Countries, like a person living at a specific address, also occupy a specific place on the planet. And every person has his own neighbors - rich and poor, friendly or envious; and from each window there is a different view, picturesque or not so picturesque. The same analogies can be used to characterize any country in the world.
The current geographical position of Russia - what is it like? And how profitable is it? We will try to assess the economic and geographical position of Russia in this article.
GP - what is it?
One of the most important concepts geographical science is the concept of the geographical location of a country or territory. Geographical location(abbreviated as GP) is a position geographical area(or object) relative to other objects and territories. At the same time, in physical geography it is defined on the one hand (the emphasis is on the natural features of the country), but economic geographers characterize it from their side, taking into account socio-economic aspects.
By by and large, geography is precisely the science that determines and evaluates the location of certain objects in space. This makes her different from everyone else scientific disciplines. After all, determining the geographical location, as it turned out, not only provides information about the specific location of an object, but also explains its individual features. In addition, the assessment of GP even makes it possible to predict the development of the territory in the future.
Historians of geography believe that the very concept of “geographical location” appeared around late XVIII century. But the first serious work that reveals this concept can be considered the book by L. Guicciardini entitled “Description of the Netherlands” (1567). In it, the Italian author evaluates the role of the sea in the development of the country, which can be considered the first attempt to analyze the geographical location of the territory.
What is the economic-geographical position of a country (EGP)?
One of the types of GP is the economic-geographical position of the country (abbreviated as EGP).
Economic-geographical position is understood as the position of a country or territory in relation to those external objects that have an impact on the development of the economy of a particular state. These objects can be of both natural and anthropogenic origin. These can also be other countries or their unions.
Geographers identify the following components (aspects) of the territory’s EGP:
- transport and geographical location;
- geopolitical;
- agricultural;
- market;
- demographic;
- recreational and tourist, etc.
There are also several types of economic and geographical location. So, EGP of the country or territory may be:
- central;
- peripheral;
- isolated;
- borderline;
- seaside;
- or transit.
Geographical position of Russia - what is it? And what are its strengths and weaknesses? This will be discussed further.
Economic and geographical position of Russia, its brief characteristics
The Russian Federation is the largest state in the world today in terms of area (the country occupies about 17 million square kilometers of land). Therefore, the geographical position of Russia is very advantageous and is distinguished by its versatility.
Russia is located on the Eurasian continent. Moreover, a third of it is located in Europe, and most- in Asia. Extreme western point The country is located on the coast of the Baltic Sea, but the easternmost one is on the Bering Sea, near the border with the United States. Thus, the territory of the state is very elongated from west to east and is divided into ten time zones.
Total length Russian border- 60 thousand kilometers, of which 2/3 are sea borders. This aspect turns our country into one of the most powerful sea powers planets. The territory of Russia is washed by the waters of three oceans of the Earth. Sea corridors connect the Russian Federation with such the most important countries world like China, Japan, USA and Germany.
On land, Russia borders 14 independent states peace. These are Norway, Finland, Estonia, Lithuania, Latvia, Poland, Belarus, Ukraine, Georgia, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, China, North Korea and Mongolia.
Assessment of Russian EGP
In order to assess the EGP of our country, it is necessary to determine its position in relation to external economic centers, raw material bases and transport corridors. This is precisely what the science of geography does.
The geographical location of Russia largely determines economic level its development. It is assessed, as a rule, at three different levels. This:
- macro level ( global level assessments) - evaluates the position of the state in relation to continents and oceans, the main transport corridors, as well as the leading centers of the world economy;
- meso level - determines the position of the state in relation to historical and geographical regions;
- micro level - assesses the position of the country relative to its immediate neighbors (in in this case These are the 14 states that border the Russian Federation).
An assessment of a country's EGP is usually expressed in the form of a list of its strengths and weaknesses. It is worth noting that the geographical location European Russia will be somewhat different than the situation of its Asian part. This is due to huge territory state and its elongation in the sublatitudinal direction.
EGP of Russia: strengths and weaknesses
The peculiarities of Russia's geographical location are best characterized in terms of its strengths and weaknesses.
So, the positive aspects of Russian EGP include:
- huge area of territory;
- diversity natural conditions and resources;
- variety of relief forms;
- free access to the World Ocean;
- rich forest resources;
- a large number of neighboring countries;
- the presence of large navigable rivers.

