— the basis of the primary sector of the economy, which collects industrial and agricultural raw materials and their primary processing for subsequent consumption.
Natural resources include:
- Mineral
- Land
- Forest
- Water reserves
- Resources of the World Ocean
Resource supply is expressed by the ratio between the amount of natural resources and the extent of their use.
Mineral resources
Mineral resources is a collection of specific forms minerals V earth's crust, which are a source of energy, various materials, chemical compounds and elements.
Mineral resources form the basis for the production of industrial products in the world economy. changes in the production and consumption of raw materials in international trade influence not only economic situation in individual countries and regions, but have a global character. Over the past 25-30 years, the commodity sector has changed significantly due to the policies of developed countries, which have tried to overcome dependence on the supply of raw materials from developing countries and reduce production costs. During this period, geological exploration work intensified in developed countries, including the development of deposits in remote and hard-to-reach areas, including the implementation of programs for saving mineral raw materials (resource-saving technologies; the use of recycled raw materials, reducing the material intensity of products, etc.) and developments in the field of alternative replacement of traditional types of raw materials, primarily energy and metal.
Thus, there is a transition of the world economy from an extensive path of development to an intensive one, reducing the energy and material intensity of the world economy.
At the same time high supply of mineral resources to the farm of this or that country or their deficit ultimately are not a factor determining the level of socio-economic development. In many countries there are significant gaps between the level of development of productive forces and the provision of material and raw materials (for example, in Japan and Russia).
The industrial significance of resources is determined by the following requirements:- Technical feasibility and economic profitability of production, transportation and processing.
- Environmental permissibility of development and use
- Favorable political and economic international situation
Accommodation mineral resources characterized by extreme unevenness and high concentration of prey. 22 types of mineral resources account for more than 90% of the value of mining products. However, 70% of metal production comes from the 200 largest mines; more than 80% of oil reserves and production are concentrated in 250 fields, which is only 5% total number oil developments.
There are seven countries in the world based on the diversity and volume of mineral resources they possess:- Russia (gas, oil, coal, iron ore, diamonds, nickel, platinum, copper)
- USA (oil, copper, iron ore, coal, phosphate rocks, uranium, gold)
- China (coal, iron ore, tungsten, oil, gold)
- South Africa (platinum, vanadium, chromium, manganese, diamonds, gold, coal, iron ore)
- Canada (nickel, asbestos, uranium, oil, coal, polymetals, gold)
- Australia (iron ore, oil, uranium, titanium, manganese, polymetals, bauxite, diamonds, gold)
- Brazil (iron ore, non-ferrous metals)
On industrial developed countries accounts for about 36% of the world's non-fuel mineral resources and 5% of oil.
On the territory developing countries contains up to 50% of non-fuel mineral resources, almost 65% of oil reserves and 50% natural gas, 90% of phosphate reserves, 86-88% of tin and cobalt, more than 50% of copper ore and nickel. There is a significant differentiation in the supply and distribution of mineral resources: the vast majority of them are concentrated in approximately 30 developing countries. Among them are: the Persian Gulf countries (about 60% of oil reserves), Brazil (iron and manganese ores, bauxite, tin, titanium, gold, oil, rare metals), Mexico (oil, copper, silver), Chile (copper, molybdenum), Zaire (cobalt, copper, diamonds), Zambia (copper, cobalt), Indonesia (oil, gas), Algeria (oil, gas, iron ore) , countries Central Asia(oil, gas, gold, bauxite).
From countries with economies transition period reserves of mineral raw materials having global significance, Russia has, where about 8% of the world's oil reserves, 33% of natural gas, 40% of coal, 30% - iron ore, 10% - diamonds and platinum.
