks rushing to the City of London in the morning carry all the folders with papers in their arms.
National cuisine
Real British cuisine is different either high quality and high cost, or, if you are content with simple food, it is inexpensive and is included in the menu of any of the cafes found at every step. The pubs will offer many of the best beers and high-quality inexpensive food, and most importantly the opportunity to socialize, relax and feel the breath of English traditions.
Wine bars are popular - something between a pub and a restaurant. In all major hotels, it is customary to serve “Afternoon tea” (five-o "clock tea), accompanied by a special ritual. If desired, a guest of London can perform a real culinary " trip around the world" The menu of the city's 14,000 restaurants most often includes Indian cuisine; Chinese restaurants are also famous; continental African and Middle Eastern cuisine is offered. In sandwich cafes and bars you will be offered an “English breakfast”, which usually consists of a huge sandwich, a light snack, tea or cappuccino coffee. Such cafes operate from early morning before noon.
Chippie (open from 11.00 to 23.00) serves hearty and mouth-watering dishes: fish and potatoes fried in boiling oil, grilled chicken, sausages and pies. The best chippie, according to Londoners, is the Upper Street Free Shop on the street of the same name. The brasserie has an excellent selection of drinks and a variety of light snacks. The most visited in London are Soho Brasserie on Old Compton Street, La Brasserie on Brampton Road, L'Oreil on Sloan Square. As for restaurants, the best roast beef in London can be enjoyed at Simpson-in-the-Strand, the best dishes of English cuisine - at the Ritz Hotel they are famous for their roast beef, English leg of lamb, English pork pies, English trifle (pastries).
The shops
It's hard not to get shopping fever in London. The latest designs from the world's best couturiers can be found in the shops at Knightsbridge and Brompton Cross, Bond Street and Sloane Street. Trendsetters are concentrated around Beauchamp Place, and decent clothes can be bought at reasonable prices in the shops on Oxford Street. Avant-garde and exotic clothing is sold on King's Road, as well as at Kensington Market on High Kensington Street. During seasonal sales (Sales) in late January - early February and late June - early July, prices drop quite significantly.
In Covent Garden, which is full of shops with outlandish goods, you will certainly find something exotic, for which it is sometimes difficult to find a name. There you will also meet street actors, fakirs, and sword swallowers. One of the oldest covered markets in London is located in this same square. Shops are usually open from 9-10 am to 5-6 pm, some are open until late.
All goods sold in UK stores are subject to Value Added Tax of 17.5%, which is usually included in the price of the goods. If the purchase price exceeds £100, then when crossing the border within three months of purchase, you can claim a VAT refund of 11% of the price of the goods (for tourists from non-EU countries). In the store, when purchasing, you must ask for a certificate.
CurrencyThe country's currency is the pound sterling (GBP). The UK is part of the European Union, but not the euro area. One pound is equal to 100 pence. In addition to the Bank of England, five other banks issue pounds sterling in the UK: the Bank of Scotland, three Northern Irish banks and a bank on the island of Jersey. Each of them issues its own banknotes. A tourist may be given a non-convertible Scottish pound instead of an English pound. The Northern Irish pound can only be exchanged in the British Isles. Travelers are less likely to encounter the Jersey pound, but there are scammers who specialize in slipping such local pounds to foreigners.
Holidays
The country's national holiday is the birthday of the reigning Queen Elizabeth II. In fact, she was born on April 21st. On this day she is congratulated in the press. The official celebration is moved to the second Saturday of June. Christmas is celebrated on December 25th, New Year December 31 - January 1. At this time, the country is on Christmas holidays, which applies to most enterprises and institutions. December 26 (Boxing Day) is also a day off. Easter is a moving spring holiday. The day off is Good Friday on the eve of Easter. In Wales, the day off is St. David's Day (patron saint of the Welsh) - March 1st. In Scotland, November 30 is celebrated as St. Andrew's Day, the country's patron saint (shared with Russia). March 17 is the Day of St. Patrick, the Enlightenment of Ireland. In England, St. George's Day is celebrated (April 23). May 1 is an official holiday; since the 20th century it has been celebrated as Labor Day, but in fact it is one of the oldest pan-European holidays of the arrival of spring. October 31 is Halloween - the eve of All Saints' Day. On this day, children dress up as witches and various small evil spirits and ask for sweets and inexpensive gifts. November 5th is Guy Fawkes Day. This is not a hero, but a participant in the so-called Gunpowder Plot in 1605, when Catholics tried to blow up Parliament, where the king was supposed to speak. Since then, the effigy of Guy Fawkes has been ceremonially burned late in the evening.