To the most important negative aspects The EGP of Russia includes the following facts:
- huge area;
- about 25% of the territory lies beyond the Polar climate, where a very harsh climate is observed;
- large number Russian seas and the rivers freeze on long period year, which makes navigation very difficult;
- The territory is too elongated from west to east.
It should be noted that the large territory of the country is included in the list of both strengths and weaknesses of the EGP. Indeed, on the one hand, the vast territory offers a wide range of natural conditions and resources, which opens up great prospects for industrial development. On the other hand, too large spaces are very difficult to manage. In addition, it is almost impossible to create a complete and high-quality system transport infrastructure in such territory.

Natural resource potential
The relief of the territory of Russia is very diverse. About 70% of its expanses are occupied by plains, but there are also high mountain ranges - the Caucasus, Altai, Sayan Mountains, Sikhote-Alin, Byrranga Mountains and others. Kamchatka is famous for its numerous volcanoes, among which Klyuchevskaya Sopka is the highest volcano on the mainland. There are even deserts in Russia. In particular, the Tsimlyansk Sands, with an area of 1000 square kilometers, is the largest desert in Russia.
The geographical location of the country is largely determined by its climate. Climatic features Russia is the most diverse, the country's territory lies in four climatic zones. However, most of it is located in temperate zone, which is characterized by the most favorable conditions for human life and economic activity.
Russia is extremely rich in water, mineral and forest resources. The country has the world's largest reserves fresh water. From minerals global significance has oil, natural gas, coal and non-ferrous metal ores.

The country has enormous forest reserves. However, the geographical location of Russian forests is distinguished by such features that hinder the development of the country's forestry industry. The fact is that most of Russia’s forest resources are located in regions that are difficult to access (in terms of transport), which greatly complicates the process of their development.
Transport and geographical position of Russia
The economic development of any territory largely depends on its transport and geographical location. It is very beneficial for Russia, although after the collapse of the USSR, the country’s external transport links have become much narrower. On at the moment The northern basin is the most promising for the development of maritime transport links in Russia. Although this has its own problems and difficulties, primarily related to the fact that most of the waters of the northern seas freeze for a long period of the year.

The possibility of fully using the railways remains limited. Today, the country's railway network requires complete reorganization and modernization.
Geopolitical situation
Russia borders on 14 countries of the world. At the same time, the lack of proper border demarcation with many of the neighboring countries remains a very serious problem.
The geopolitical position of a state is determined by the nature of its relationships with its immediate neighbors. Unfortunately, Russia does not have good neighborly relations with all neighboring countries. Thus, a number of countries (officially or unofficially) have territorial claims to Russia. These are Japan, Latvia, Estonia, and Finland. Russia's relations with countries such as Georgia and Ukraine have become no less tense.
In general, experts note that Russia’s geopolitical environment has noticeably worsened over the past five years.
Economic zoning
The territory of the Russian Federation is divided into 12 economic regions (they should not be confused with federal districts):
- Central.
- Central Black Earth.
- East Siberian.
- Far Eastern.
- Northern.
- North Caucasian.
- Northwestern.
- Povolzhsky.
- Ural.
- Volgo-Vyatsky.
- West Siberian.
- Kaliningrad.
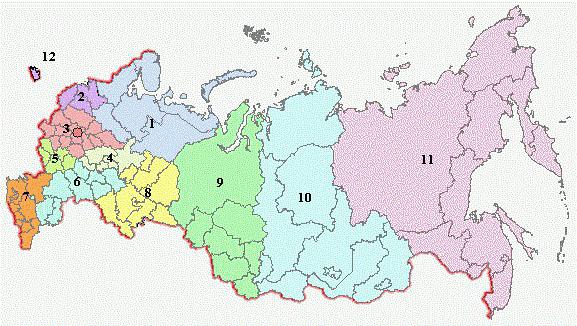
Geographical location of Central Russia
This area is the most densely populated in the country. About 30 million inhabitants live here. In addition, the most developed industry is typical for Central region Russia. The geographical position of this economic region is very favorable and has several features.
Central economic region located at the intersection of the most important transport arteries(land and water). This is where river system Volga - the river that has always played important role in the life of Russia. Even despite the absence of significant mineral deposits in the region, several sectors of the national economy are successfully developing here: mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, chemical industry, construction industry and agro-industrial complex. And it is precisely the convenient and advantageous geographical location Central Russia became the basis for rapid economic development this region.