Extraction of main types of mineral raw materials*, 2004Assessment based on the content of useful components
Source: Mineral Commodity Summaries 2005.U.S. Geological Survey. Wash., 2005.
| Type of raw material | Measurements | Production | Leading countries in production |
| Oil | million tons | 3800 | Saudi Arabia, Russia USA, Iran, China, Venezuela |
| Gas | billion cubic meters m | 2700 | Russia, Canada, USA, Algeria |
| Coal | million tons | 5400 | China, USA, Russia |
| Uranus | thousand tons | 45 | Canada, China, USA |
| Iron Ore | million tons | 780 | Brazil, Australia, China, Russia, USA |
| Bauxite | million tons | 130 | Guinea, Jamaica, Brazil |
| Copper ore | million tons | 14,5 | USA, Chile, Russia, Kazakhstan |
| Gold | T | 2500 | South Africa, USA, Australia, Canada |
| Diamonds | million carats | 70 | Congo, Botswana, Russia, Australia, South Africa |
| Phosphate ores | million tons | 140 | USA, Morocco, China |
Land resources
Land resources, soil cover- the basis of agricultural production. However, only 1/3 land fund The planet is agricultural land (4783 million hectares), that is, land used for the production of food and raw materials for industry.
Agricultural land consists of arable land, perennial plantings (gardens), natural meadows and pastures. In different countries of the world, the ratio of arable land to pastures in agricultural land is different.
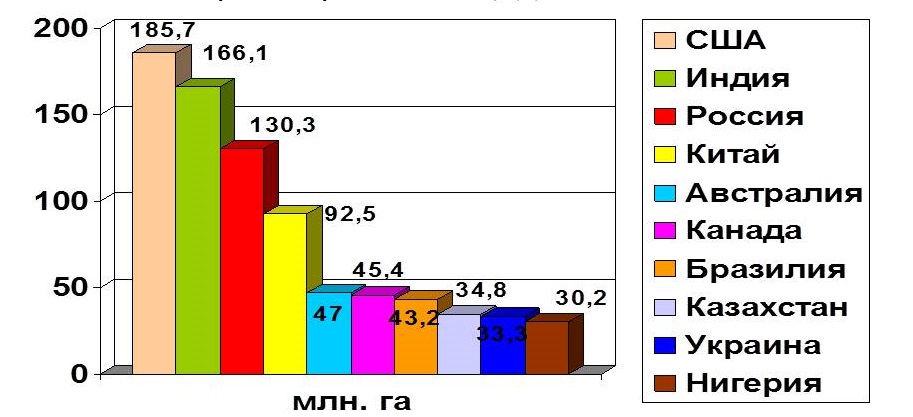
Currently, in the world, arable land accounts for about 11% of the total land area (1350 million hectares) and 24% of the land (3335 million hectares) is used in livestock farming. Countries with the largest tracts of arable land (million hectares): USA - 186, India - 166, Russia - 130, China - 95, Canada - 45. The provision of arable land per capita per capita (ha/person) varies among regions: Europe - 0.28, Asia - 0.15, Africa - 0.30, North America — 0,65, South America- 0.49, Australia - 1.87, CIS countries - 0.81.
If in developed countries the increase in yield and productivity, agricultural production is largely ensured through the extensive use of land, then most The most accessible and fertile lands are already occupied by agricultural production, and those that remain are infertile.
Production of main types of agricultural products in the world, average for 2002-2004.Source: FAO Production Yearbook, 2004; Rome, 2004. FAO Yearbook of Fishery Statistics. Rome, 2005; FAO Yearbook of Forest Products. Rome, 2005.
| Types of products | Measurements | Production, collection | Countries are the main producers of products |
| Cereals - total | million tons | 2300 | China, USA, India |
| Potatoes and root vegetables | million tons | 715 | China, Russia, Nigeria |
| Vegetables | million tons | 880 | China, India, USA |
| Fruits | million tons | 510 | China, India, USA |
| Raw sugar | million tons | 1500 | Brazil, China, USA |
| Coffee bean | million tons | 7,7 | Brazil, Colombia, Mexico, Indonesia, Ethiopia |
| Cocoa beans | million tons | 3,8 | Ivory Coast, Ghana, Brazil |
| Cotton plant, fiber | million tons | 65 | China, USA, India |
| Meat - total | million tons | 265 | China, USA, Brazil |
| Cow's milk, fresh | million tons | 560 | USA, India, Russia, Germany, France, China |
| Cleaned wool - total | thousand tons | 1700 | China, Russia, Kazakhstan, Australia, South Africa |
| Fish catch - total | million tons | 100 | China, Japan, Peru, Russia |
| Wood removal | million cubic meters m | 4000 | Russia, USA, Brazil, Canada |
Forest resources
Forests cover about 4 billion hectares of land (about 30% of the land). Two forest belts are clearly visible: the northern with a predominance of coniferous trees and the southern (mainly tropical forests developing countries).