Conclusion
Thus, the geographical position of Russia is distinguished by both its strengths and weaknesses. RF - huge country, which has extensive access to the World Ocean. The presence of the richest natural resource potential, as well as the possibility of cooperation with many countries of the world, opens up wide opportunities for Russia for its own successful economic development.
The concept of "territory". Geographical location: concept, types, properties. Territory of the country and its parameters.
Coastal areas.
Territory and geographical location are the supporting elements of complex regional and regional studies characteristics that have universal significance for them. In encyclopedic dictionaries and, accordingly, in the literature, territory is defined as a part of the earth's land surface with its inherent natural, as well as those created as a result human activity(i.e. anthropogenic) properties and resources.
Very often the concept of “territory” is used as a synonym for the concept of “space”. Without going into the subtleties of the philosophical and geographical interpretation of the latter, we nevertheless note the differences between them. Geographic space is three-dimensional, but territory, from the point of view of geometry, is two-dimensional. The territory is distinguished by its specificity and attachment to certain coordinates.
The territory is considered as special kind resources. It brings together all types natural resources, population, production capacity, cultural and intellectual potential. The territory turns out to be more important than resources natural substances (mineral, aqueous, plant, etc.). The latter, one way or another, can be replaced by natural or artificial resources, and the territory is an exhaustible and non-renewable resource, it is almost impossible and extremely expensive to increase it technical means. It is no coincidence that Academician A.A. Mintz characterized the territory as a summing, generalizing resource.
In concept "territorial resources"(and it is more capacious and more complex than the concept “ land resources") usually include three elements: area, richness, sustainability of landscapes.
Territory area- it's clean physical quantity, which must be assessed objectively. The territory of Yakutia is equal in area to almost six France, but settling 360 million people on it (the population of France is 59.5 million) would be an obvious utopia.
Wealth(territory resources) is an element that requires economic approach, comprehensive assessment all types of resources.
Landscape sustainability- this is the natural base of the territory, ability landscape to maintain its structure and ability to function in space and time under changing conditions environment. “Easily injured” landscapes of tundra and forest-tundra react painfully even to minor human impacts (for example, to a trench dug for a pipeline). Ignoring this feature of the northern territories can lead to irreversible changes in the landscape and its loss of stability.
Territorial resources are unevenly distributed both between parts of the world and between countries.
Table 1
Security territorial resources parts of the world
The size of a territory, together with the wealth of material resources, determines its economic capacity, and, taking into account sustainability, its environmental capacity (that is, the limit of possible development of a particular landscape). For the first time, the capacity of a territory, based on its natural properties, was calculated by G. Taylor: in 1918, he determined the maximum capacity of Australia - 30 million people (so the limit of the capacity of this continent-state, according to Taylor, is still far from being reached: the population of Australia is now – 19.7 million people). Currently, attempts are being made to calculate the ecological capacity of the entire biosphere of the Earth from the point of view of the possible limits of its development.
The territory, being a summing, generalizing resource, is assessed on the basis of three blocks of phenomena: the natural resource potential of the landscape (mineral, water, agroclimatic, soil and biotic); ethno-demographic potential (national, labor, settlement and social); potential economic development territory (production, accommodation and infrastructure).
Territory, due to belonging to a certain natural complex, has a number physical properties, type (or types) natural landscape(the nature of the relief, soils, vegetation, etc.), features of the geographical location.
Geographical location(GP) is characterized by the relationship of an object with its external environment. At the core this concept lies the category “relation” - the position of an object relative to the surface of the Earth, as well as to other objects with which it is in interaction. It is the geographical location that specifically reveals personality traits and properties of any territory.
“Geographical location has the greatest methodological significance. The place occupied by any area, be it a country, region, city, etc., in the system of geographical division of labor is largely determined by geographical location,” wrote N.N. Baransky. A N.V. Gogol emphasized: “first of all, you need to take a look at the geographical location... which must certainly precede everything...”.
Geographic location is different from location. The first contains the answer to the question: in relation to what? The second involves the questions: where and what is it part of? That is, location reveals localization or affiliation, while position reflects attitude.
The geographical position of countries, regions (“internal”, world) is the relationship to any other objects taken outside their territory, with which countries and regions interact and which influence their development. The latter is determined by various types of geographical location.