In developed countries V last decades Forests covering an area of about 30 million hectares are mainly affected by acid rain. This reduces their quality forest resources.
Most third world countries are also characterized by a decrease in the provision of forest resources (deforestation of territories). Up to 11-12 million hectares per year are cut down for arable land and pastures, and the most valuable forest species are exported to developed countries. Wood also remains the main source of energy in these countries - 70% of the total population uses wood as fuel for cooking and heating their homes.
The destruction of forests has catastrophic consequences: the supply of oxygen to the atmosphere is reduced, greenhouse effect, the climate is changing.
The provision of forest resources in the regions of the world is characterized by the following data (ha/person): Europe - 0.3, Asia - 0.2, Africa - 1.3, North America - 2.5, Latin America - 2.2, Australia - 6 .4, CIS countries - 3.0. About 60% of temperate latitude forests are concentrated in Russia, but for industrial use 53% of all forests in the country are suitable.
Water resources
Rational use water resources, especially freshwater ones, is one of the acute global problems world economy.
About 60% total area land on Earth is in areas where there is no sufficient quantity fresh water. A quarter of humanity feels a lack of it, and over 500 million residents suffer from lack and poor quality drinking water.
Most of the water on the globe is the waters of the World Ocean - 96% (by volume). On groundwater accounts for about 2%, glaciers - also about 2%, and only 0.02% falls on surface water continents (rivers, lakes, swamps). Fresh water reserves account for 0.6% of the total water volume.
Current water consumption in the world is 3500 cubic meters. km per year, i.e., there is 650 cubic meters of water for every inhabitant of the planet. m per year.
Fresh water mainly used in industry - 21% and agriculture - 67%. The waters of the World Ocean are not suitable not only for drinking, but also for technological needs, despite the achievements of modern technology.
World ocean resources
The resources of the World Ocean play an increasingly important role in the development of productive forces.
They include:- biological resources (fish, zoo- and phytoplankton);
- significant mineral resources;
- energy potential;
- transport communications;
- the ability of ocean waters to disperse and purify the bulk of the waste entering it through chemical, physical and biological influences;
- the main source of the most valuable and increasingly scarce resource - fresh water (the production of which through desalination is increasing every year).
The development of ocean resources and its protection is undoubtedly one of humanity’s global problems.
The use of sea shelf resources is of particular importance for the world economy. Currently, about 30% of produced oil is of shelf origin. In the EU, the sea provides up to 90% of the oil produced, in Australia - up to 50%. The vast majority of oil (85%) on the shelf is extracted at depths of up to 100 m. About 60 countries produce oil on the shelf.
All earth's surface, located above sea level and which can be used by a person in his life and activities, is called land resources. Land resources are quite important element human life, many of them grow food for our livelihoods. For land resources There have always been struggles and wars. After all, land has always been more valuable than gold, platinum or diamonds.
General concept
Land resources are a type of natural resource that is not man-made and that does not have a specific price.
Land resources are characterized by many factors: relief, area, soil quality, climate and other conditions that help a person to live comfortably. The most important element of land resources is soil.
Soil
Fertile soil is an important part of bioexchange; it is what feeds us, provides air and proper circulation of micro and macroelements. Soils form groundwater, their balance and quality, provide micro and macro elements to plants and, subsequently, animals and people. Soil cover depends on fertility, which in turn depends on climate, weather conditions, structures nutrients and influence sun rays to the soil surface.
Soils and lands are divided into three large groups:
- productive soils and lands;
- unproductive soils and lands;
- unproductive soils and lands.
Land resources in the world
Of the 510 million square kilometers of our planet, only 149 million. square kilometers belongs to the land. Agricultural land makes up about 11% of total number sushi, not so much, but provides food for 100% of the world's population to one degree or another. 23% of them are in meadows that have never been cultivated, 30% are in forests, which produce huge amounts of oxygen for our lives and are the habitat of many species of animals. To top it off, a third of the planet's land resources are lifeless and barren or partially suitable for life and cultivation.
 The world's land reserves are calculated by the amount of land available per person. Residents of Asia and Europe account for a little more than a hectare of land, while in Australia this figure is 37. The quality of land also depends on population density. Virgin lands are quite fertile, lands where there is a huge population are exhausted and constantly require replenishment.
The world's land reserves are calculated by the amount of land available per person. Residents of Asia and Europe account for a little more than a hectare of land, while in Australia this figure is 37. The quality of land also depends on population density. Virgin lands are quite fertile, lands where there is a huge population are exhausted and constantly require replenishment.
Types of land resources
Land is a means of prime necessity and the basis for housing, industrial enterprises and agricultural land. In many countries, land resources are regulated by law. Initially, land resources are classified according to their purpose. According to this parameter, the following are distinguished:
- agricultural land;
- lands for forestry and water management;
- industrial lands;
- residential lands in cities and towns;
- energy lands;
- lands of communications, radio broadcasting;
- and other special purpose lands.
The division of land resources brings rationality to the distribution and use of land. Thus, soils with poorer or no fertility are excellent for locating industrial enterprises, although this does not apply to countries former USSR. Soils with fertile qualities perfectly realize their potential when agricultural enterprises are located on them.
Cities are mainly located on fertile soils oh, because previously urban areas did not include multi-storey buildings and mainly consisted of private houses with a garden area. Allocation of land for energy allows you to determine a certain territory for the production of electricity, without thus polluting other land resources with the products of your activities.
Distribution of land resources
Land resources are distributed evenly throughout our planet, but their quality varies widely. This leads to the most unexpected consequences. For example, due to poor quality land, about 1 billion people in the world are hungry or malnourished. Every day, humanity consumes food comparable to 37 million tons of wheat. With an annual increase of 70-80 million people, agricultural production should increase by an average of 24-30 million tons annually. This is only possible with an intensive approach to agriculture.
Every year, every inhabitant of the earth requires 3000 square meters territory for growing food and 7000 square meters for living. Therefore, the food problem can only be solved if integrated approach to the development, protection and use of fertile lands.
Land use
Land use varies from continent to continent. Let's say that in Europe most of the fertile land is sown with agricultural crops, in Africa the land is reserved for meadows and pastures for grazing livestock. Australia uses its land resources more economically and rationally; here, half of the country is desert and only coastal zone a depth of 200-300 kilometers is suitable for life and cultivation of crops, forests and pastures.
Irrational use
The problem is not rational use land resources arose against the background of the fact that the land fund is used irrationally. Due to mining, industry, dumping household waste A huge amount of not just land stock is lost, but fertile soils that could be used for good.
Second reason irrational use this is an attack on agricultural lands, cities and villages. This in turn reduces the area under cultivation, and the area under cultivation takes away this area from pastures, forests and deserts. Forests are cut down, and instead of hunger, the problem of breathing low-quality, polluted air occurs.
Modern humanity does not understand the role of correct, rational use of land resources, for which it pays with human lives.
Protection of land resources
We have recently begun to engage in the protection of land resources. This problem is mainly faced by developed countries: the USA, the countries of the European Union, Australia, and also China. Main problem, which arises as a result of irrational land use, leads to a decrease in high-quality fertile soils and forests. The task of governments is to ensure soil fertility and arable land productivity.
Main measures to conserve land resources:
- reduction of erosion factors on land;
- rational use of land;
- combating salinization, waterlogging, over compaction, and soil pollution.
 With a proper approach to the problem of loss of land resources, the problem of extensive development will disappear agriculture by increasing the area under cultivation. The yield of even very poor soils will increase significantly, which is already an excellent result.
With a proper approach to the problem of loss of land resources, the problem of extensive development will disappear agriculture by increasing the area under cultivation. The yield of even very poor soils will increase significantly, which is already an excellent result.
US land resources
The area of land in the United States devoted to food production is no less than 567 million hectares out of a total land fund of 940 million hectares. This area includes arable land, pastures and forests. Approximately 220 million hectares are used for cultivation and pasture, of which 62-63% is soil with high fertility. Basically these are lands located in the best climatic zones, provided with regular watering and which have an optimal ratio of micro and macro elements.
The 151 hectares of US land used for livestock pasture production are potentially fertile. Every year, 1,200,000 hectares of land are taken from US agriculture for urban needs, of which a third is best performance fertility. Agriculture, in this case, begins to take away forest land.
According to experts, in 20 years, all pasture land in the United States will be converted to crop production, and pastures will be located on lands that were not previously considered fertile.