In physiographic position is the relationship a) in a geographic coordinate grid, i.e. in degrees of latitude and longitude, giving the most accurate address of the object (country, region); b) in real physical-geographical space - with its natural areas, orography, distribution of land and sea, etc. That is, a physical-geographical location is a position relative to natural objects that influence the characteristics of nature this place, – seas, rivers, forests, natural areas, etc.
IN economic-geographical position(EGP) is an attitude towards economically significant objects, various data of a socio-economic nature. At the same time, the category of economic-geographical location also includes the position relative to natural objects (ice-free seas, mineral deposits, forests, etc.). Since the economically significant objects in relation to which the economic-geographical position of the territory is determined are diverse, they, in turn, are divided into a number of “positions”: transport-, energy-, resource-, industrial-geographical, etc.
EGP is one of the most important factors determining the location, nature, and dynamics of development of productive forces.
IN political-geographical location it is an attitude towards political givens. Within countries, it can, for example, be determined by the territorial distribution political forces, on the world stage - centers of international political forces (world, regional powers, international unions etc.). The position of some territory (world region, country, internal region) relative to the centers and countries of concentration military power, military hotbeds, hotbeds of tension are usually called military-geographical position.
Closely related to the political-geographical, military-political, economic-geographical types of geographical location geopolitical situation.
According to Ya.G. Mashbitsu, geopolitical situation reflects the position of the territory relative to “centers of power,” centers of economic and military power, various political, economic and military blocs, political and religious associations.”
The geopolitical position of many regions and countries is quite stable due, first of all, to the deep essence of its geographical roots. After all, in the very general view geopolitics studies geographical conditionality political processes. But, nevertheless, it is also subject to dynamic changes. In 1985, Chile received its own access to the Atlantic Ocean as a result of the transfer to the country of three islands in Beagle Bay. Thus, the geopolitical position of Chile has changed significantly in better side, because its capabilities have expanded foreign economic relations, strategic positions have changed. The latter is due to the fact that currently the importance of South Atlantic due to geologists' forecasts about the presence of the largest underwater oil deposits here.
IN ecological-geographical position essential is the attitude towards environmentally significant objects, towards countries and regions that determine environmental situation, or to countries and regions, on ecological state which this territory may influence.
GP has always been and remains important factor for the development of regions and countries. The uniqueness of Russia, among other things, lies in the fact that it is the northernmost of all large states world: after the collapse of the USSR, the northern territories began to occupy almost 2/3 of its territory. The “northern” geographical location of Russia imposes severe restrictions on the possibilities of agriculture and on the development of the territory in general. Compared to the vast majority of developed countries, Russia incurs enormous costs associated with protection from the cold. This includes increased energy costs for heating buildings, and increased volumes of construction materials, and the production of warm clothing, shoes, and construction, and maintaining the road transport network in proper condition, etc.
GP influences general lines development of macroregions of the world. GP Eastern Europe less favorable than its western part - the first is more continental, it receives more massive volumes of pollution due to Atlantic transport air masses from west to east, etc.
It is well known that the economic progress of the United States and Canada was largely determined by their interoceanic position. It facilitated their connections with the countries of the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans. The oceans, moreover, before the advent of rocket and nuclear weapons, reliably protected America from outbreaks major conflicts and world wars.
Geographical location - historical category. Ancient Rus' was an open society, in general it developed in line with European processes. Due to, first of all, historical circumstances, Muscovite Rus' found itself on the periphery European development. Portugal and Spain before the Great geographical discoveries were on the outskirts of Europe, but the exit of these countries broad front to the Atlantic turned them into powerful colonial powers. Geographical location of the USA in the 19th and early 20th centuries. after the Erie Canal was dug, the first Transcontinental Railroad was built, the Panama Canal appeared, as N.N. noted. Baransky, from a position “at the edge of the world” turned into a position “between two oceans”.
Geographical location has certain properties(attributes). As a rule, the main properties of GP are the following:
attitude. This attribute is reflected in the very definition of GP;
potentiality. This property reflects the fact that GP is both a prerequisite and a consequence of the development of all kinds of connections, as well as the development of the territory itself.
History knows many examples of how some areas are in the process of historical development turned into leaders, others lost their role. In this regard, we can recall, for example, the role of the Mediterranean in antiquity and in subsequent centuries, Kuzbass - at the beginning of the 20th century. and currently, about the change in the geographical position of many states of the world as a result of the implementation of such major international projects, such as the construction of the Suez, Panama, Kiel canals, etc.;
distance. It is impossible to meaningfully characterize GP without taking into account distances and other metric indicators. At the same time, these indicators do not fully characterize the GP: while the physical distance between objects remains unchanged, their position may change, for example, with the improvement of infrastructure, the expansion of economic and political ties. Russia is separated from Japan by only 500 km, but Japan is “closer” to the United States and countries Southeast Asia, Australia, and this “proximity” is determined not by metric distance indicators, but by the scale and strength of economic ties.
The territory with all its properties and resources, being a space for the life of the people inhabiting it, has an impact on all spheres of this life - economic, social, political, as well as spiritual and cultural.
A specific element of the Russian mentality, according to many, is will. Will is a special understanding of freedom, generated by immensity Russian spaces, the endless horizons of the Russian plain. And if the concept of “freedom” is found in all languages, then the concept of “will” is specific to the Russian language.
It is obvious that population density and limited space, for example, in Japan, to a large extent contributed to the clear regulation of all aspects of the life of Japanese society through many carefully protected traditions, rituals, and rules of politeness.
The same can generally be said about Western Europe. The practical absence of space where one could, on occasion, escape, leave, hide, forced Europeans to establish and observe fairly clear rules of behavior, and, conversely, the “open and abundant” space of Russia, in the words of the Russian philosopher I. Ilyin, taught them to do without strict regulation. Another philosopher agrees with I. Ilyin - N.A. Berdyaev, who wrote: “There is a correspondence between the immensity, boundlessness, infinity of the Russian land and the Russian soul, between physical geography and mental geography. In the soul of the Russian people there is the same immensity and boundlessness, aspiration to infinity, as in the Russian plain. Therefore, it was difficult for the Russian people to take possession of these vast spaces and formalize them. The Russian people had enormous elemental power and comparative weakness of form” (Quoted from: Shapovalov V.F. Russian Studies: training manual for universities. – M.: FAIR PRESS, 2001. – P. 105).
An interesting observation by the writer and historian I. Mozheiko. He wrote, for example, that the Egyptian pyramids are undoubtedly part of the landscape, but of this particular country. If they are erected near the mountains or in our Russian forest, they will not create the effect that the proximity of the desert gives. “The bold planes of deserts, the severity of sand and rocks give birth to laconic, monumental buildings, give birth to pyramids, the chopped-up look of Babylon,” wrote I. Mozheiko (I. Mozheiko. 7 and 37 wonders of the world. From Hellas to China. - M.: Veche, 2006. – P. 371).
Of course, in all these and other similar examples We are not talking about the direct automatic impact of the territory on people’s livelihoods. We must not forget about the opposite impact - the impact of this life activity on the territory. Nevertheless, the participation of resources and properties of the territory in all spheres of human activity is undeniable.
In comprehensive regional studies (and regional studies), the most important territorial unit is the state. Territory of the state (country) is a part of the globe that is under the sovereignty of a certain state.
IN composition of the territory of the state includes land within borders, internal and territorial waters and airspace over land and waters. The subsoil located under land and water territories is also the property of the state.
Most of the world's countries are coastal countries. For them important have coastal areas.
Coastal areas are:
Territorial waters. Within their boundaries, the state has full jurisdiction. More than 100 coastal states have territorial waters ranging from 3 to 12 miles. 22 countries after World War II declared the establishment of a 200-mile zone of territorial waters.
200-mile coastal economic zones. They are not included state territories, but coastal states have sovereign rights to explore and develop the natural resources of the seabed and subsoil of these zones. Other countries enjoy freedom of navigation and have access to surplus allowable catches.
Continental shelf. The shelf is a continental shelf, the depth of which is from 133 to 550 m. The shelf has the same geological structure, as the adjacent land. The shelf is an economic property of coastal states, but is not part of their state territories. Countries have the exclusive right to explore and exploit “their” shelf, but do not have sovereign rights to the corresponding water area.
The compromise formula for defining the outer limit of the continental shelf says it should not exceed 350 miles from the coast.
Marine economic zones and the continental shelf of some coastal countries often exceed the area of land territory and significantly increase their resource potential.