The USA has the most large area of arable land in the world, most of the arable land is highly fertile soil. High soil fertility, long period growing season and a good climate with the right amount of precipitation create excellent growing conditions in the USA huge amount agricultural crops in large quantities.
Land resources of the Russian Federation
The total land resources of Russia are 1,700 million hectares. Of these lands, 64,000,000 hectares are given over to arable land and pastures, settlements account for 20-23 million hectares, the rest of the territory is occupied by forests and.
Russia is a country quite well endowed with resources various kinds, and the land fund is the most useful and valuable of them.
The state's soil resources are quite large, however, the quality of the soil for sowing crops is very low. The main problem of unproductivity soil resources- this is their incorrect operation. Agriculture is developing extensively, due to an increase in sown areas, which is not modern world great luxury.
If we talk about cities, then land in cities is used extremely productively and for the development of apartment buildings, offices and manufacturing enterprises.
According to many experts, Russia will one way or another come to an intensive development path and begin to develop its land fund in the right direction. It is also noted that the state is pursuing a policy of forest protection, which will prevent arable land from being transferred to forestry lands.
In general, the main land fund in Russia is not in the most favorable conditions: taiga, tundra.
Brief summary
The land fund is the most important and most valuable thing for the country and the world. Everything is connected to the earth in one way or another. All enterprises, minerals, water and other resources are located within or on land resources. The main task humanity is to preserve the land fund in normal conditions without polluting it. It is necessary to take care of its condition and fully support and not destroy the remaining flora and fauna.
It is unfortunate, but many cannot understand the value of natural resources, which include land resources. Main value is the land on which you and I walk. Only with proper treatment of the earth will we receive best result from cultivating soils and pastures.
In the future, soil resources, as a composition of land resources, will be especially valuable, because according to scientists, the amount of oil and gas is already at the very bottom, and effective fuel can only be obtained from the ground by growing agricultural crops for fuel.
The earth is the main platform for all species. Its participation in the regulation of the ecosystem is difficult to overestimate, as is its role in food supply population. Distinctive feature The soil layer, compared to other forms of production processes, is indispensable. At the same time, the land resources of the world can be considered as an eternal tool with the help of which a person can provide himself with the necessary raw materials and food. Unfortunately, in the practice of land exploitation, many problems arise that are still acutely facing agrotechnical and
What are the world's land resources?
Land resources do not include the entire surface of the land, but only that part of it that can be considered from the point of view economic use. However, the general land fund usually refers to the entire land mass, with the exception of the territory of Antarctica. In terms of area, the world's land resources are about 13,400 million hectares. In percentage terms, this is about 26% of the total area of the planet. But this does not mean at all that all the land potentially suitable for cultivation is in economic use. Today, about 9% of the land surface is used for agricultural and other production needs. There are many reasons for this low level environmental management, however, this percentage is gradually increasing, which makes it possible to solve problems with ensuring unfavorable regions food.

Classification of land resources
Among the resources of the land fund there are three large categories. The first includes productive lands that can potentially produce high yields and generally have favorable conditions for cultivation. It is important to note that productivity is determined not only by the properties of the soil, but also external factors, among which climate is of significant importance. The second category is unproductive areas. These are the land resources of the world and Russia, a significant part of which is represented by tundra, forest-tundra, swamps and steppes. Theoretically, these lands may meet the requirements of the agrotechnical complex in terms of use in for different purposes, but, again, operational difficulties also arise due to indirect factors. For example, this may be inaccessibility or unfavorable climatic conditions. The third category is unproductive land. As a rule, these are built-up areas, as well as lands with a disturbed structure and unfavorable chemical composition.

Land as a means of production
People have been using the fruits of the earth in one form or another since ancient times. The first forms of such use had the nature of appropriation, but as the tools of labor developed, full-fledged features of production activity began to form. Today, there are several areas of such land use, including the cultivation of arable land, the organization of pastures and meadows, and the planting of gardens and plantations. At the same time, the world's land resources and their use can also be considered from the point of view of indirect production. This means that agriculture, in one form or another, can act as a link in the chain industrial production. However greatest distribution Nevertheless, the main branches of agricultural activity, such as vegetable growing, floriculture, growing grains, melons and fodder plants, received.