In 1988, Japan spent a large sum - 30 billion yen - to preserve the tiny uninhabited island of Okinatori (its bottom part was about to break. The loss of the island threatened Japan with a reduction in its maritime economic zone by 400 thousand km 2, which exceeds the entire Japanese land territory
The economic importance of coastal areas will increase even more in the near future, because, according to experts, the share of underwater fields in oil production may soon reach 40–50%. This circumstance explains the struggle for the Arctic continental shelf, which is unfolding before our eyes between the “Arctic countries.”
The territory of each country has its own characteristics. The latter are determined by such parameters as size, geographical location, boundaries, configuration, risk exposure natural disasters and disasters.
Let's consider the specifically named parameters.
Territory size. The size (area) of a country’s territory is one of its constant parameters. Its impact on the life of the country, its fate is obvious. The larger the country, the more diverse and richer its resources, as a rule, the wider the opportunities for creating more full set sectors of the economy. A large territory can counterbalance an unfavorable geographical position; there are more opportunities for economic maneuvers. But in countries with large areas The problem of inter-district connections is more acute, and it is more difficult to overcome the temptations of extensive development. All this is clearly demonstrated by Russia, a country that ranks first in the world in terms of territory size.
Territorial resources are unevenly distributed not only across parts of the world, but also across states.
Table 2
Provision of territorial resources of individual countries
The largest countries by area are Russia (17.1 million km2), Canada (9.9), China (9.5), USA (9.3), Brazil (7.7), India (3.2) . These 7 states account for more than 48% of the land area (excluding Antarctica).
As you can see, Russia ranks first in the world in terms of territorial resources. But in science there is a concept of the effective territory of a country, that is, that part of it that lies outside the space with extreme unsuitable conditions. These are considered to be those territories where the average annual temperature is below minus 2º C, and the altitude above sea level exceeds 2000 m. In Russia, the effective territory is only 5.51 million km 2 out of 17.1 million km 2. Russia owns 15% of all the world's lands practically untouched by human activity, 46% of the world's area of non-tropical forests. That is why our country is considered one of the few globe biosphere stabilization centers - 2/3 of the country's area has practically preserved natural biosystems.
The Vatican, Monaco, Nauru, San Marino, Tuvali, Liechtenstein, Andorra, etc. are microcountries. The first of them has an area of 44 hectares, Andorra - 465 km 2.
Geographical location. As has already been shown, GP is one of the most important parameters, individualizing the territory of a region or country. According to the figurative remark of Ya.G. Mashbitsa, “it’s like a fingerprint, unique for every person.”
Geographical location may or may not be very favorable to countries. Known, for example, special role coastal (especially oceanic) position of countries. It is typical for most countries. But 42 countries in the world do not have access to the open sea. In Asia, these are Afghanistan, Laos, Mongolia, Bhutan, Nepal, Azerbaijan, Armenia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan.
Boundaries. State border- this is a line and an imaginary vertical plane passing along it, defining the limits of the territory of a state (land, water, subsoil, airspace) and separating it from neighboring states and open sea.
The history of mankind, unfortunately, is the history of wars, and most of the latter were aimed at revising borders. Borders are the object of study in many disciplines - geographical, social, etc. Within the framework of geography, a special field has been formed scientific knowledge– limology (from Greek word"limes" - border).
According to N.S. Mironenko, reflecting the situation in the world before 1991, the distribution of state borders by parts of the world was as follows. Africa accounted for 36% of their total length, Asia - 30%, America - 23%, Europe - 11%.
There are two main stages in establishing state border– delimitation and demarcation. The latter represents the transfer to the terrain (indication by appropriate boundary markers) of the results of delimitation, i.e. agreements on general direction passing the border and plotting it on a geographical map.
When studying borders, geographers use four main theoretical approaches: historical-cartographic, classification, functional, geographical-political.
Within classification approach The division of boundaries on the following grounds is well known: morphology, natural geographical features, genesis, functions.
Based on morphology, boundaries are divided into “geometric”, “astronomical”, winding, straight, etc.
About 42% of the total length land borders in Africa - astronomical and geometric, i.e. drawn along parallels and meridians, equidistant lines, etc., without any correspondence to social and ethnic realities. Typical setting geometric boundaries serve as borders between states in the USA, between the USA and Canada - all of them are drawn, regardless of natural and historical boundaries. The border between the DPRK and the ROK runs along the 38-degree parallel.