Land use levels
The model for structuring the global agricultural complex usually involves the identification of three levels of land use. On the first are industry participants who are engaged in the production of technical means for agriculture. It should also be noted here that enterprises process agricultural raw materials in order to obtain products for further use in the industry. We can say that this is an area that serves agricultural production in terms of infrastructure. The second level represents individuals and enterprises that directly process land resources. Lands depending on the region may involve different shapes operation, but the tasks of their maintenance must necessarily include the production of a specific product. The third level of the agricultural complex is the industrial processing and marketing of raw materials and products obtained as a result of cultivating the land.
Problems of land use
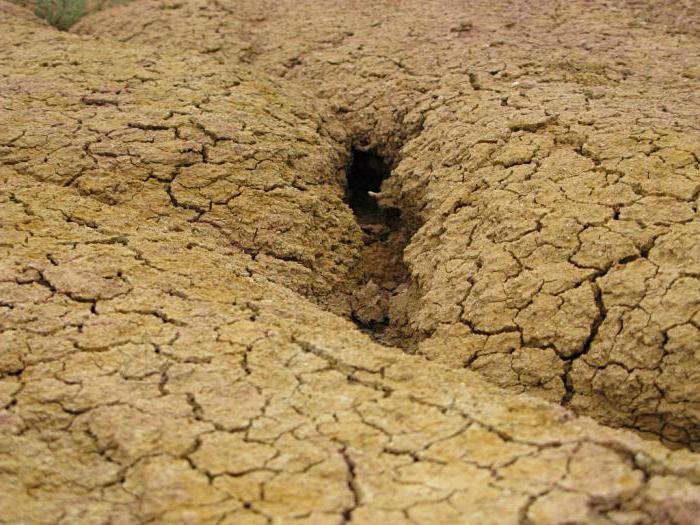
Although experts usually bring to the fore underutilization available resources, many argue that the lands under development are gradually degrading. This means that even a cutting-edge facility can eventually become unusable as a production site. And by that time, interested enterprises will be forced to develop the world’s unattractive land resources. The photo below shows an example of soil depletion. It is precisely these processes that worry many experts in the agricultural industry.

Land Use Trends
The structure of land distribution is constantly changing. On the one hand, the changes are caused by the expansion of the areas of cultivated land, and on the other, by the reorientation of territories that were previously under development. At the current stage of land development, there is an increase in the rate of land cultivation. To provide this opportunity, enterprises irrigate deserts, drain swamps and cut down forests. Such measures make it possible to increase the world's land resources suitable for industrial activities. Moreover, this process is stimulated not only by the need to move to virgin lands due to the unsatisfactory qualities of old lands. This is also facilitated by an increase in population - accordingly, the demand for food is growing.
Prospects for expansion of agricultural land
WITH more likely In the coming years, some parts of tropical forests and deserts will be converted to agricultural cultivation. Modern technical means allow economic activity to be carried out even in such conditions. Moreover, the world's productive land resources can be increased by expanding coastlines. The construction of dams and canals makes it possible to move settlements towards the sea. Similar processes are already observed in Japan, Singapore and Belgium.
![]()
Conclusion
In addition to expanding the acreage, experts pay a lot of attention to the tasks of more rational and efficient use of primary agricultural areas. Latest technologies agrotechnical complexes allow for more careful use of the world's land resources without causing harm ecological system. There are different directions in this area, some of which are subordinated to the tasks of increasing productivity by stimulating soil fertility. At the same time, many states and international organizations are developing new concepts of rules for regulating environmental management, which are focused on optimizing the processes of exploitation of land resources.
Land resources are among those natural resources without which human life is unthinkable. There are as many land resources on the planet as there are dry land.
Land resources are the earth's surface that is suitable for human habitation, construction and other types of economic activity. Land resources are characterized by relief, soil cover and a complex of other natural conditions. The structure of the land fund is a characteristic of land resources. The land fund is the ratio of areas occupied by crops, forests, pastures, industrial enterprises etc.
Land resources and soil cover of the Earth have been created over thousands of years - this is the basis of wildlife and agricultural production.
A third of the planet's land is agricultural land, i.e. land that is used to produce food. About 3/4 of all soil resources on the planet have reduced productivity due to insufficient heat and moisture.
Agricultural land is arable land, perennial plantings, natural meadows and pastures.
The land fund consists of inconvenient lands (deserts, highlands). Structure of the land fund: cultivated lands - 11%, pastures and meadows - from 23 to 25%, forests and shrubs - 31%, settlements - 2%, and the rest of the territory is occupied by unproductive and unproductive lands (mountains, swamps, glaciers, deserts) . Cultivated lands provide about 88% of the food needed for humans. Humanity is fighting to expand the lands that become suitable for agriculture and habitation. Russia, the USA, Kazakhstan, China, Canada, and Brazil are engaged in land development.
Preserving the planet's land resources is one of the most important tasks humanity.
Land resources are declining as productive lands are allocated for mining and construction, destroyed by cities and other settlements, are flooded during the construction of reservoirs, etc.
The problem of agriculture is soil degradation due to improper land use.
Soil erosion reduces soil fertility and damages crops. Land in agricultural areas becomes inconvenient due to potholes, gullies, and ravines.
Due to the erosion process, 6–7 million hectares of land are being removed from global agricultural production, and another 1.5 million hectares are being lost due to salinization and waterlogging.
The top fertile layer of soil is gradually depleted.
The process of desertification is the expansion of the area of deserts and their encroachment on agricultural land. This process is typical for many regions of the world.
The surface of the earth that is above sea level is classified as land resources. These lands are used by humanity for its livelihood.
The earth is important resource human life activity. It has long been cultivated and food was grown on it. There have been numerous battles over land wars of conquest. The earth weighs more than gold and diamonds.
Determination of land resources
Land resources include those not made by human hands. natural resources, which do not have a specific value.
Land resources can be characterized by the following factors:
- relief;
- soil fertility;
- climatic conditions of the environment.
Most Valuable biological resource soils are considered. Fertile cover is part of biological metabolism, which depends on climate, the amount of sunlight received, and the content of nutrients and minerals.
There are three main sections of ground cover lands:
- Productive ground cover resources.
- Unproductive land areas.
- Unproductive ground cover.
Land, as a means of production, is endowed with features that distinguish it from all production resources:
- land is a miraculous natural resource;
- its cover is limited;
- it is irreplaceable with other production resources;
- the use of land is associated with the constancy of the terrain;
- in the field of agricultural production, the soil quality is uneven;
- land is an imperishable method of production and correct use and application increases the quality and quantity of production.
Types of land resources
Ground cover resources are allocated to accommodate housing, production and agricultural resources. Most states regulate the use of ground cover resources by legislative law.
Land reserves can be grouped according to their purpose:
- Soils for agricultural purposes.
- Lands of the housing stock of settlements.
- Soil reserves for industry, energy, radio communications, defense and other socio-economic purposes.
- Specially protected lands and territories of specially protected objects.
- Forest protection resource.
- Water protection reserve.
- Strategic reserve territories.
Land reserves are the basis of agricultural production. These include a third of the entire ground cover of the planet, that is, a reserve used for the production of food and raw materials for industry.
In the world, approximately 11 percent of the total land reserve is allocated to arable land:
- in the USA - 186 million hectares,
- in India - 166 million hectares,
- in Russia - 130 million hectares,
- in China - 95 million hectares,
- in Canada - 45 million hectares.
The division of ground cover resources brings rational grain to the distribution of land. Infertile soils are excellent for locating industrial complexes. Fertile soils are allocated for the agricultural sector.
Land resources in the world
All countries of the world have an individual classification of the purpose of land resources. The exploitation of land is actively developing and the integrity of anthropogenic reliefs is constantly changing.

In Europe, 30 percent of ground cover is cultivated. In the European part of the Russian Federation, only 10 percent of the territory is allocated for the agricultural fund.
Lands of forests and chernozem steppes are actively involved in agricultural purposes.
Territories from Northern Kazakhstan to Southern Siberia, the plateaus from India to China are different high degree cultivability of land.
In India, half of the total territory is allocated to agriculture.
In the tropics of Asia, meadows are cultivated with industrial crops, and fruits and palm trees grow in the middle of fields and near villages.
In the Near and Middle East, cultivated areas are found in separate areas. A huge part of these areas is a pasture resource, stretching from Asia Minor to Mongolia.
In Africa, 27 percent is under grazing land. Vast territories here are represented by deserts.
The eastern part of the United States and Southern Canada have developed only twenty percent of the arable land of the entire territory. Multicultural field reliefs dominate, producing continuous patches.