According to natural geographical natural features– boundaries can be oro- and hydrographic, that is, tied to some natural boundaries.
By genesis, origin, history, duration of existence, boundaries are distinguished by compensatory, “imposed”, colonial, controversial, “post-war”, etc. In Africa, about 20% of land borders were drawn by the British administration, 17% by the French, as a rule, with full ignoring ethnic, economic, socio-cultural space.
By functions allocate barrier boundaries, filtering, contact reflections, regulation, separation and comparison. In principle, all boundaries perform barrier, filtering, and contact functions; the only question is their relationship. All of them reflect the characteristics of society, political system, maintain a certain economic equilibrium regime on state territory. That is, the borders are transparent for some flows (certain categories of people, goods, products, etc.) and closed for others. The borders of countries with totalitarian regimes have pronounced barrier functions (“locked borders”), dividing people according to the principle of “we” and the rest of the hostile world.
Discipline programPreparation of bachelors studying the discipline " Introduction V regional studies". This program developed in accordance with... literature: Ivanova M.V. Introduction V regional studies. Tomsk, 2008. Voskresensky A.D. Complex regional studies// Intelligence on...
1 What does the subject “introduction to regional studies” study 3
Document1. What does the subject study? introduction V regional studies" 3 2. The main directions of regional policy for... dictionary: 38 1. What the subject studies “ introduction V regional studies"Regional studies- scientific and educational direction studying regional...
Introduction V regional studies Introduction V regional studies
State exam program in comprehensive regional studies
ProgramInterdisciplinary exam General professional disciplines Introduction V regional studies New story countries of Asia and Africa... international relations. PROGRAM AND LITERATURE Section 1. Introduction V regional studies Asia-Pacific region (APR): approaches...
Geographical location
Geographical location
position of a geographical object on the Earth's surface within given system coordinates and in relation to any data located outside it that has a direct or indirect impact on this object. At specific study Geographic taxa are divided into micro-, meso- and macrogeographical positions. The first describes the geographic location of an object in a small area, where local interactions with components of the geographic environment are significant, and is used in the study of small taxa, for example. cities. The second (on a wider scale) is used when studying a large region and country, the third - on the scale of parts of the world and the Earth as a whole (for example, the macro position of Russia relative to the countries of Western Europe and East Asia). Socio-economic geography studies the geographical location for different levels spatial hierarchy and its change over time, which is directly related to at various stages socio-economic development, technical progress in the means of communication and changing priorities in world trade. That's why special attention always paid attention to the transport and geographical position, which was especially reflected in the emergence and growth of capital cities, including Moscow and St. Petersburg. No less important was and remains the geographical location in political geography, where it influenced the formation of potential and actual theaters of military operations in all historical eras.
Geography. Modern illustrated encyclopedia. - M.: Rosman. Edited by prof. A. P. Gorkina. 2006 .
See what “geographical location” is in other dictionaries:
geographical location- Characteristics of the location of the object on earth's surface relative to others geographical objects and countries of the world... Dictionary of Geography
The position of any point or other object on the earth’s surface in relation to other territories or objects; relative to the Earth's surface, the geographical position is determined using coordinates. Geographical location is distinguished by... ... Encyclopedic Dictionary
The position of any point or area of the earth's surface in relation to territories or objects located outside this point or area. In mathematical geography, geographic location means the latitude and longitude of given points or areas, in... ... Great Soviet Encyclopedia
Position k.l. point or other object on the earth's surface in relation to another territory. or objects; relative to the surface of the Earth, the geometric area is determined using coordinates. G. p. are distinguished in relation to natural objects and to economics geogr... ... Natural science. Encyclopedic Dictionary
- ... Wikipedia
- ... Wikipedia
- (EGP) is the relationship of an object of a city, region, country to external objects that have this or that economic importance, it doesn’t matter whether these objects are of a natural order or created in the process of history (according to N.N. Baransky). In other words... ... Wikipedia
The position of a region or country relative to other objects of economic importance to it. E. g. p. category is historical, may change in connection with the construction of the railway. or a power plant, the beginning of the development of a useful deposit... ... Geographical encyclopedia
The position of a deposit, enterprise, city, region, country or other economic and geographical object in relation to other economic geographical objects having for him economic importance. The assessment of the EGP of an object depends on its position... Financial Dictionary
Books
- Essays on the history of geographical discoveries, Magidovich I.. The purpose of the proposed book is to show how, as a result of many hundreds of journeys, from antiquity to the middle of the 20th century, the modern (as of 1956) idea of a physical map...
- Geographical location and territorial structures. In memory of I. M. Maergoiz, . The collection is dedicated to the memory of the outstanding Soviet economic geographer Isaac Moiseevich Maergoiz. The collection received its name - GEOGRAPHICAL POSITION AND TERRITORIAL STRUCTURES - from two...
The geographical position of a state is the location of a territory, a country relative to other objects, territories, water areas, and countries.
Geographical location is one of the fundamental categories economic and social geography. The concept of “geographical location,” known in science since the 18th century, has found particular application in anthropogeography late XIX c., when the German scientist Ratzel began to apply it to characterize the positional properties of the country.
In the context of globalization, the theory of geographical location acquires the status of an interdisciplinary theory, since it allows us to see the world in all its diversity, determined by many regional, state and local characteristics.
The socio-economic space is heterogeneous. Objects do not spatially coincide with the conditions necessary for their existence in the system. Properties of socio-economic space that reveal the spatial divergence of the object under study and necessary conditions its existence (functioning and development) can be defined as the geographical location of the object.
The external environment, through its components, actively influences the object, the geographical location of which is determined. The object itself also affects its own environment.
The concept of “geographical location” is based on the category of “relationship”. According to M. Baransky, the economic-geographical position is the relationship of any place, region or city to objects that lie outside it and have one or another economic significance for it.
The main idea of geographical location as a concept is to reveal a territorial relationship:
In physical-geographical position, this is a relationship in a geographic coordinate grid, in real physical-geographical space with its natural zones, regions, orography, distribution of land and sea, etc.;
In economic-geographical position - this is the relationship to economically significant objects;
In the socio-geographical position - to socially significant objects.
In the political-geographical position - to political realities. Methodologically, this means recording and forecasting military, international political, geo-economic, environmental and cultural force fields;
In the ecological-geographical position - to environmentally significant objects, in particular to countries and regions that determine the environmental situation, to countries and regions whose ecological state can be influenced by a given country.
One of the quantitative indicators of geographic location is geographical coordinates object.
To clarify the content of the concept of geographical location, it is worth noting the significant discrepancy between geographical location and location. When characterizing a geographic location, it is necessary to answer the question: regarding what? The location of an object has a different meaning, which lies in the answer to the question: where and what is it part of? So, location reveals localization or belonging, while position reflects relationships in the system. From a methodological point of view, these concepts should be distinguished.
Therefore, when studying the geographical location, you should find out which objects are outside the object and which are inside. In other words, geographic location is characterized by the relationship of an object with its external environment.
When studying the geographical location, it is necessary to build on the results of the impact of the geographical location on the development of the object. The situation is complicated by the fact that the connections (economic and non-economic) of an object are influenced not only by its geographical location.
Analyzing a problem, the researcher “weighs” real and potential relationships: he discovers real ones empirically, and among potential ones he identifies those that can be realized (actually possible connections). However, the researcher must also establish theoretically possible connections. Thus, when analyzing a geographical location in a relationship, one cannot understand only the actual economic and other connections. A complete and comprehensive study of a geographic location involves taking into account real, potential and theoretically possible connections.
Geographical location is not only a capacious and multifaceted concept, but also a relative one. In the first case, it is distinguished by several types, in particular natural, environmental, social, economic or political-geographical location. In the second - we're talking about about its constant transformation in space and time, simultaneous presence in the assessment current state geographical location, its past development and factors of its further functioning.
For regional studies, the determining role is played by the concept of the political and geographical location of the state. This is placing it on political map the world, a continent or a separate region in interaction with political realities that influence it in one way or another. At the same time, politics is understood as activity aimed at winning the struggle for own interests. It can be government, a specific organization or an individual.
In the spatial-territorial sense, we can distinguish the global, regional and local-neighboring political and geographical position of countries. The global position is the place of a particular state on the political map of the world in the context of its global connections and relations with other states of our planet. The regional political and geographical position includes the location and relationships with the countries of its own historical and geographical region. Local-neighborly political-geographical position is the location of a country surrounded by neighboring states and interaction with them. His assessment is a study complex history confrontations and partnerships. She is very dynamic. At this level, a real analysis of all types of relationships and interconnections between individual states and interstate integration entities.