A huge proportion of grassland is found in the southern and western United States. Vast spaces Northern Canada is not cultivated.
IN Latin America a good half of the territory is occupied by forests, cultivated areas cover only 7 percent of the land, and pasture fund - 26 percent. In Australia, 75 percent of the area is cultivated.
In world land resources, orientation in the redistribution of land use is clearly visible.
Municipal and industrial zones are transferred to arable land, expanded using the resources of pasture farms, and the pasture fund is increased by taking away forest and desert areas.
In the United States, 350 thousand hectares of arable land are being lost due to the growth of megacities. Consumption of forest resources on Earth has doubled over the past three hundred years.
Distribution of land resources
Land reserves are distributed moderately throughout to the globe, yet their quality factor varies entirely. This leads to disastrous results. Due to poor soils, about a billion people on Earth are malnourished.
Every day society consumes an amount of food comparable to 37 million tons of grain. Humanity increases by 70–80 million people annually, which means that agricultural production should be increased by 25 million tons annually.
It is necessary to more actively promote the development of the agricultural sector.
Every year the population of the planet requires everything for life large areas. Thus, for human life support, 3 thousand square meters are required and for agricultural production 7 thousand square meters.
Only by approaching the issue of providing food resources in a comprehensive manner will it be possible to solve the current situation.
Agrarian territories of the Russian Federation are assigned to land users, who can be classified into two groups:
- lands of cooperative economic ownership, collective or private;
- federal and municipal reserve lands.
There are two different concepts of land resources:
- The total area of the site, which includes part of the territory assigned to the agricultural complex.
- The area of agricultural land, consisting of land on which agricultural products are produced.
Land use
The rational use of land resources is given great importance, both in the Russian Federation and throughout the world.
The agricultural resources of the earth have a great impact on the economy, so agricultural production cannot be neglected.
Features of land as an instrument of production:
- Land is a non-man-made resource of nature.
- The land is territorially reduced. It cannot be increased.
- Land cannot be replaced by other productive resources.
- The earth is heterogeneous in its properties in different regions.
- It is impossible to transport land from one territory to another.
- The earth is an eternal means of production; when cared for, it does not wear out, but improves its qualities.
Irrational consumption of ground cover resources occurs against the background of irrational designation of territories.
By giving priority to extractive industries, ground cover is depleted due to the large runoff of domestic industrial waste.
Municipalities also occupy areas of cultivated land, reducing their area. The agricultural resource is replenished through deforestation and the elimination of pastures and deserts.
Protection of land resources
The main issue arising from the irrational use of territories is the depletion of fertile lands. The task of the heads of government of the world community is to change the priority use of fertile lands.
Changing the use of ground cover resources of the earth entails two antagonistic processes:
A positive aspect is the expansion of agricultural land:
- study of fallow areas;
- land reclamation;
- drainage;
- irrigation;
- research of coastal areas.
Negative – depletion of agricultural land:
- erosion of ground cover areas;
- waterlogging;
- salinization;
- desertification.
By correctly approaching the problem of land resource distribution, you can avoid the loss of fertile soils and even increase their productivity.
Land resources Russian Federation amount to 1.7 billion hectares. 64 million hectares are allocated for arable land and pastures, the municipal fund occupies 23 million hectares, the entire remaining territory belongs to the forest fund and water management.
Russia's soil resources are enormous, but the sown soils are low-yielding, so the agricultural industry is developing in an extensive way, which is irrational.
Municipal lands are used for housing, as well as for the construction of commercial and industrial buildings and structures.
More than 27 thousand hectares of conserved land resources of the Russian Federation are located in unfavorable conditions: taiga and tundra.
Currently in Russia there is a struggle for the preservation of forests, which does not allow arable land to occupy forest protection zones. According to experts, Russia will very soon achieve intensive development of its land fund in the right direction.
To sum it up
Land resource is the most valuable fund of developed countries and has a global and political significance. Minerals, water and forestry, manufacturing enterprises, housing stock - all this is located on the ground.
An important task of humanity is the conservation of land resources and their proper intensive development. It is very important to remember and understand that everything most valuable to humanity grows and lies in the ground.
Everything is interconnected in the world. It is necessary to restore flora and fauna, as well as reanimate the environment.








